- Atropine: A prototype non-selective antagonist. Used for bradycardia and as an antidote for cholinergic poisoning. It is derived from plants like Atropa belladonna.
- Scopolamine: Similar to atropine but with greater CNS effects; available as a transdermal patch for motion sickness.
- Ipratropium & Tiotropium: Quaternary amines, which limits their systemic absorption and CNS effects when inhaled, making them ideal for respiratory conditions. Tiotropium is long-acting.
- Oxybutynin & Tolterodine: Used for overactive bladder. Tolterodine is more selective for the bladder and generally has fewer side effects like dry mouth compared to oxybutynin.
- Benztropine: Centrally acting, used for Parkinson’s disease to correct the dopamine-acetylcholine imbalance.
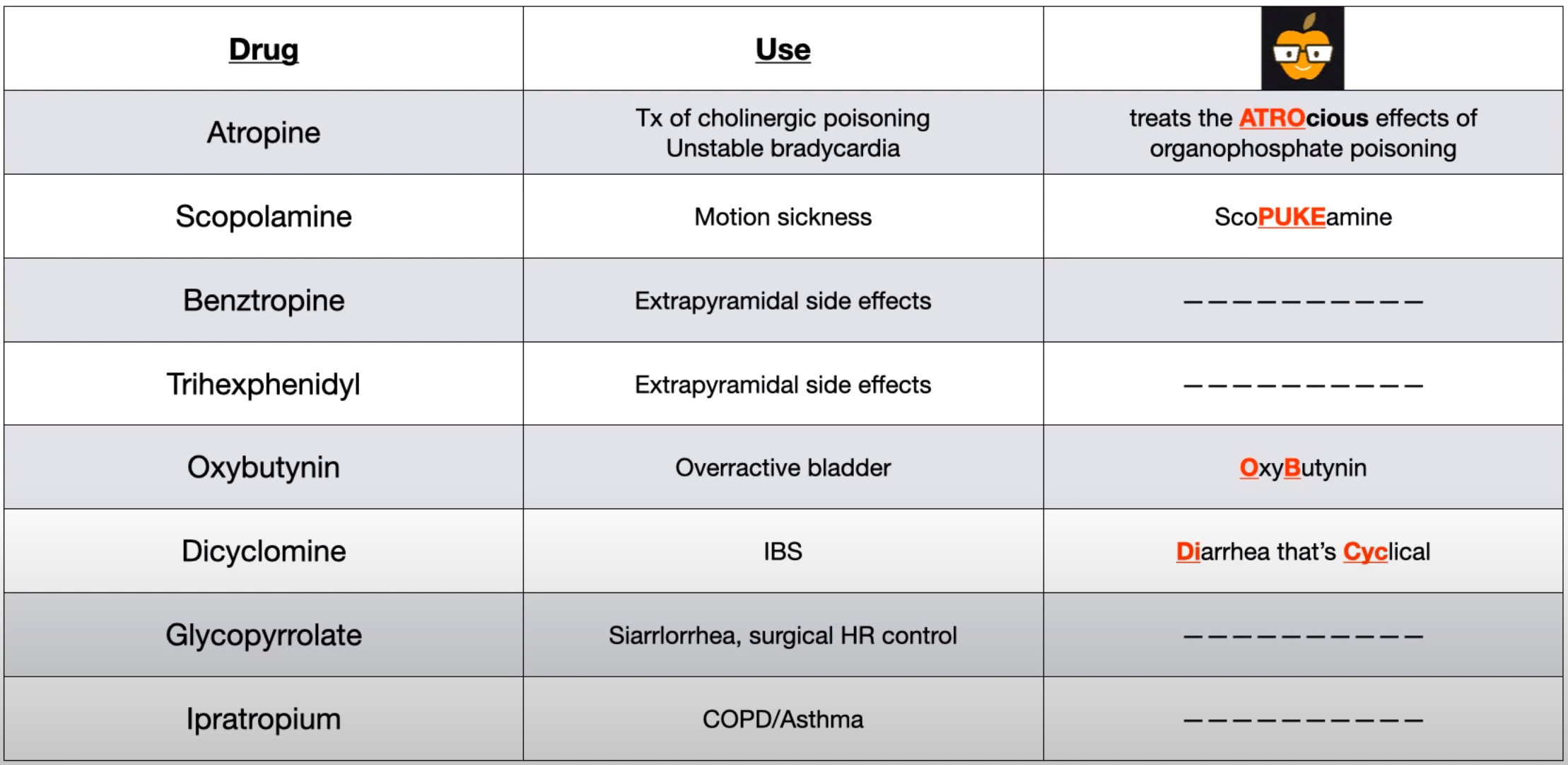
- Glycopyrrolate
- Effects: ↓ GI and respiratory secretions
- Indications
- Peptic ulcer disease
- Drooling
- Preoperative IV use to decrease respiratory secretions
GlycoDRYRATE
- Glyco: Represents glycopyrrolate.
- DRY: Represents its ability to reduce excessive salivation (sialorrhea).
- Rate: Emphasizes the therapeutic effect on heart rate control.
Anticholinergic syndrome (overdose)
- Etiology
- Belladonna poisoning