Health care system
Health care payers
Government-funded health insurance
Mnemonic
- MedicarE is for Elderly.
- MedicaiD is for Disadvantaged.
Medicare
Medicare is funded by the federal government.
- Eligibility
- Individuals ≥ 65 years old who:
- Are US citizens or lawful permanent residents
- And have worked and paid Medicare taxes for a minimum of 10 years
- Irrespective of age, individuals with any of the following may be eligible:
- End-stage renal failure on dialysis or with a kidney transplant
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Permanent disabilities
- Individuals ≥ 65 years old who:
Mnemonic
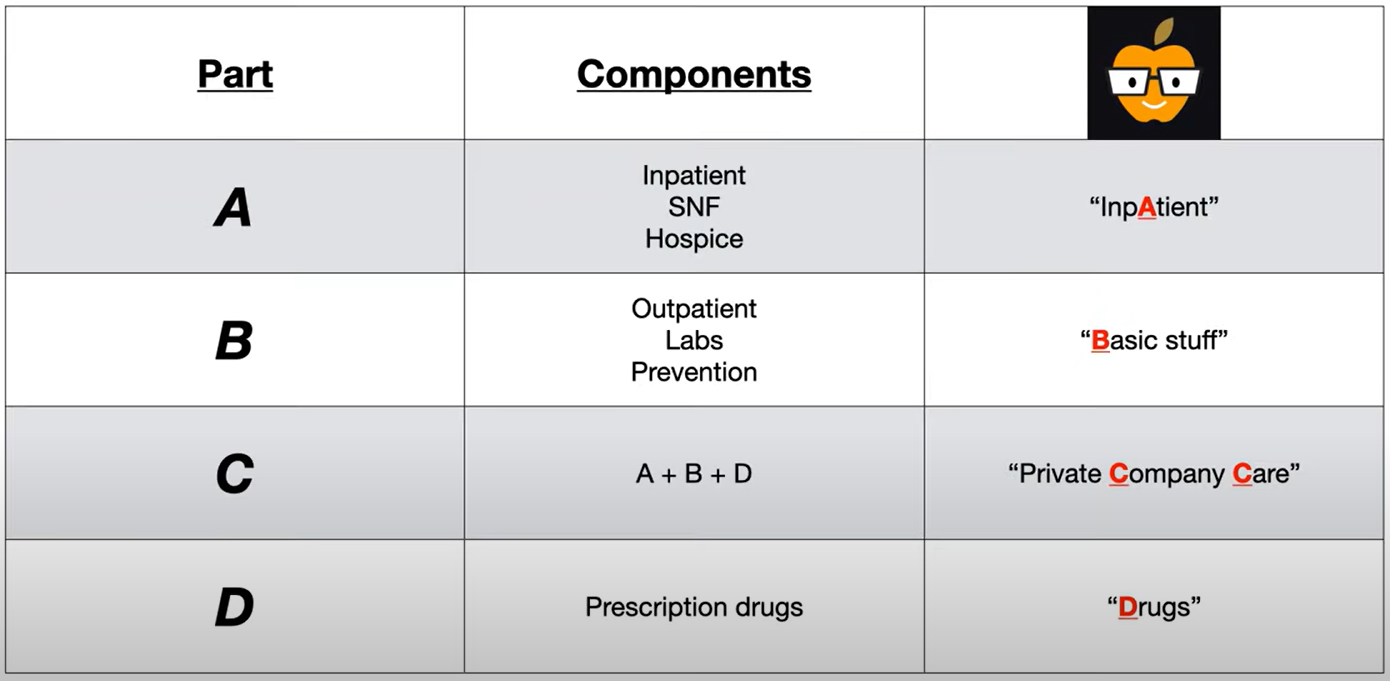
- Part A: hospital Admissions, including hospice, skilled nursing
- Part B: Basic medical bills (eg, physician fees, diagnostic testing)
- Part C: (parts A + B = Combo) delivered by approved private companies
- Part D: prescription Drugs
Medicaid
Medicaid is jointly funded by federal and state governments.
- Eligibility: Individuals must meet both nonfinancial and financial criteria.
- Nonfinancial
- US citizen or lawful permanent resident
- Residence in the state in which coverage is received
- Financial: Factors that impact financial eligibility include household income, presence of children in the home, pregnancy, disability, age, and state of residence.
- Children and pregnant individuals living in households with income ≤ 133% of the federal poverty level (FPL) are eligible in every state.
- Eligibility for adults < 65 years of age with a household income ≤ 133% of the FPL is decided by each state.
