Rule of 4s
- 4 CNs in:
- Medulla
- Pons
- Above Pons (midbrain)
- 4 CNs divide into 12 are in the midline
- III, IV, VI, XII
- 4 CNs do not divide/12 are in the lateral
- V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI
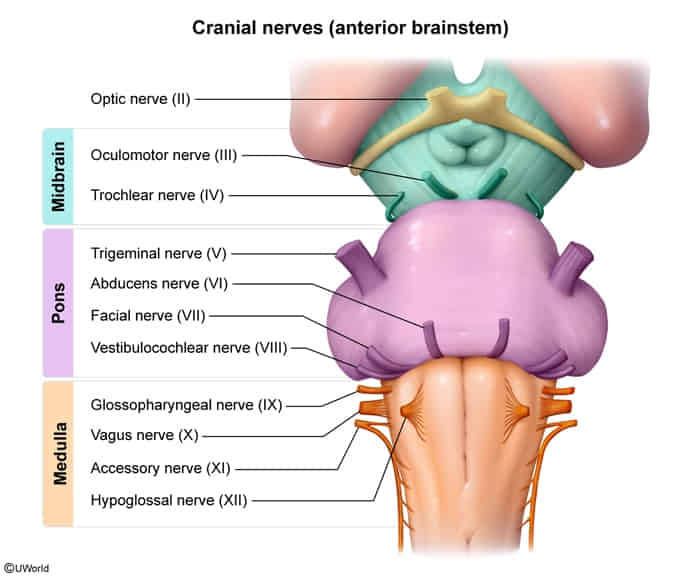
- V, VII, VIII, IX, X, XI
- 4 midline columns -> motor
