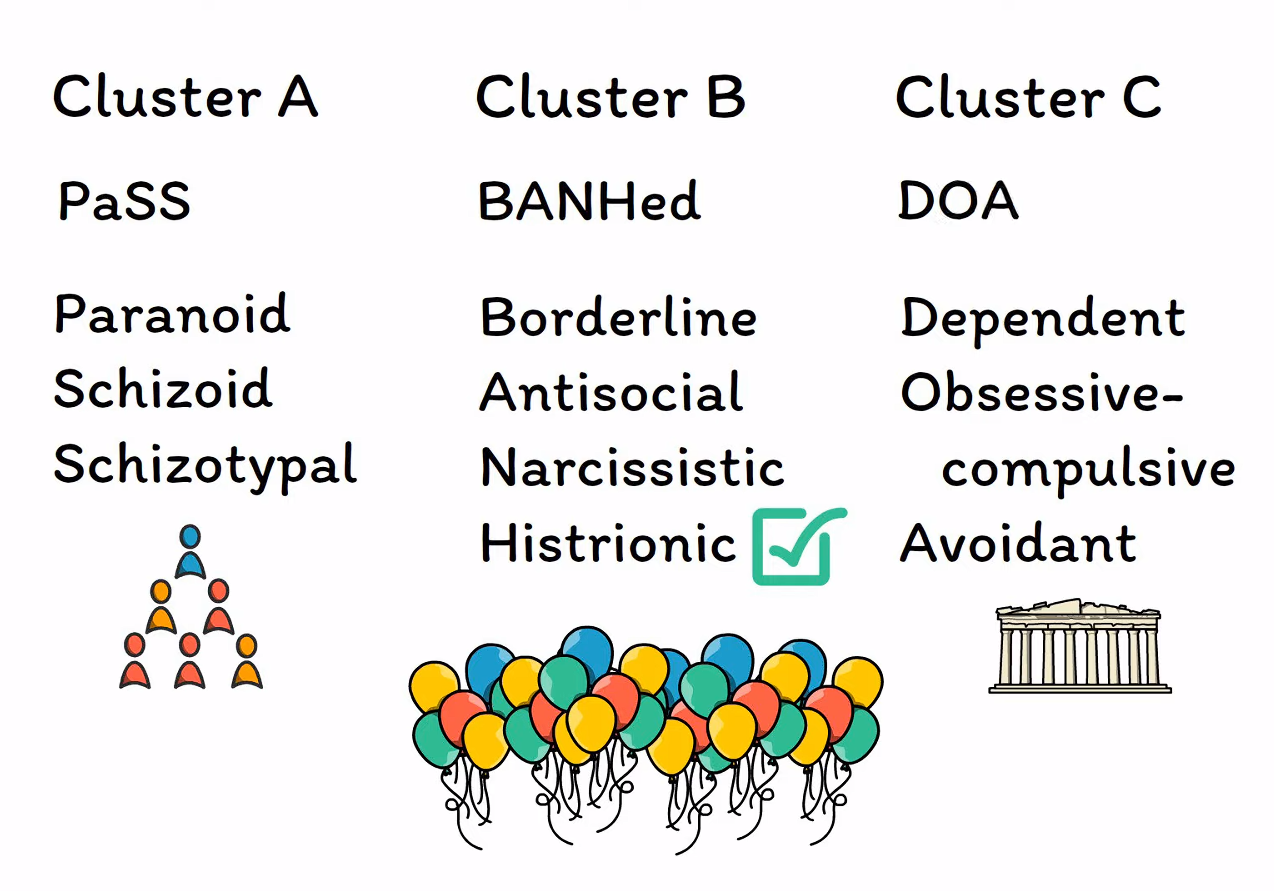
Mnemonic
- Cluster A (weird) will pass the party
- Cluster B (wild) will come to the party, but they are likely getting banned from future parties
- Cluster C (worried) will come to the party, but the party will be dead on arrival, because they will drag down the spirit
Tip
Personality disorders are not diagnosed when the behavior is better explained by another mental disorder and are generally not diagnosed before age 18.
Cluster A
Paranoid personality disorder
Don’t trust others, but do not involve specific delusions (eg, persistent false, fixed beliefs).
Schizoid personality disorder
- Voluntary detachment from social relationships (e.g., family) t
- Comfortable with social isolation (unlike in avoidant personality disorder)
- The “schizo-” prefix is more of a historical artifact, reflecting an early conceptualization of profound social and emotional detachment as a form of “splitting” from the interpersonal world. It does not imply the presence of psychotic symptoms or a direct progression to schizophrenia in most cases. The key feature is a pervasive lack of interest in social interaction, not a distorted perception of reality.
Mnemonic
Schiz-avoid
Schizotypal personality disorder
Unusual/magical thoughts, perceptions & behavior
Cluster B
Antisocial and borderline tend to be severely socially disabling (e.g. cannot find a job or maintain a relationship), while histrionic and narcissistic are mild.
Borderline personality disorder
- It is called ‘borderline’ because doctors previously thought that it was on the border between two different disorders: neurosis and psychosis.
