Brain anatomy
Sagittal section of the brain

Meninges and spaces
1. Anatomical Relationships and Size of Spaces
The meninges consist of three layers surrounding the brain and spinal cord:
- Dura mater (outermost, tough layer)
- Arachnoid mater (middle, web-like layer)
- Pia mater (innermost, delicate layer adherent to the brain surface)
Between these layers, there are spaces:
-
Epidural space: Between the dura mater and the skull (or vertebral bones).
- In the cranial cavity, this space is a potential space because the dura is tightly adherent to the skull. Has Middle Meningeal Artery.
- In the spinal canal, the epidural space is a real space containing fat and venous plexuses.
- Thickness: In the spinal canal, approx. 1-3 mm, variable by location.
-
Subdural space: Between dura mater and arachnoid mater.
- This is a potential space; normally the arachnoid and dura are in close contact. Has Bridging Veins.
- Thickness: Minimal under normal conditions, expands pathologically if bleeding occurs (subdural hematoma).
-
Subarachnoid space: Between arachnoid mater and pia mater.
- This is a real space filled with cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), trabeculae, and blood vessels.
- Thickness: Variable depending on location; generally about 1-5 mm.
- This space extends around the brain and spinal cord.
2. Functions of Each Layer and Their Spaces
-
Dura Mater
- Function: Provides a tough protective outer covering; dural septa compartmentalize brain regions (falx cerebri, tentorium cerebelli).