- Motor nucleus
- Motor pathway
- MLF
- Medial Lemniscus
- 4 lateral (side) columns -> sensory
- Sympathetic
- Spinothalamic
- Sensory
- Spinocerebellar
Cranial nucleus in brainstem
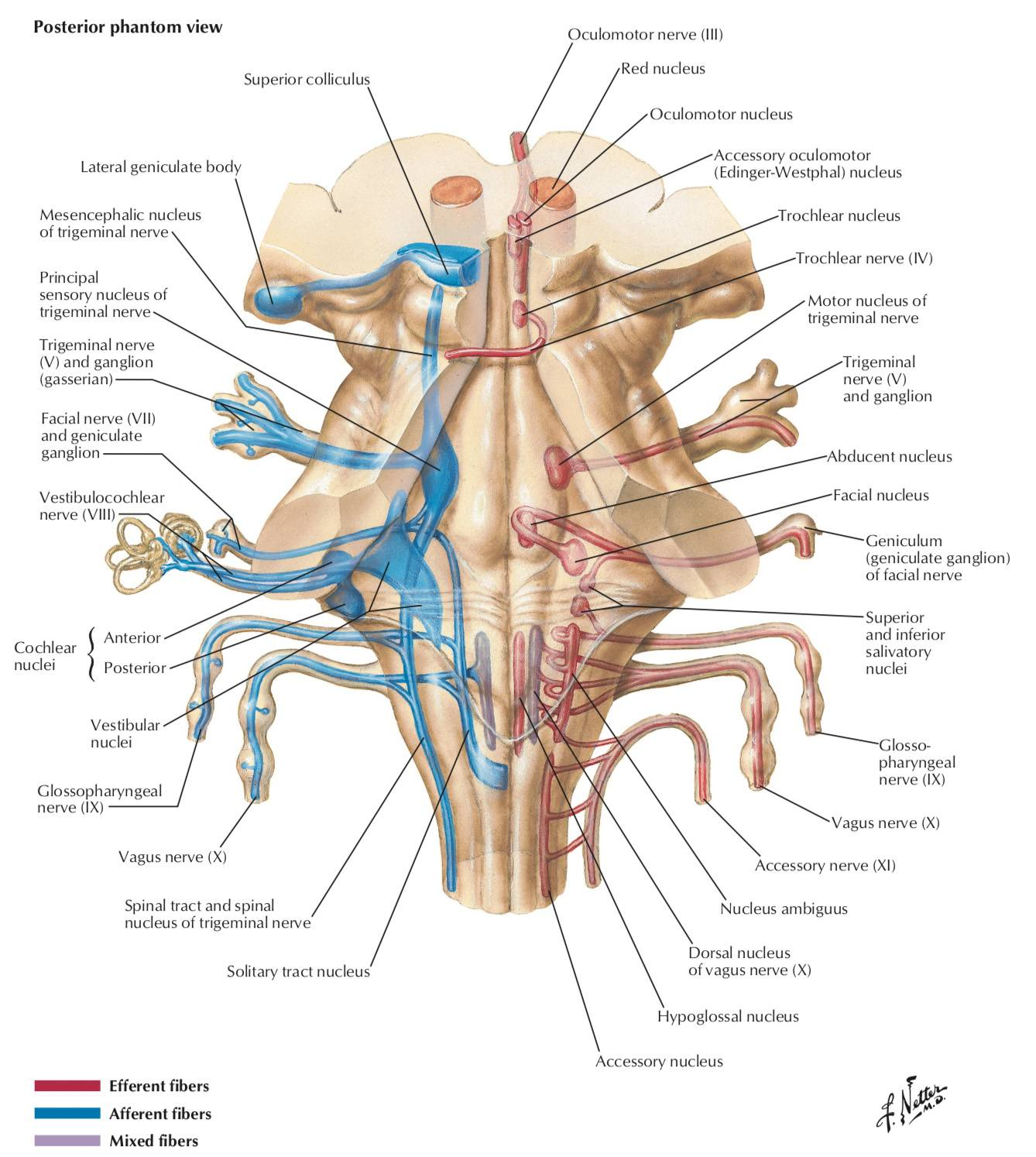
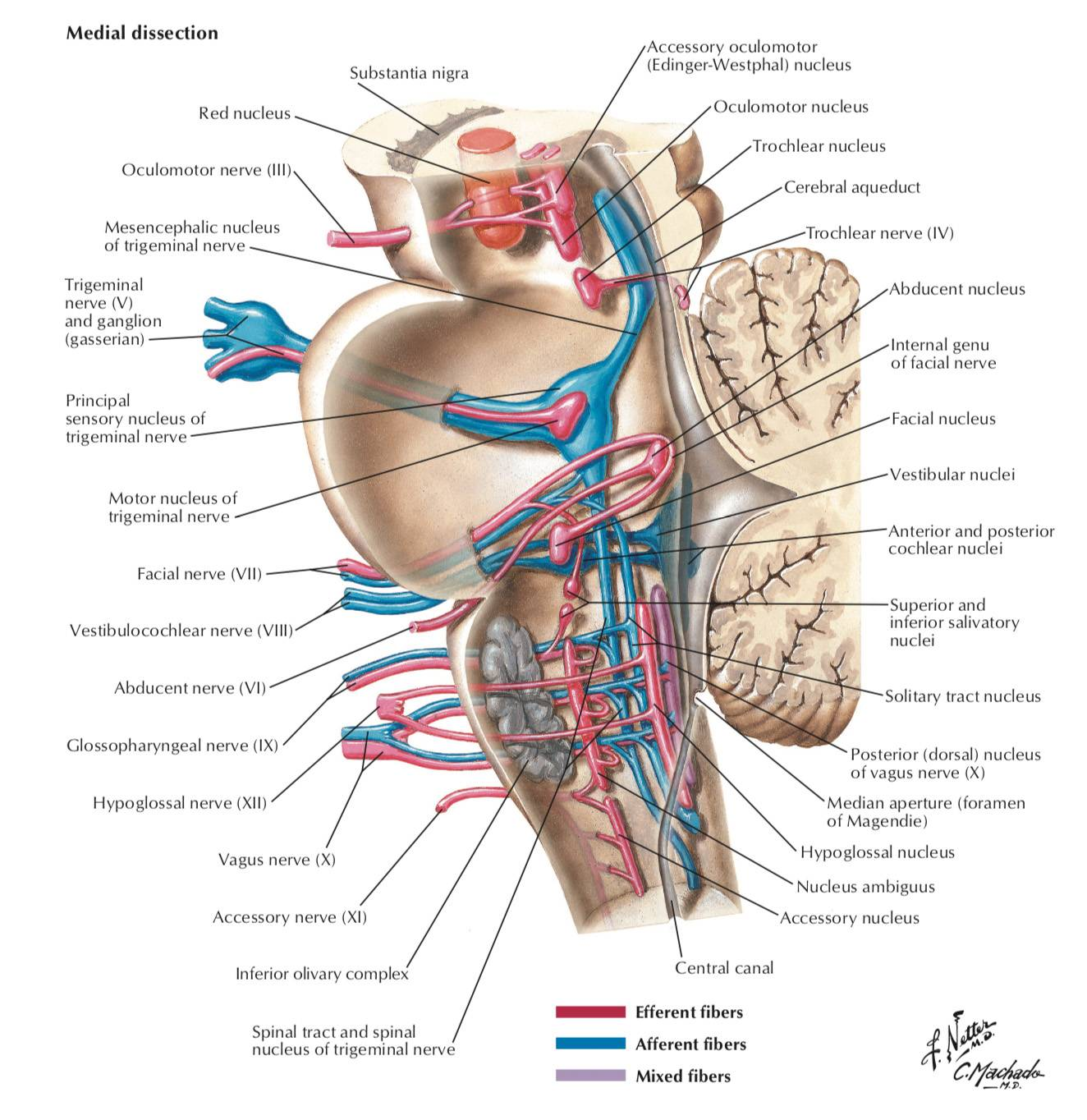
Midbrain (Mesencephalon):
