Epidemiology
- AMD is the leading cause of blindness in individuals > 65 years in developed countries.
- Age of onset: usually > 55 years
Etiology
- Risk factors
- Age (>50 years) is the primary risk factor.
- Smoking (major modifiable risk factor).
- Caucasian ethnicity.
- Family Hx.
- Hypertension, hypercholesterolemia.
Pathophysiology
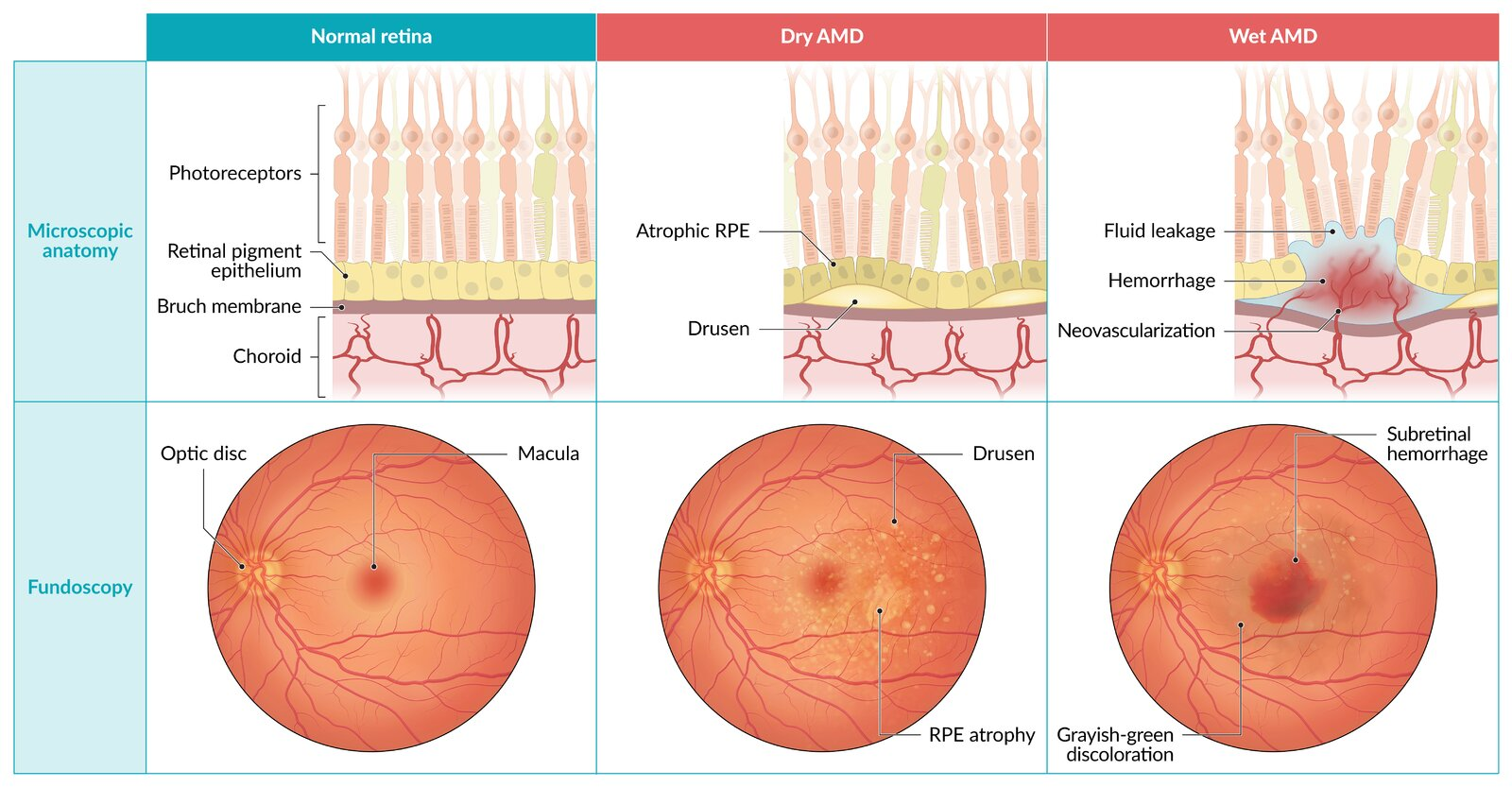
- Degeneration of the macula (central area of retina), causing progressive loss of central vision.
- Dry (Atrophic) AMD (85-90% of cases)
- Slow, gradual process.
- Characterized by deposition of yellowish extracellular material (Drusen) between Bruch’s membrane and the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE).
- The condition likely results from chronic oxidative damage to the retinal pigment epithelium and choriocapillaris, leading to subretinal inflammation with abnormal extracellular matrix formation (eg, confluent drusen, basement membrane thickening).
- Leads to gradual RPE atrophy.
- Wet (Exudative/Neovascular) AMD (10-15% of cases)
- Rapid, more severe vision loss.
- Caused by choroidal neovascularization secondary to local ischemia and ↑ VEGF production.
- New, abnormal vessels grow under the retina, are fragile, and leak fluid/blood, leading to retinal detachment, hemorrhage, and scarring.