- Excessive impulsivity and unstable self-image, emotions, and relationships with others
- Often driven by abandonment fears
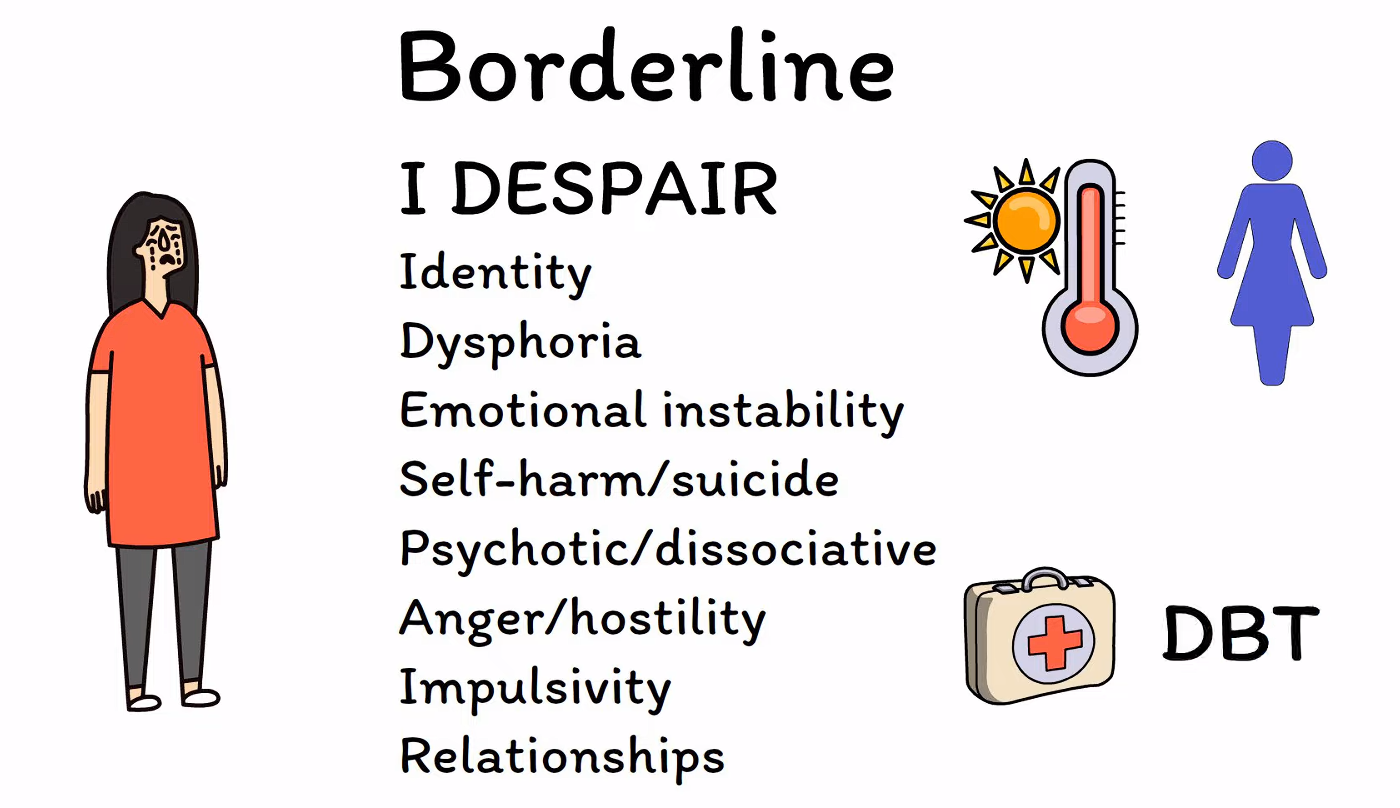
- Other features: splitting (psychiatry), a defense mechanism in which relationships are categorically good or bad
Mnemonic
Borders split countries.
Antisocial personality disorder
Clinical features
- Violates rights of others, social norms, laws
- Impulsive, irritable, aggressive (fights, assaults)
- Consistently irresponsible, lies, is deceitful
- Lack of remorse
- Age ≥18
- Evidence of conduct disorder before age 15 t
Differential diagnosis
- Borderline personality disorder (exploitative behaviors related to abandonment fears)
- Conduct disorder (pattern of violating societal norms & rights of others; age < 18)
- Narcissistic personality disorder (no pattern of violence or criminal activity)
Histrionic personality disorder
- Presentation: Excessive emotionality and attention-seeking. Often theatrical, sexually provocative, and easily influenced. Considers relationships to be more intimate than they are.
Narcissistic personality disorder
- Presentation: Grandiosity, need for admiration, and lack of empathy. Has a sense of entitlement and exploits others for personal gain. Fragile self-esteem, sensitive to criticism (“narcissistic injury”).
Cluster C
- Avoidant: avoidance due to fears of criticism & rejection
- But they strongly desire relationships and social acceptance, different from schizoid
- Dependent: submissive, clingy, needs to be taken care of
- Obsessive-compulsive: Preoccupation with orderliness, perfectionism, and mental/interpersonal control, at the expense of flexibility and efficiency. Often rigid, stubborn, and perfectionistic to the point that it interferes with task completion.