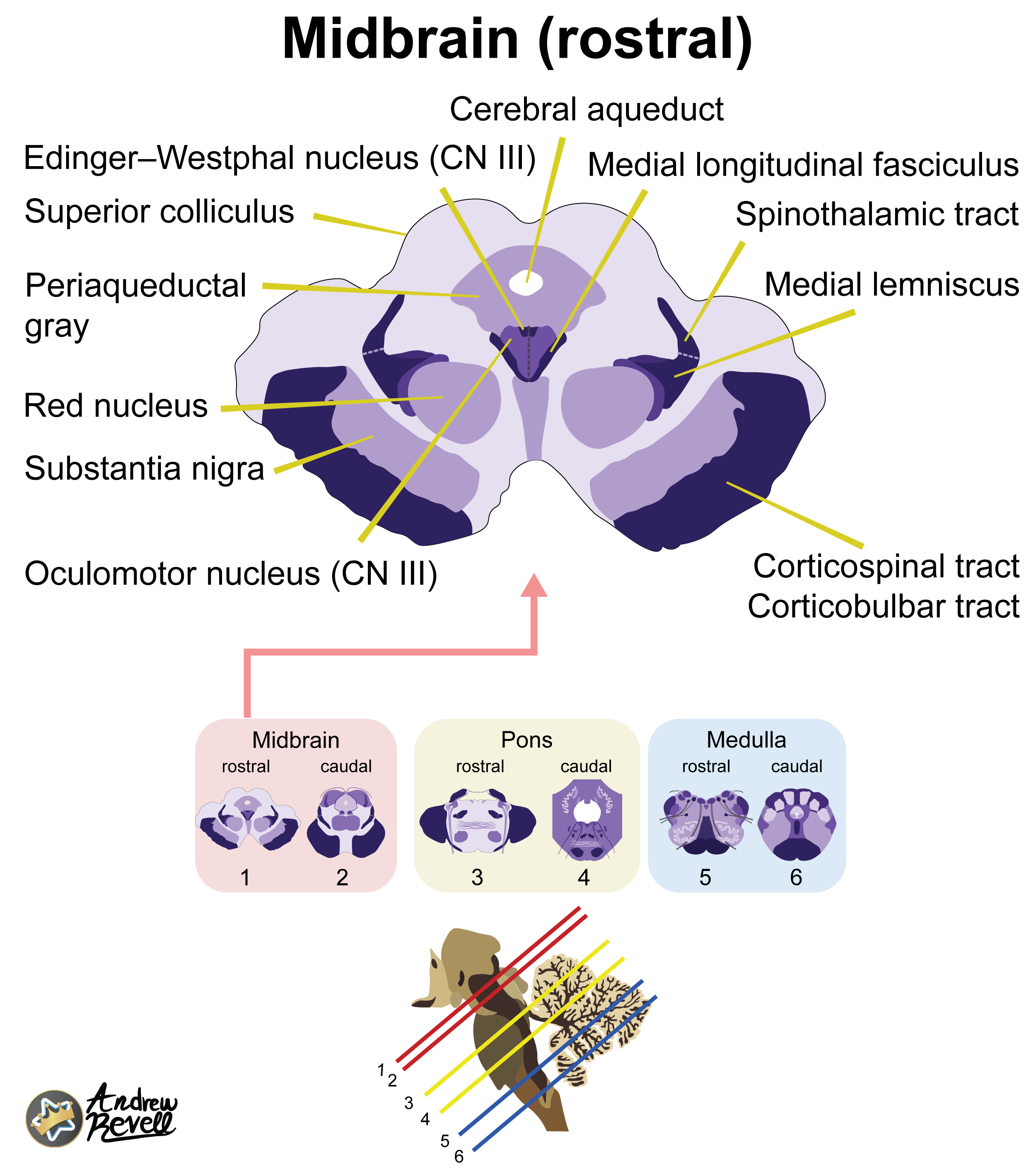
Tip
-
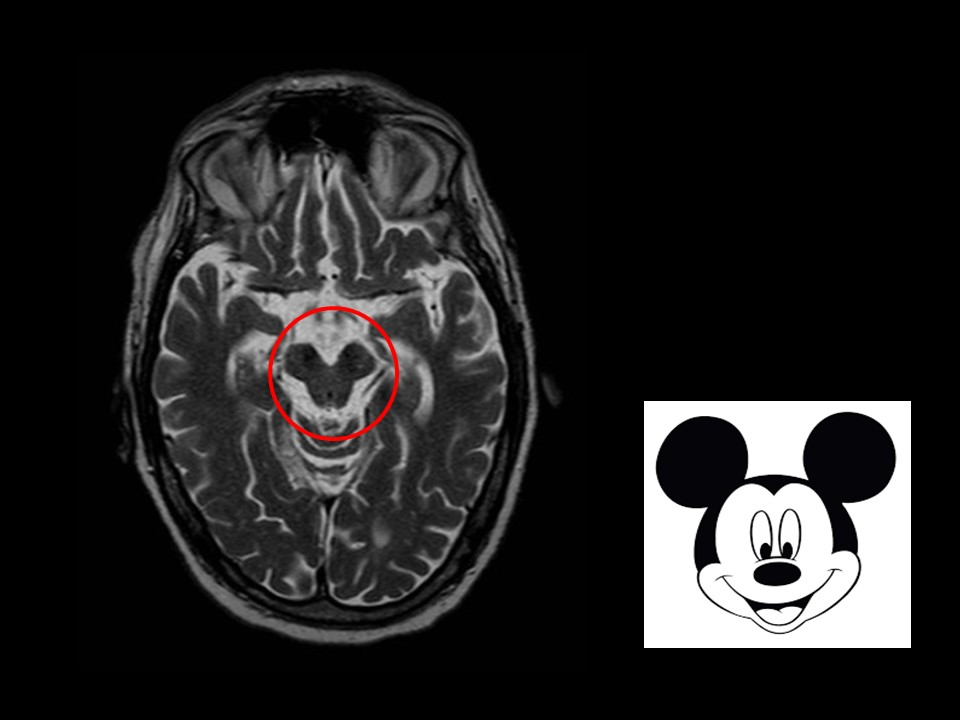
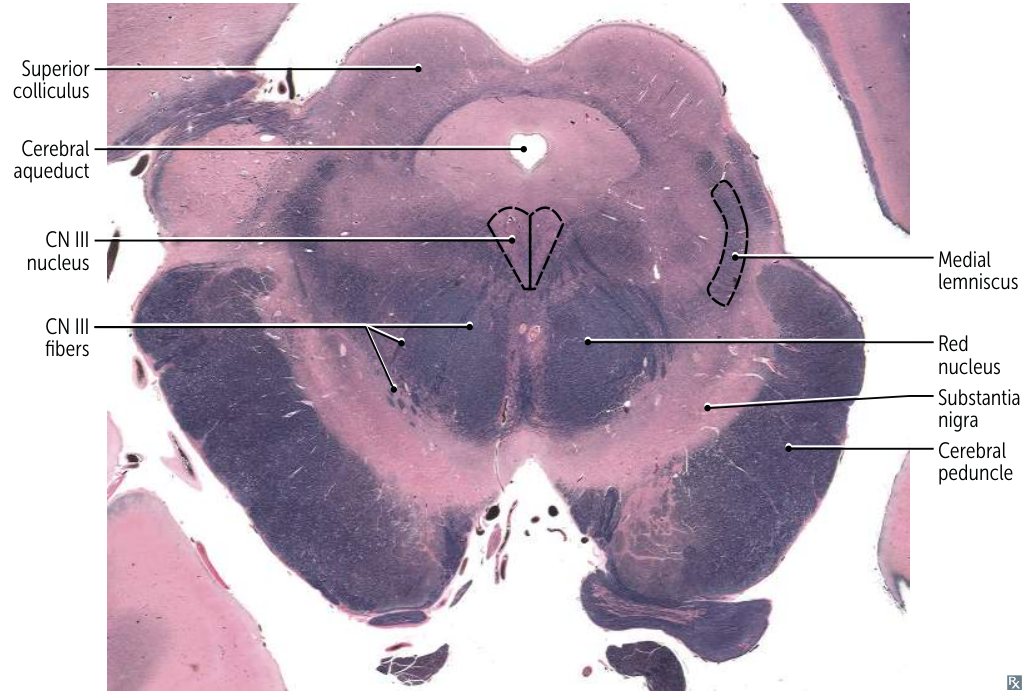
Rostral Midbrain (at Superior Colliculus):
- Most Distinctive Feature: Presence of the large, circular Red Nucleus and the Superior Colliculus. CN III nucleus/fibers are also visible.
