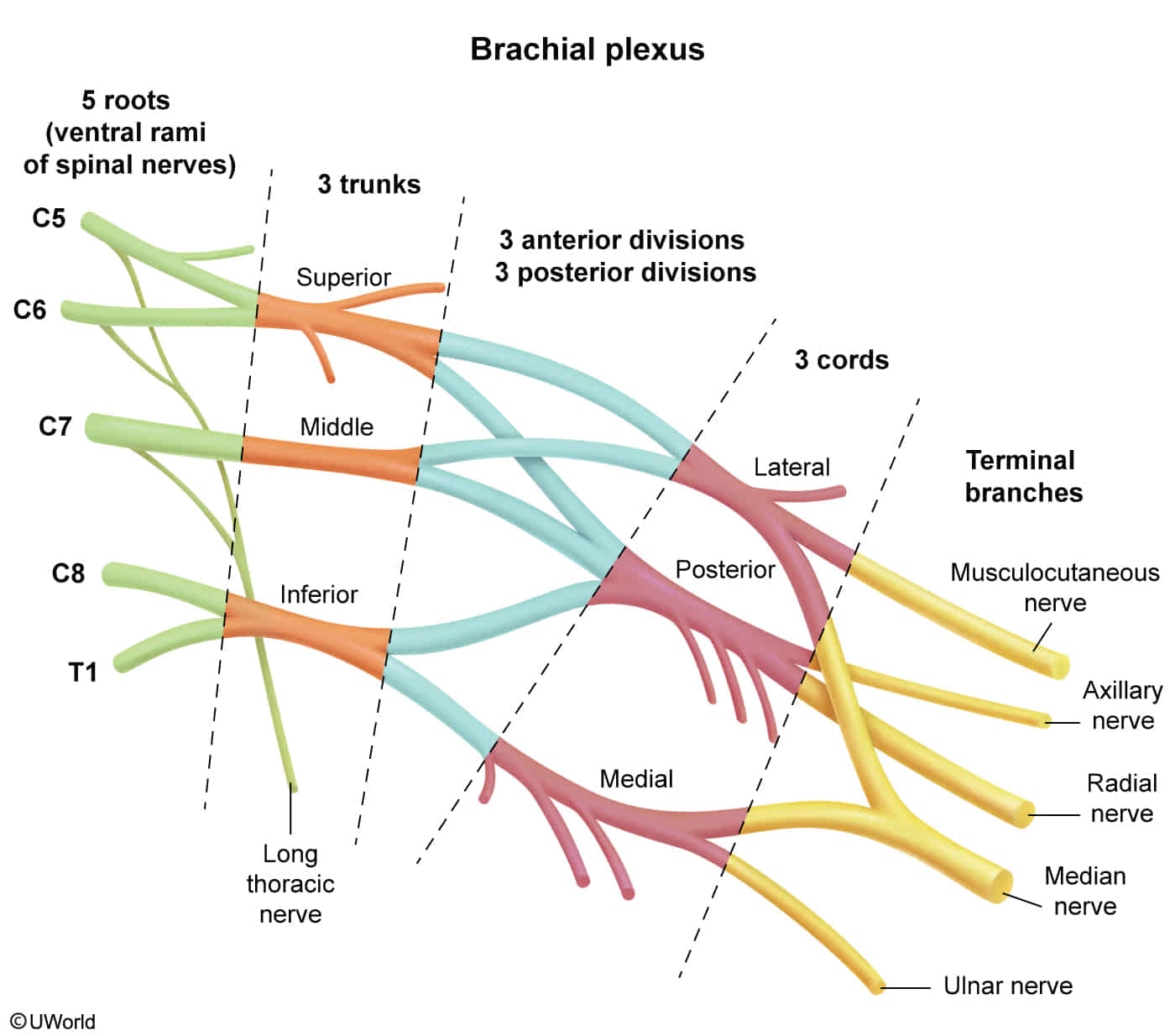
The brachial plexus is organized by the mnemonic: Really Tired Drink Coffee Black (Roots, Trunks, Divisions, Cords, Branches).