- Nonfinancial
Commercial health insurance
| Plan Type | Providers Eligible | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Health Maintenance Organization (HMO) | Restricted to a limited panel of physicians | - Requires referrals from PCP - Strict in-network coverage |
| Preferred Provider Organization (PPO) | Out-of-network providers allowed, but cost more. | - Tends to be more expensive - No referrals necessary (OON) |
| Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO) | Restricted to a limited panel of physicians | - Similar to HMOs, but network tends to be smaller |
| Point of Service (POS) | Out-of-network providers allowed, but designated "in network" to reduce costs. | - Requires referrals from PCP (OON) - Can be thought of as HMO + PPO |
Consolidated Omnibus Budget Reconciliation Act (COBRA)
Designed to cover gaps in health insurance coverage while individuals are between jobs (e.g., job loss, changing jobs, reduction in hours) by extending medical coverage that was provided through the previous employer's health plan
Health insurance basics
Out-of-pocket expenses
- Definition: health care costs that are paid by an individual rather than by an insurance company, e.g., deductibles, coinsurance, and copayments
- Out-of-pocket maximum
- A limit on the amount of money that an individual has to pay for covered health care services in a year (not including premiums).
- After this amount is reached, all covered health services are paid in full by the health plan for the rest of that plan year.
- Deductibles, copayments, and coinsurance apply to the out-of-pocket maximum.
Copayment
- A fixed fee that must be paid to receive covered care
- Example: $40 every time you see a specialist
Coinsurance
- A fixed percentage that must be paid by the insured
- Example: if your coinsurance is 25%, and a doctor bills insurance $100 for a visit, you are responsible for $25
Deductible
- A fixed amount that must be paid out of pocket BEFORE insurance pays for your care
- Example: if your deductible is $4,000, and you haven't met it yet, and your doctor bills you for $265, you are responsible for paying the entirety of the $265. You have now paid $265 out of $4,000 toward your deductible.
Example Scenario:
Imagine you have a health insurance plan with the following features:
- Annual deductible: $2,000
- Coinsurance: 20% after deductible
- Specialist copay: $50 per visit
Throughout the Year:
January:
- You visit your primary care physician for a routine check-up, which costs $200
- Since you haven't met your deductible yet, you pay the full $200
- Your remaining deductible: $1,800
March:
- You see a specialist for a consultation
- You pay a $50 copay (this is separate from and doesn't count toward your deductible)
- The specialist's services cost $300, which goes toward your deductible
- You pay the full $300 plus the $50 copay, totaling $350
- Your remaining deductible: $1,500
July:
- You need an outpatient procedure costing $2,000
- You pay the remaining $1,500 to meet your deductible
- For the remaining $500 of the procedure cost, your coinsurance kicks in
- You pay 20% of $500 = $100
- Insurance covers the other 80% = $400
- Total you pay: $1,600
September:
- You see a specialist again for follow-up
- You pay only the $50 copay
- The specialist bills insurance $250
- Since your deductible is met, coinsurance applies
- You pay 20% of $250 = $50 (coinsurance)
- Your total payment: $100 ($50 copay + $50 coinsurance)
Health care payment models
| Payment Model | Description | Provider Risk | Patient Experience | Examples/Usage |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fee-for-service | Payment made for each individual service provided | Low risk for providers; incentivizes volume of services | May lead to unnecessary services; less coordination of care | Traditional insurance model; Medicare Part B |
| Discounted fee-for-service | Payment for each individual service at a discounted rate pre-determined between providers and payers | Moderate provider risk due to discounted rates | Similar to fee-for-service but with potentially lower copays | PPOs commonly use this model |
| Global payment | Single payment covers all expenses for a specific episode of care | Higher risk for providers if complications arise | Simpler billing; transparent total cost | Common for elective surgeries including pre- and post-operative care |
| Bundled payment | Set payment amount for a service to be divided among all involved providers/facilities | High risk for providers if costs exceed the bundle amount | Potentially better care coordination across providers | Joint replacements, cardiac procedures, maternity care |
| Capitation | Fixed payment per patient per time period regardless of services used | Highest risk for providers; may limit unnecessary care | May improve preventive care; potential for undertreatment | Common in HMOs; Primary care capitation models |
Key differences:
- Risk allocation: Fee-for-service puts risk on payers, while capitation shifts risk to providers
- Payment timing: Fee models pay after service; capitation pays prospectively
- Incentives: Fee models may incentivize volume; capitation and bundled payments incentivize efficiency
- Coordination: Bundled and global payments encourage better provider coordination