- Mnemonic: "Red eyes on Mickey Mouse" (Red Nucleus, CN III ocular motor nucleus, Mickey Mouse shape of cerebral peduncles).
-
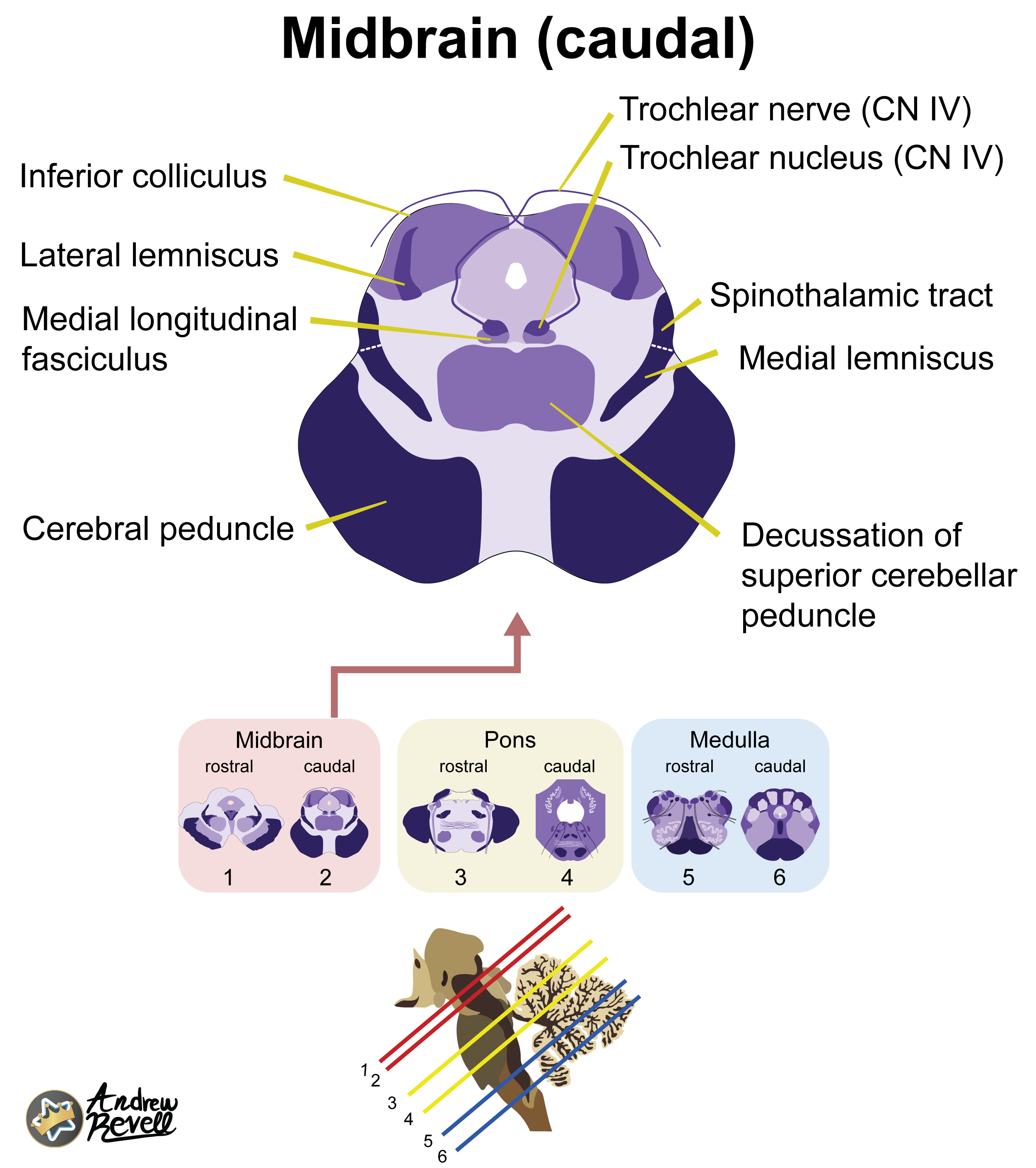
Caudal Midbrain (at Inferior Colliculus):
- Most Distinctive Feature: Decussation of the Superior Cerebellar Peduncles (looks like a large "X" of fibers in the center) sitting beneath the Inferior Colliculus.
- Most Distinctive Feature: Decussation of the Superior Cerebellar Peduncles (looks like a large "X" of fibers in the center) sitting beneath the Inferior Colliculus.
- CN III (Oculomotor) nucleus: Controls most eye movements, pupil constriction, and lens accommodation.
- CN IV (Trochlear) nucleus: Controls the superior oblique muscle of the eye.
- (Also contains the Mesencephalic Nucleus of CN V, which handles proprioception from muscles of mastication).