Upper Trunk (C5-C6) Lesion — Erb-Duchenne Palsy
- Etiology
- Infant: Lateral traction on neck during delivery.
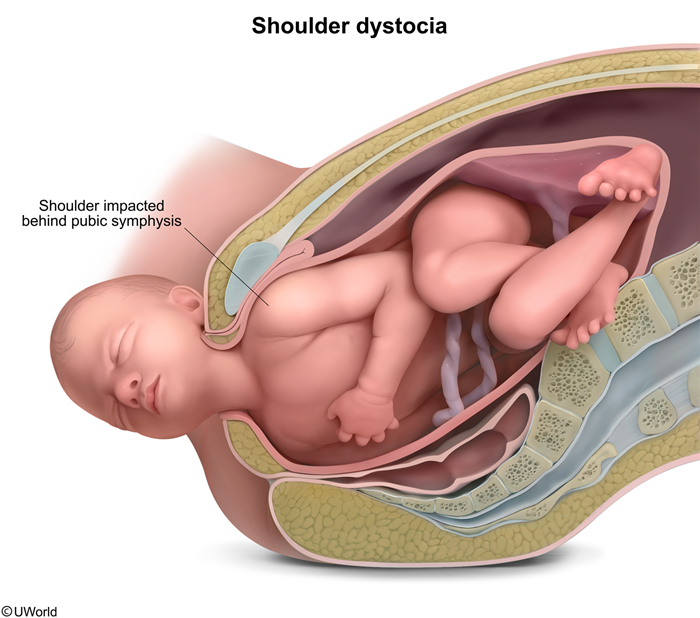
- Adult: Trauma (e.g., fall on shoulder).
- Infant: Lateral traction on neck during delivery.
- Nerves Damaged
- Primarily affects Musculocutaneous, Axillary, and Suprascapular nerves.
- Muscles Affected
- Deltoid (abduction)
- Supraspinatus (abduction)
- Infraspinatus (external rotation)
- Biceps brachii (flexion, supination)
- Clinical Presentation
- Arm hangs by the side, medially rotated, pronated forearm, extended elbow.
- Loss of abduction, external rotation, and flexion/supination.
- Classic Sign
- “Waiter’s tip” or “Porter’s tip” hand.
Lower Trunk (C8-T1) Lesion — Klumpke Palsy
- Etiology
- Infant: Upward force on arm during delivery (e.g., grabbing arm).
- Adult: Grabbing a tree branch to break a fall; Pancoast tumor; cervical rib.
- Nerves Damaged
- Primarily affects Ulnar and Median nerves (intrinsic hand muscles).
- Muscles Affected
- Intrinsic muscles of the hand (lumbricals, interossei).
- Clinical Presentation
- Paralysis of intrinsic hand muscles, leading to impaired wrist/finger flexion and finger abduction/adduction.
- Sensory loss along medial aspect of forearm and hand.
- Classic Sign
- Total “Claw Hand” (MCP joints are extended, IP joints are flexed).
- Associated Syndrome
- If T1 root is involved, can disrupt sympathetic chain → Horner’s Syndrome (Ptosis, Miosis, Anhidrosis).
Long Thoracic Nerve (C5, C6, C7) Lesion
- Etiology
- Axillary lymph node dissection (e.g., during mastectomy), stab wound, chest tube insertion.
- Muscle Affected
- Serratus Anterior. This muscle’s function is to anchor the scapula to the thoracic cage and protract the scapula.
- Clinical Presentation
- Inability to anchor scapula.
- Classic Sign
- “Winging of the scapula”, most prominent when the patient pushes against a wall.
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome
- Etiology
- Compression of the brachial plexus (most often the lower trunk) and/or subclavian vessels as they pass between the clavicle and first rib.
- Often caused by a cervical rib or hypertrophy of anterior scalene muscle.
- Clinical Presentation
- Mimics Klumpke palsy: Atrophy of intrinsic hand muscles, pain/paresthesia in C8-T1 distribution.
- Vascular compromise: Swelling, discoloration (ischemia) of the arm, weak radial pulse.
- Diagnostics
- Adson’s test: Loss of radial pulse when head is turned toward the affected side and held in inspiration.