Commonly used intracellular immunohistochemical stains
| Stain | Target / Normal Cells | Key Tumor / Disease Association |
|---|---|---|
| Cytokeratin | Epithelial cells t | Carcinoma (e.g., Squamous cell, Adenocarcinoma) |
| Vimentin | Mesenchymal cells (fibroblasts) | Sarcoma, Meningioma, Endometrial CA, RCC |
| Desmin | Muscle cells t | Rhabdomyosarcoma, Leiomyosarcoma |
| GFAP | Glial cells (Astrocytes) | Astrocytoma, Glioblastoma |
| Neurofilament | Neurons | Neuroblastoma, Pheochromocytoma |
| S-100 | Neural crest cells t | Melanoma, Schwannoma, Langerhans cell histiocytosis |
| HMB-45 | Melanocytes t | Melanoma (More specific than S-100) |
| Chromogranin, Synaptophysin | Neuroendocrine cells t | Small Cell Lung Cancer, Carcinoid, Pheochromocytoma |
| Calretinin | Mesothelium | Mesothelioma t (distinguishes from lung adenocarcinoma) |
| CD31 / vWF | Vascular endothelium | Angiosarcoma, Kaposi Sarcoma, Hemangioma |
| CD45 (LCA) | Leukocytes | Lymphoma, Leukemia (general screen) |
| CD3 | T-cells | T-cell Lymphoma, T-ALL |
| TRAP | Osteoclasts / B-cells | Hairy Cell Leukemia |
*Intermediate filaments (cytoskeletal structural components).
Intermediate filaments
- Functions: maintain cell structure
- Examples: cytokeratin (in epithelial cells), vimentin (in fibroblasts), desmin (in muscle fibers), glial fibrillary acid proteins (GFAP, in glial cells), neurofilaments (in nerve cells), nestin (in neuronal stem cells), lamins (in cell nucleus)
Microtubules
Accessory protein
- Microtubule-associated proteins (MAPs) such as tau protein
- Microtubule motor proteins: a class of ATPase proteins converting the energy derived from the hydrolysis of ATP into mechanical energy for movement of cells/organelles.
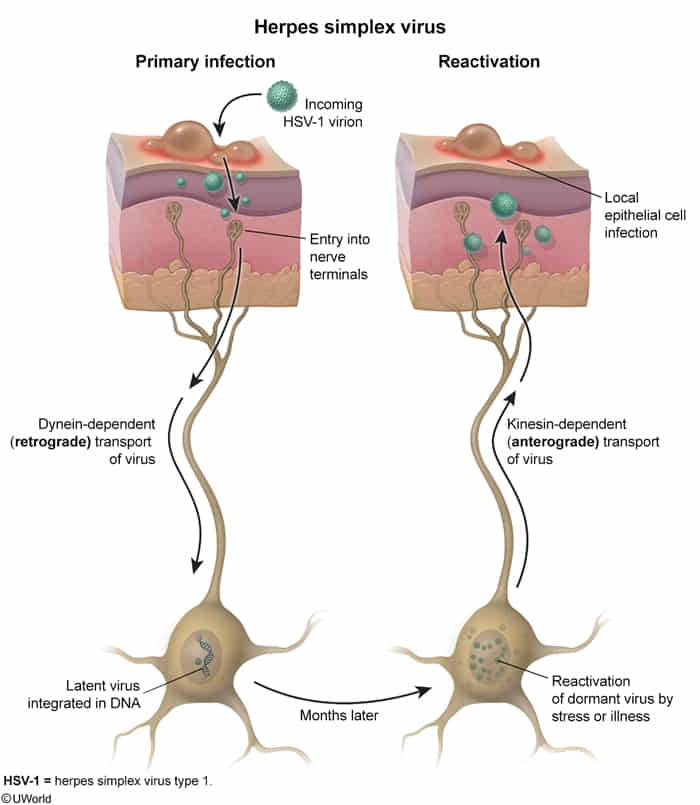
- Kinesin: anterograde transport of vesicles from the (‑) to the (+) ends of microtubules
- Kinesin is used by Herpes simplex virus to travel from sensory neurons to epithelial tissues, leading to virus reactivation from latency
- Dynein: retrograde transport of vesicles from the (+) to the (‑) ends of microtubules
- Dynein is used by Clostridium tetani, herpes simplex virus, poliovirus, and rabies virus for transport from the axon terminal to the neuronal cell body.
- Axonemal dynein: special dynein that links the peripheral 9 tubulin dimers of the axonem, which causes the cilia and flagella to bend
- Kinesin: anterograde transport of vesicles from the (‑) to the (+) ends of microtubules
Mnemonic
Kin (keen) to go out (anterograde), Dying to come back home (retrograde). t