Pons
Tip
-
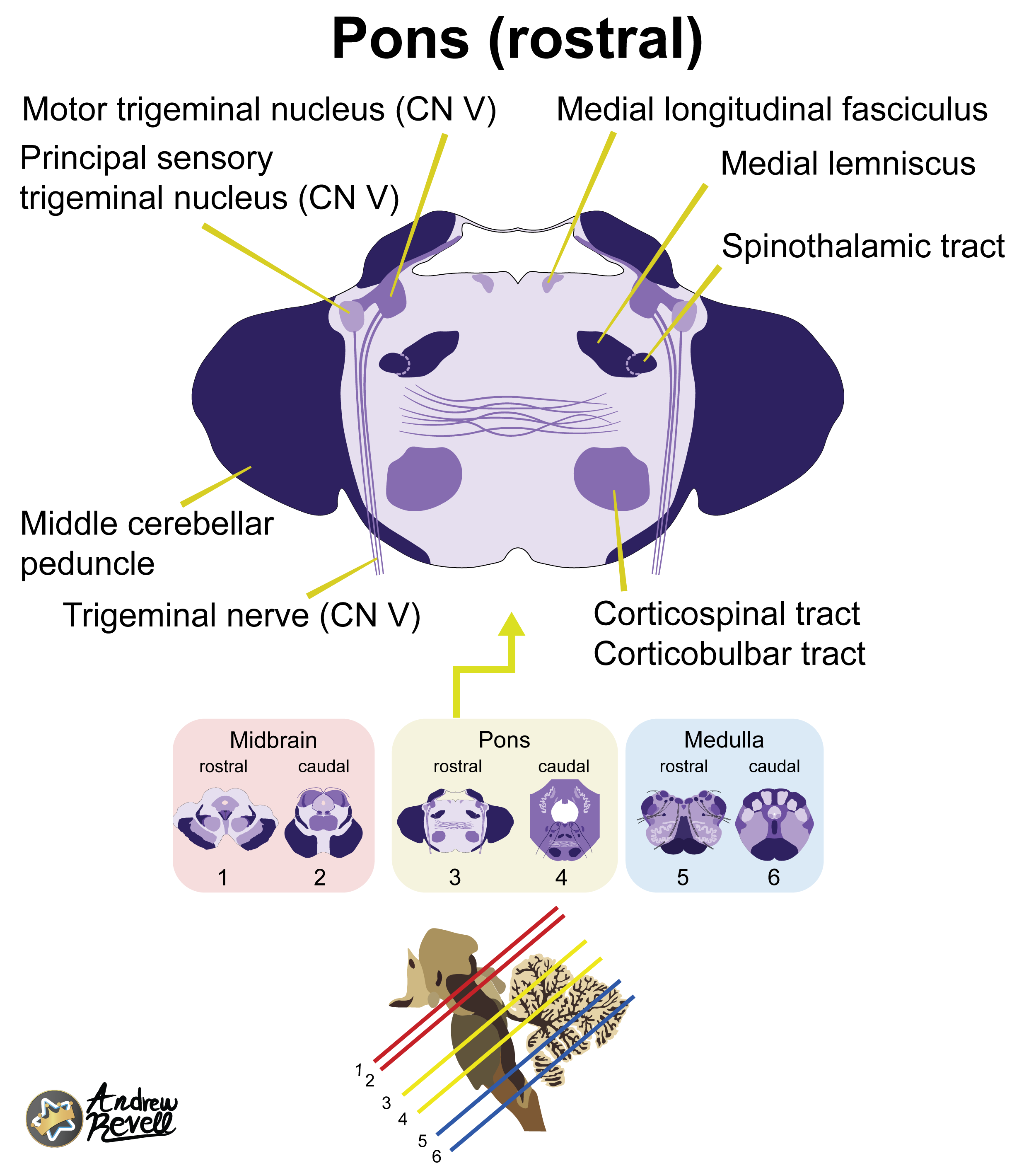
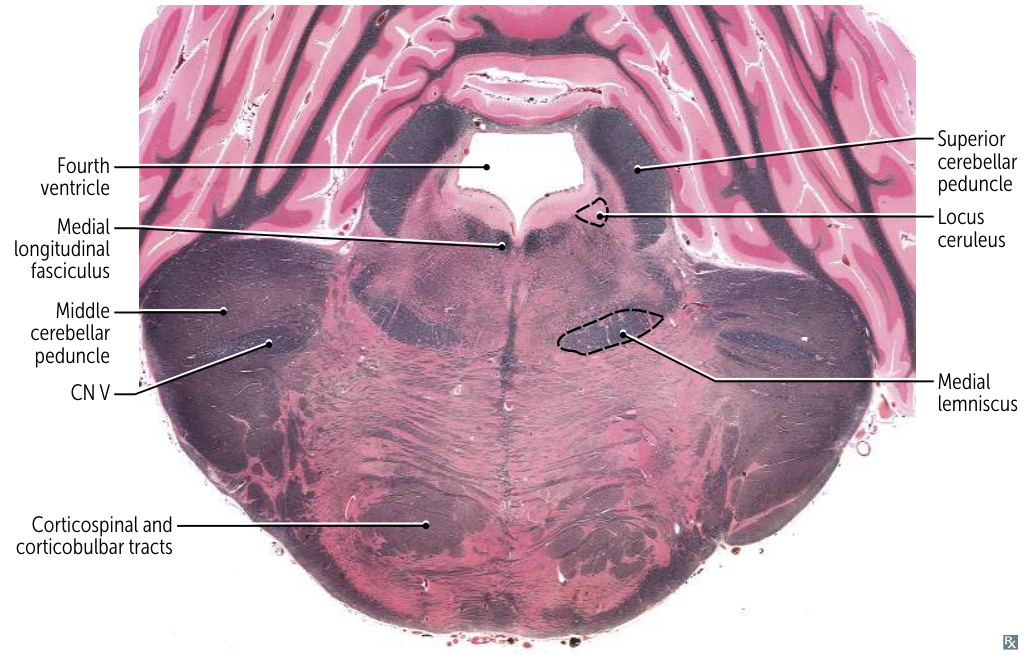
Rostral Pons:
- Most Distinctive Feature: Massive Middle Cerebellar Peduncles forming the wide, bulbous sides of the pons. Trigeminal (CN V) nuclei and nerve are present.