- In spinal cord, dura mater forms a protective covering and encloses the epidural space.
-
Epidural Space
- In the spine: provides cushioning and a route for venous return.
- Clinical use: Site for epidural anesthesia.
-
Arachnoid Mater
- Function: Thin, web-like membrane facilitating the passage of blood vessels.
- Its trabeculae extend to the pia mater.
-
Subdural Space
- Normally a potential space; no major function.
- Clinical: Site where blood can accumulate during traumatic injury (subdural hematoma).
-
Subarachnoid Space
- Function: Contains CSF, which cushions and nourishes the brain.
- Its trabeculae suspend the brain within the skull.
- Contains cerebral arteries and veins.
-
Pia Mater
- Delicate membrane tightly adherent to the brain surface.
- Supports tiny blood vessels entering brain tissue.
- Participates in blood-brain barrier and nutrient exchange.
3. Clinical Relevance
| Space | Clinical Points |
|---|---|
| Epidural Space | - In spinal epidural analgesia/anesthesia - Epidural hematomas (cranial) occurring between dura and skull are arterial and rapid |
| Subdural Space | - Subdural hematomas from bridging vein tearing; venous, slower onset - Potential space expands with blood accumulation |
| Subarachnoid Space | - Site of CSF flow; lumbar puncture accesses this space - Subarachnoid hemorrhage (from ruptured aneurysm) is life-threatening |
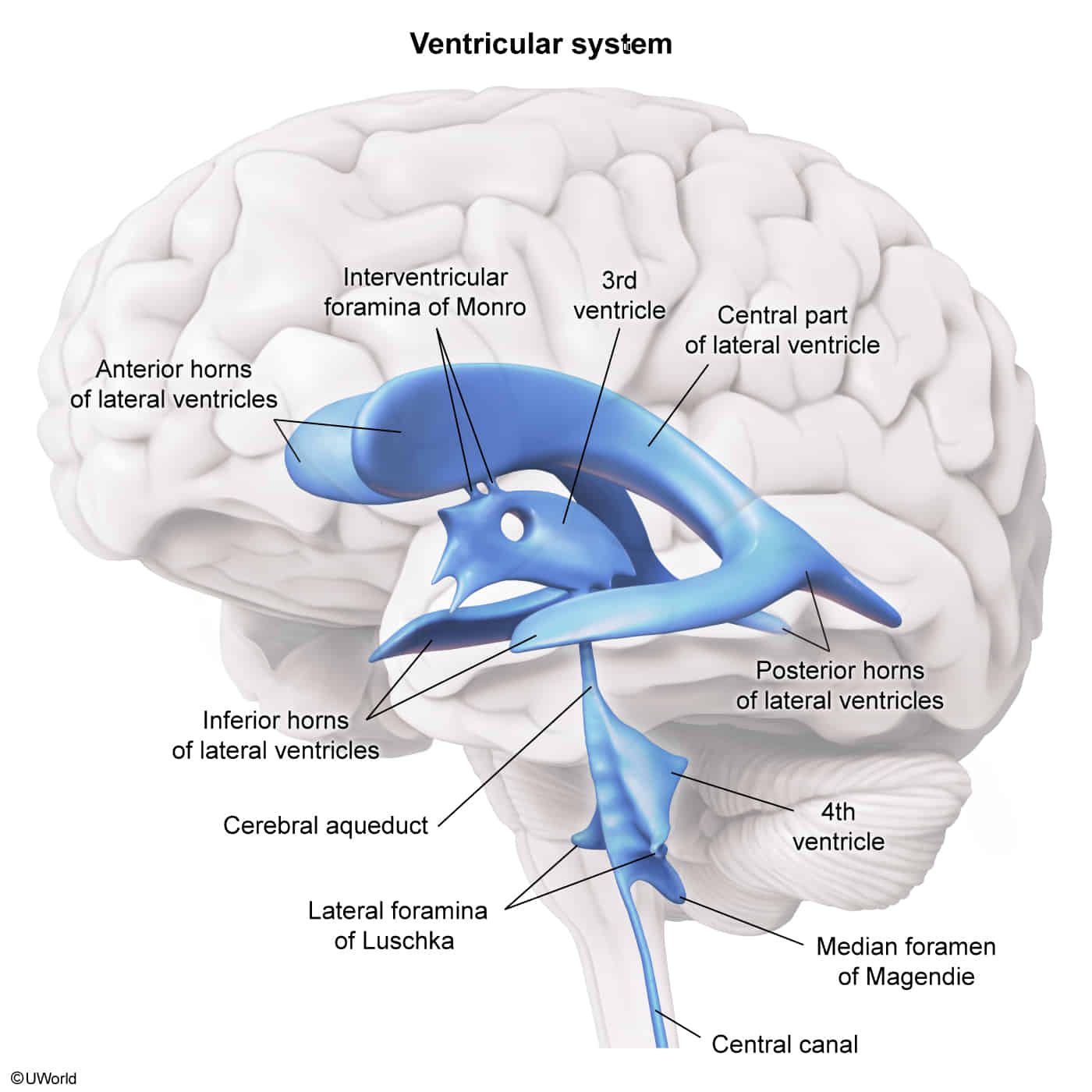
Ventricular system

