- Referred Otalgia is a Key Concept
- Ear pain in the setting of a normal ear exam is called referred otalgia. This is extremely high-yield.
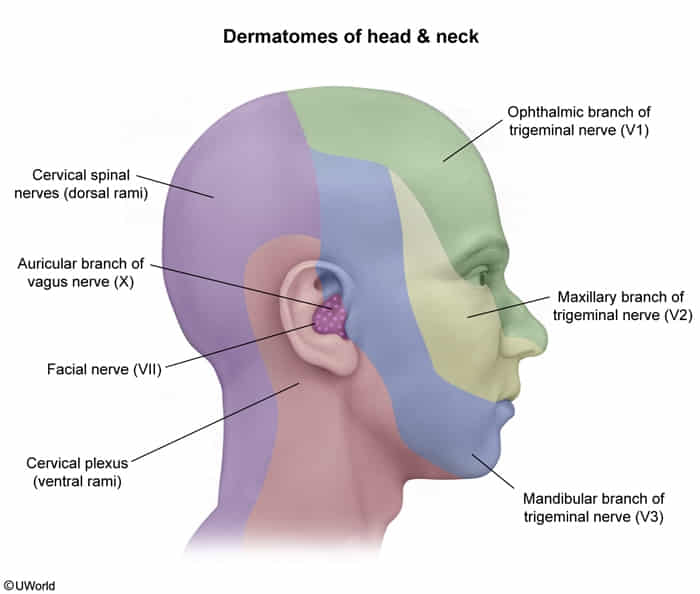
- The complex sensory innervation of the ear from multiple cranial nerves (CN V, VII, IX, X) and cervical nerves (C2, C3) is the underlying reason.
- Motor Innervation of Middle Ear Muscles
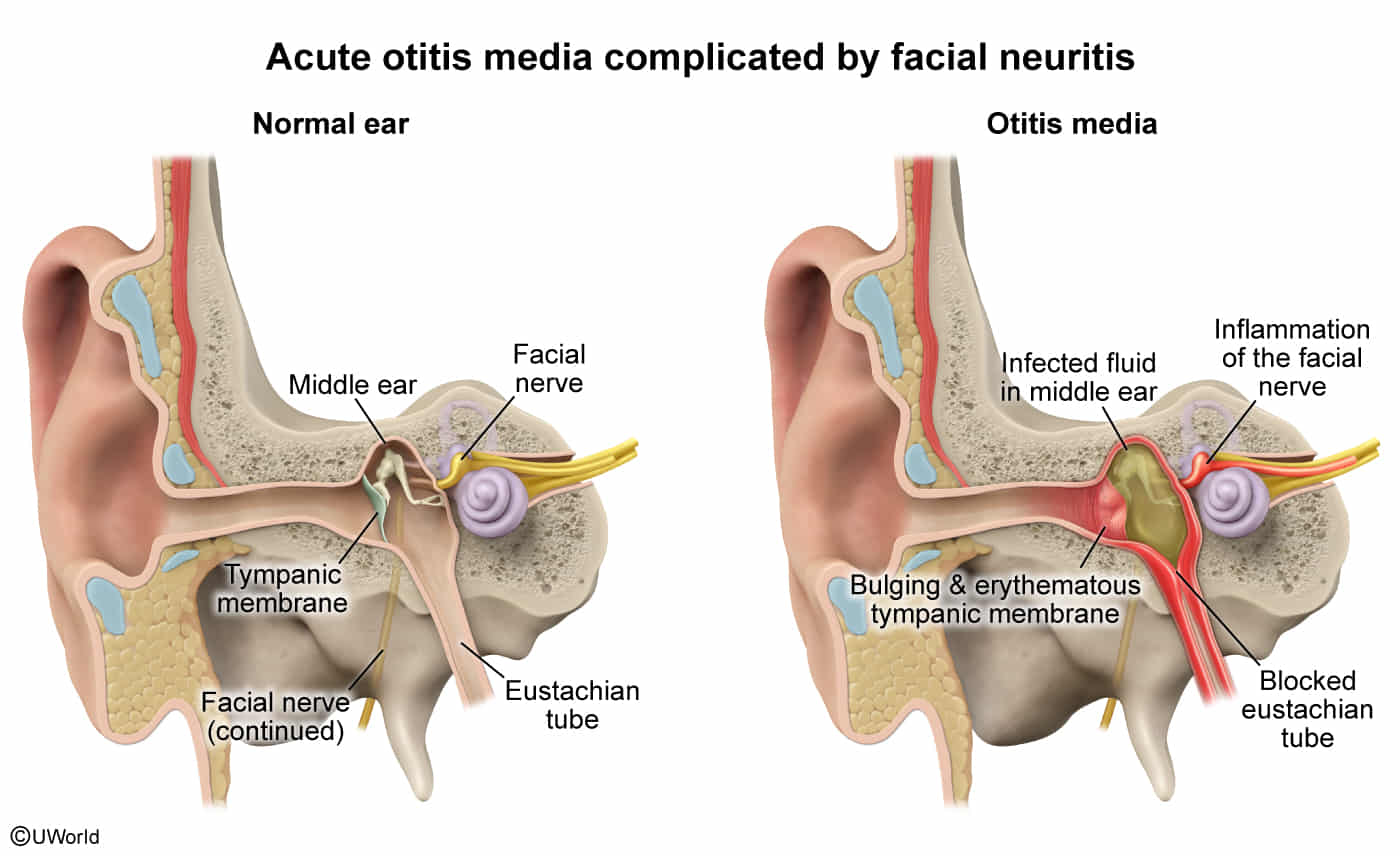
- Stapedius Muscle → Facial Nerve (CN VII): Paralysis of CN VII (e.g., Bell’s Palsy) leads to paralysis of the stapedius. This causes hyperacusis (increased sensitivity to sound) because the muscle can no longer dampen loud noises. This is a classic USMLE association.
- Tensor Tympani Muscle → Trigeminal Nerve (CN V3): Tenses the tympanic membrane.
- Mnemonic: Stapedius = Seventh Nerve (CN VII); Tensor Tympani = Trigeminal Nerve (CN V).
- General Sensation & Clinically Important Nerves
- CN V3 (Auriculotemporal Branch): Supplies the anterior/superior portions of the external canal and auricle. It is the most common pathway for referred otalgia, especially from dental disease or TMJ disorders.
- CN X (Auricular Branch - “Arnold’s Nerve”): Supplies the posterior/inferior external auditory canal and concha.
- Arnold’s Ear-Cough Reflex: Stimulating the posterior ear canal (e.g., with an otoscope) can trigger a cough. This is a classic reflex demonstrating vagal innervation. It can be a rare cause of chronic cough.
- CN IX (Glossopharyngeal Nerve - “Jacobson’s Nerve”): Supplies the medial surface of the tympanic membrane and the middle ear cavity. Referred pain often originates from the tonsils or pharynx.
- CN VII (Facial Nerve): Provides some sensory fibers to the external ear. Pain preceding facial paralysis may be a feature of Bell’s palsy or Ramsay Hunt syndrome.
- Special Sense
- CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear Nerve): Purely sensory for hearing (cochlear division) and balance (vestibular division).
- Acoustic Neuroma (Vestibular Schwannoma): A tumor of CN VIII located at the cerebellopontine angle. Presents with unilateral sensorineural hearing loss, tinnitus, and vertigo.