-
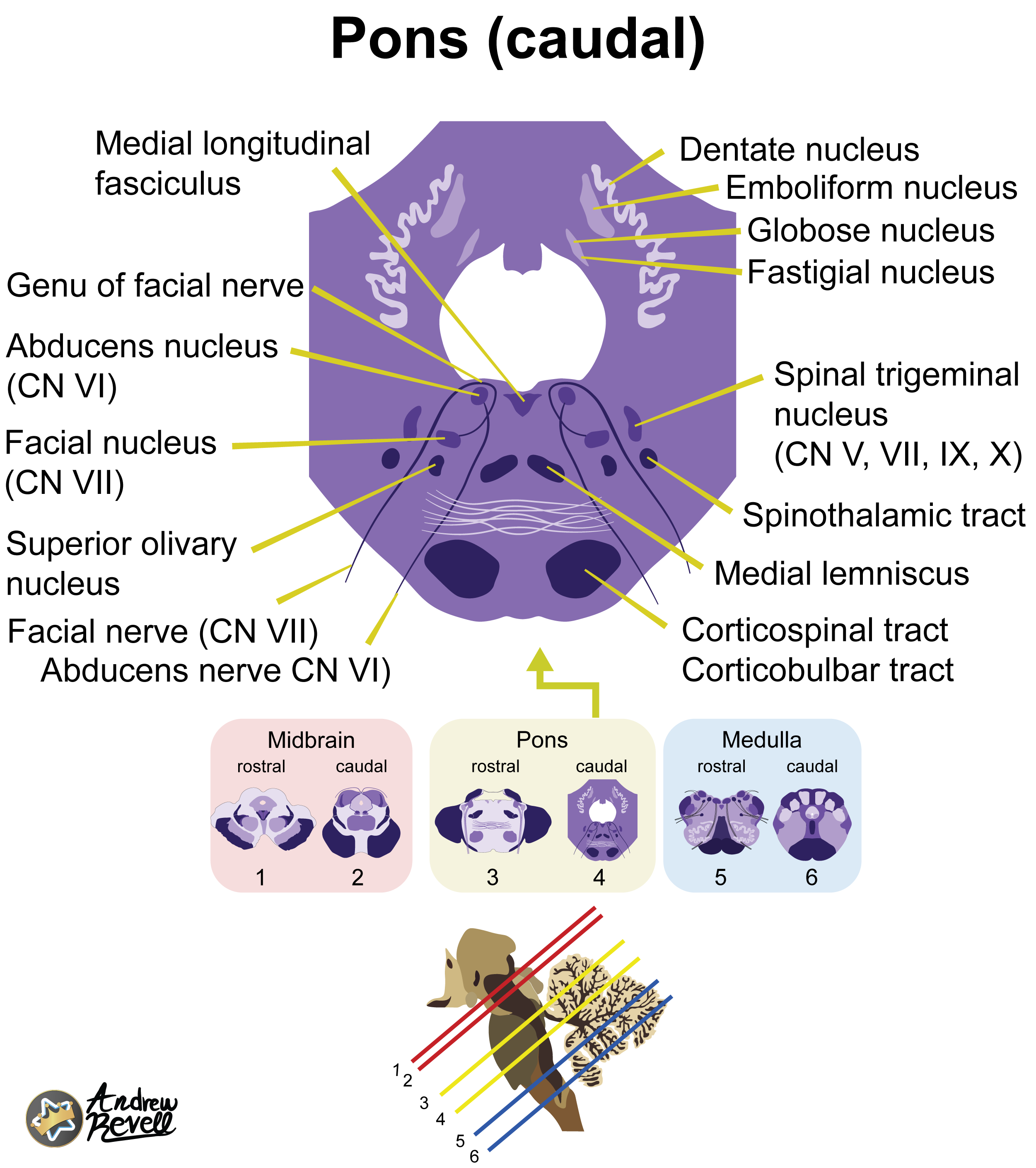
Caudal Pons:
- Most Distinctive Feature: The Facial Colliculus – a distinct pair of bumps on the floor of the wide fourth ventricle, formed by facial nerve (CN VII) fibers looping around the abducens (CN VI) nucleus.
- Most Distinctive Feature: The Facial Colliculus – a distinct pair of bumps on the floor of the wide fourth ventricle, formed by facial nerve (CN VII) fibers looping around the abducens (CN VI) nucleus.
- CN V (Trigeminal) nuclei:
- Main Sensory Nucleus: Processes discriminative touch and pressure sensations from the face.
- Motor Nucleus: Controls muscles of mastication (chewing).
- (The Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus begins here and extends down; the Mesencephalic Nucleus extends up).
- CN VI (Abducens) nucleus: Controls the lateral rectus muscle of the eye (abduction).
- CN VII (Facial) nucleus: Controls muscles of facial expression, taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and stimulates salivary and lacrimal glands.
- CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear) nuclei (partly): The Cochlear and Vestibular nuclei are located primarily at the junction between the pons and medulla (pontomedullary junction).