CSF flow: CSF production: produced by choroid plexuses in the lateral, third, and fourth ventricles by filtration of plasma → lateral ventricles → third ventricle (via interventricular foramina) → fourth ventricle (via cerebral aqueduct) → diffusion and active transfer into the subarachnoid space (via foramina of Luschka and Magendie) → reabsorption in the arachnoid granulations (a group of projections of the arachnoid mater into the dural sinuses) → drainage into the dural venous sinuses → internal jugular veins, ultimately heart
Cerebellum

- Function
- Control of balance and ocular movements
- Planning of movements that are about to occur
- Coordination of complex and sequential movements
- Maintenance of muscle tone
Vasculature of the cerebellum
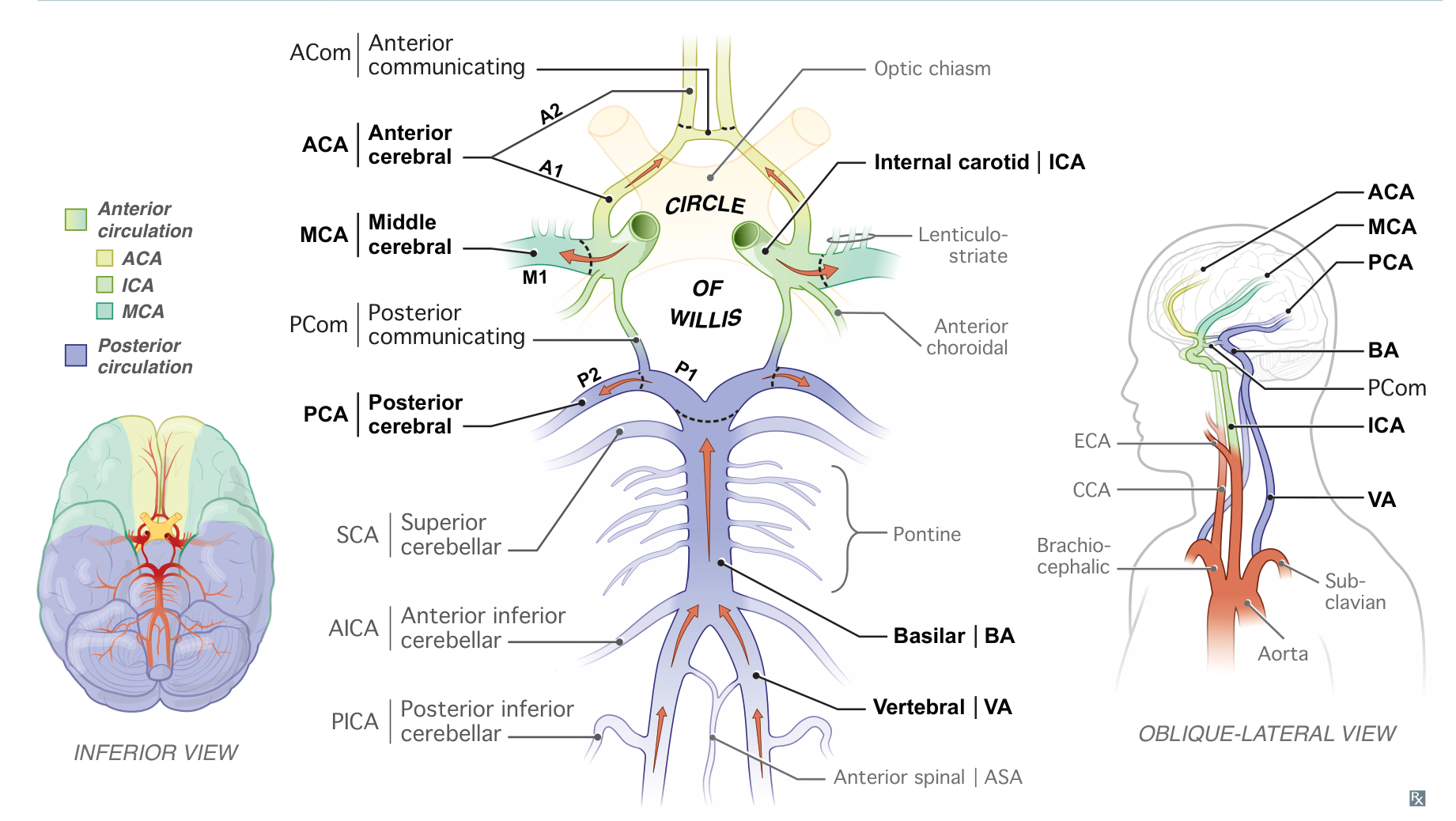

- Basilar artery
- Superior cerebellar artery (SCA) → superior surface of the cerebellum
- Also supplies the superior and middle cerebellar peduncles and the midbrain
- Anterior inferior cerebellar artery (AICA)→ anterior surface of the cerebellum
- Also supplies the middle cerebellar peduncle and inferolateral pons
- Superior cerebellar artery (SCA) → superior surface of the cerebellum
- Vertebral artery
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)→ posterior surface of the cerebellum
- Also supplies the inferior cerebellar peduncles and the inferolateral medulla
- Posterior inferior cerebellar artery (PICA)→ posterior surface of the cerebellum
Limbic system
- Function: involved in emotional and behavioral responses, motivation, memory, olfaction, and autonomic nervous system function


- Components
- Areas of the cerebral cortex: hippocampal formation (hippocampus, dentate gyrus, entorhinal cortex), cingulate gyrus
- Nuclei: mammillary bodies, amygdala, anterior thalamic nuclei
- Nerve fiber tracts
- Cerebral fornix: C-shaped nerve fiber bundle that represents the major output tract of the hippocampus
- Cingulum: nerve fiber bundle connecting cingulate gyrus and entorhinal cortex
- Mammillothalamic tract
- Striae terminalis