Medulla Oblongata
Tip
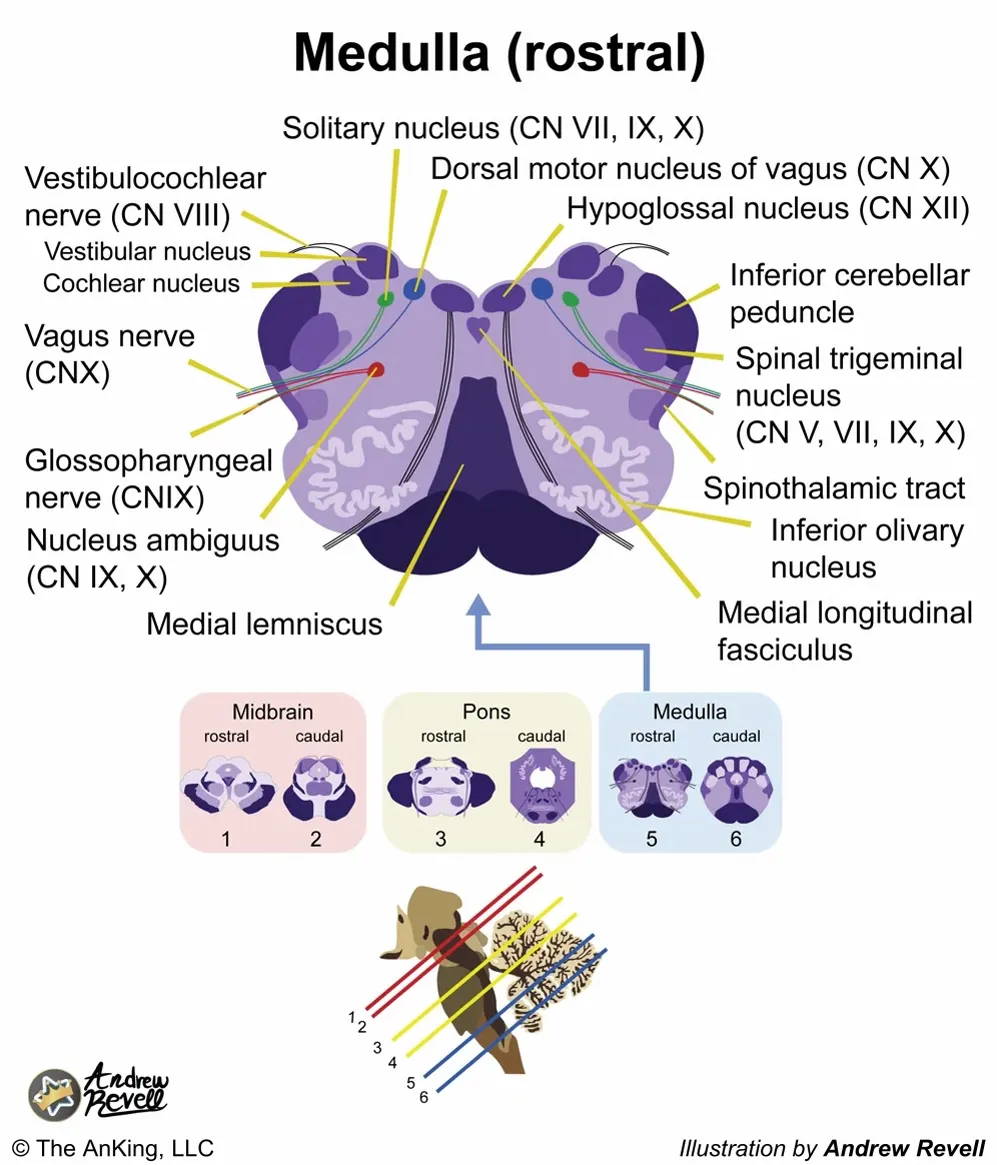
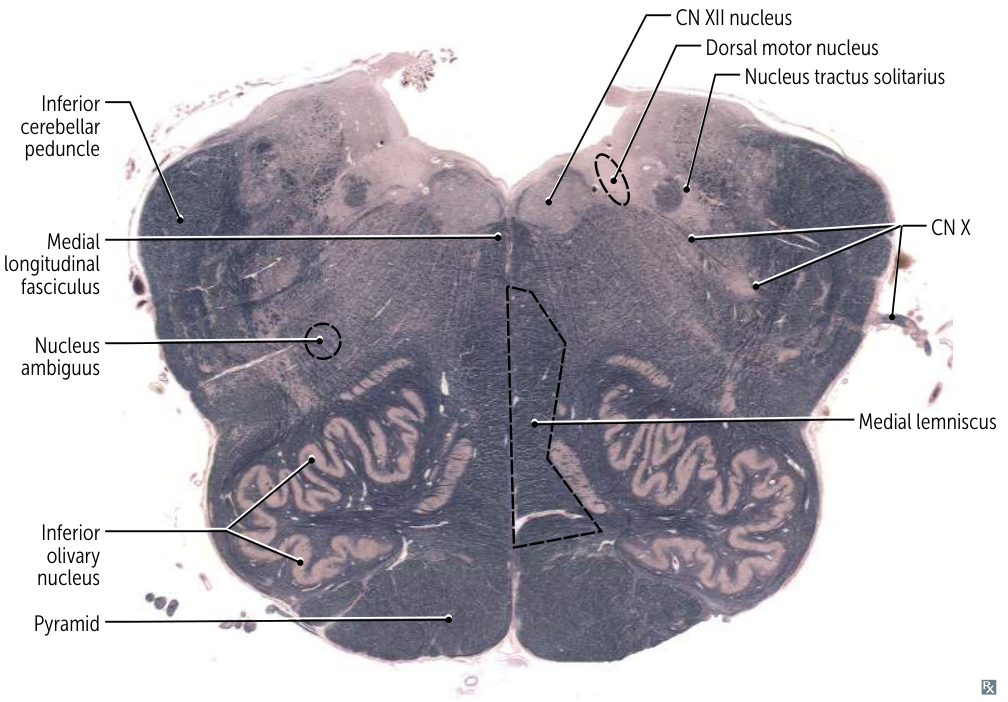
- Rostral Medulla (Open Medulla):
- Most Distinctive Feature: The large, highly convoluted ("squiggly") Inferior Olivary Nucleus. The fourth ventricle is open ("open medulla").
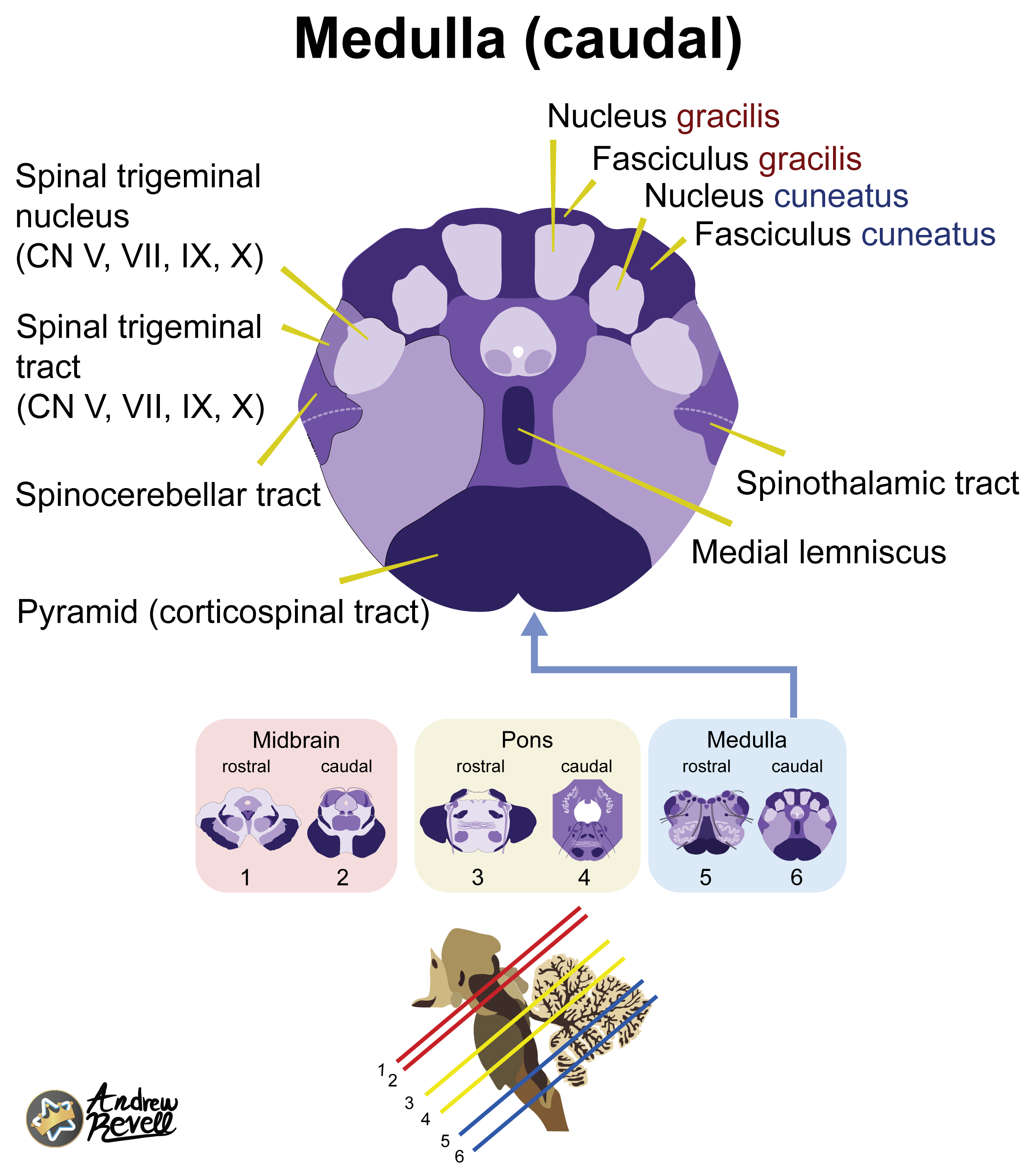
- Caudal Medulla (Closed Medulla):
- Most Distinctive Feature: The Pyramidal Decussation (corticospinal tracts crossing over) on the anterior aspect. The dorsal column nuclei (Nucleus Gracilis & Cuneatus) are prominent dorsally. The fourth ventricle has closed to a central canal.
- Most Distinctive Feature: The Pyramidal Decussation (corticospinal tracts crossing over) on the anterior aspect. The dorsal column nuclei (Nucleus Gracilis & Cuneatus) are prominent dorsally. The fourth ventricle has closed to a central canal.
- CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear) nuclei (partly): The Vestibular nuclei extend significantly into the medulla.
- CN IX (Glossopharyngeal) nuclei: Involved in taste from the posterior third of the tongue, sensation from the pharynx, salivation (parotid gland), and swallowing. Key nuclei include parts of the Nucleus Ambiguus, Solitary Nucleus, and Inferior Salivatory Nucleus.
- CN X (Vagus) nuclei: Involved in swallowing, speech, parasympathetic control of the heart, lungs, and abdominal organs, sensation from the pharynx and larynx, and taste from the epiglottis. Key nuclei include the Dorsal Motor Nucleus of the Vagus, Nucleus Ambiguus, and Solitary Nucleus.
- CN XI (Accessory) nucleus (Cranial Part): The cranial root originates from the Nucleus Ambiguus and joins the vagus nerve to innervate laryngeal muscles. (The main spinal part arises from the cervical spinal cord).
- CN XII (Hypoglossal) nucleus: Controls tongue movements.
- (Also contains the lower part of the Spinal Trigeminal Nucleus (CN V) processing facial pain and temperature).