Clinical features
- Bilateral, though often asymmetric.
- Painless, progressive loss of central vision (scotomas).
- Patients report difficulty with reading, driving, or recognizing faces.
- Metamorphopsia: Type of visual distortion in which straight lines appear wavy (hallmark of wet AMD). An Amsler grid is used for patient self-monitoring.
- Peripheral vision is preserved.
| Feature | Dry AMD (Atrophic) | Wet AMD (Exudative) |
|---|---|---|
| Pathophys | Drusen deposition, RPE atrophy | Choroidal Neovascularization (CNV) |
| Prevalence | Common (~90%) | Less common (~10%) |
| Progression | Gradual, slow vision loss | Rapid, severe vision loss |
| Fundoscopy | Drusen, geographic atrophy | Hemorrhage, subretinal fluid |
| Treatment | Vitamins (AREDS2), supportive | Anti-VEGF injections |
Diagnostics
- Amsler grid: detection of metamorphopsias and scotomas
- Fundoscopy
- Dry AMD
- Drusen
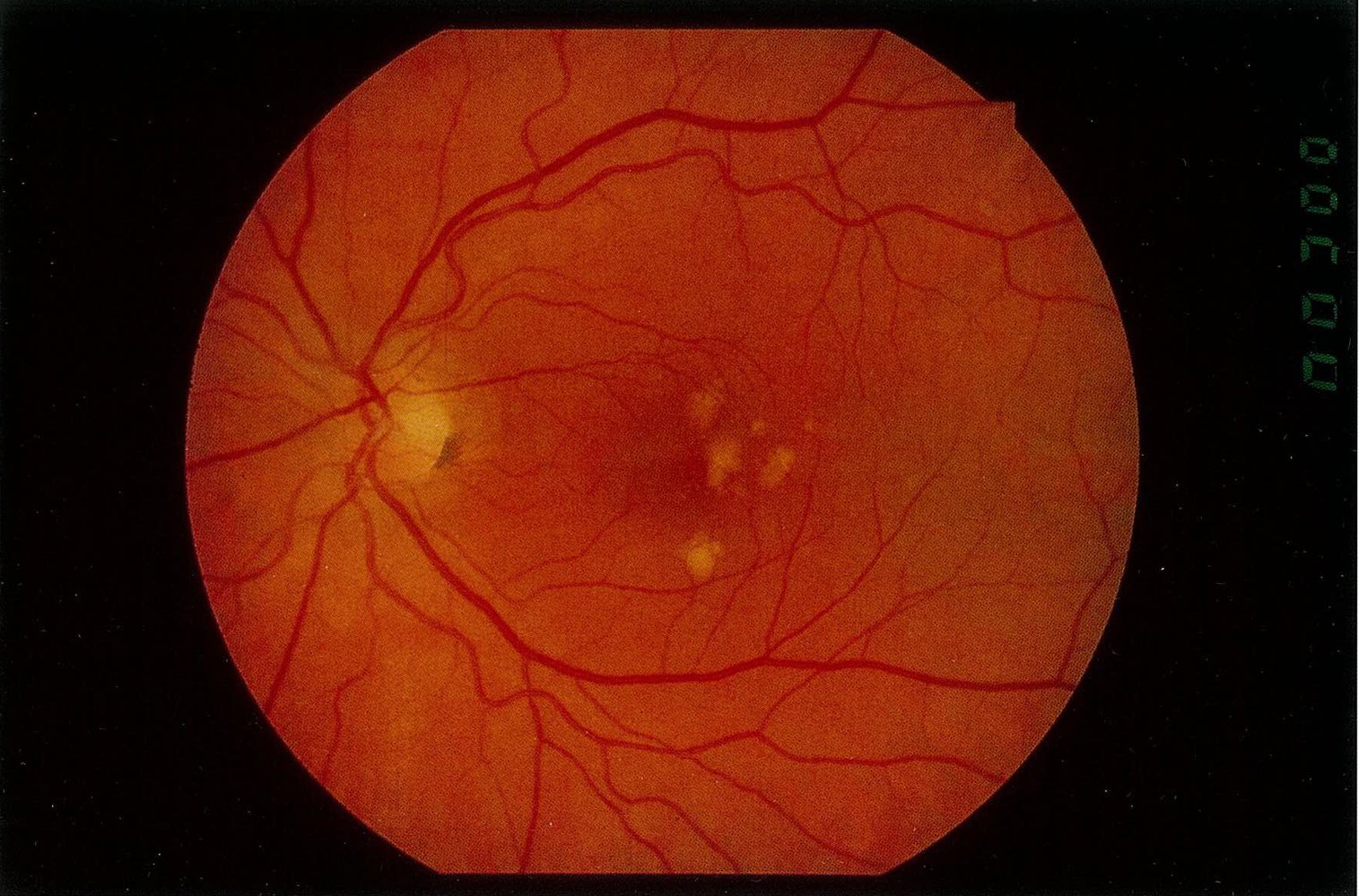
- Drusen
- Wet AMD
- Subretinal and intraretinal hemorrhage and/or exudate
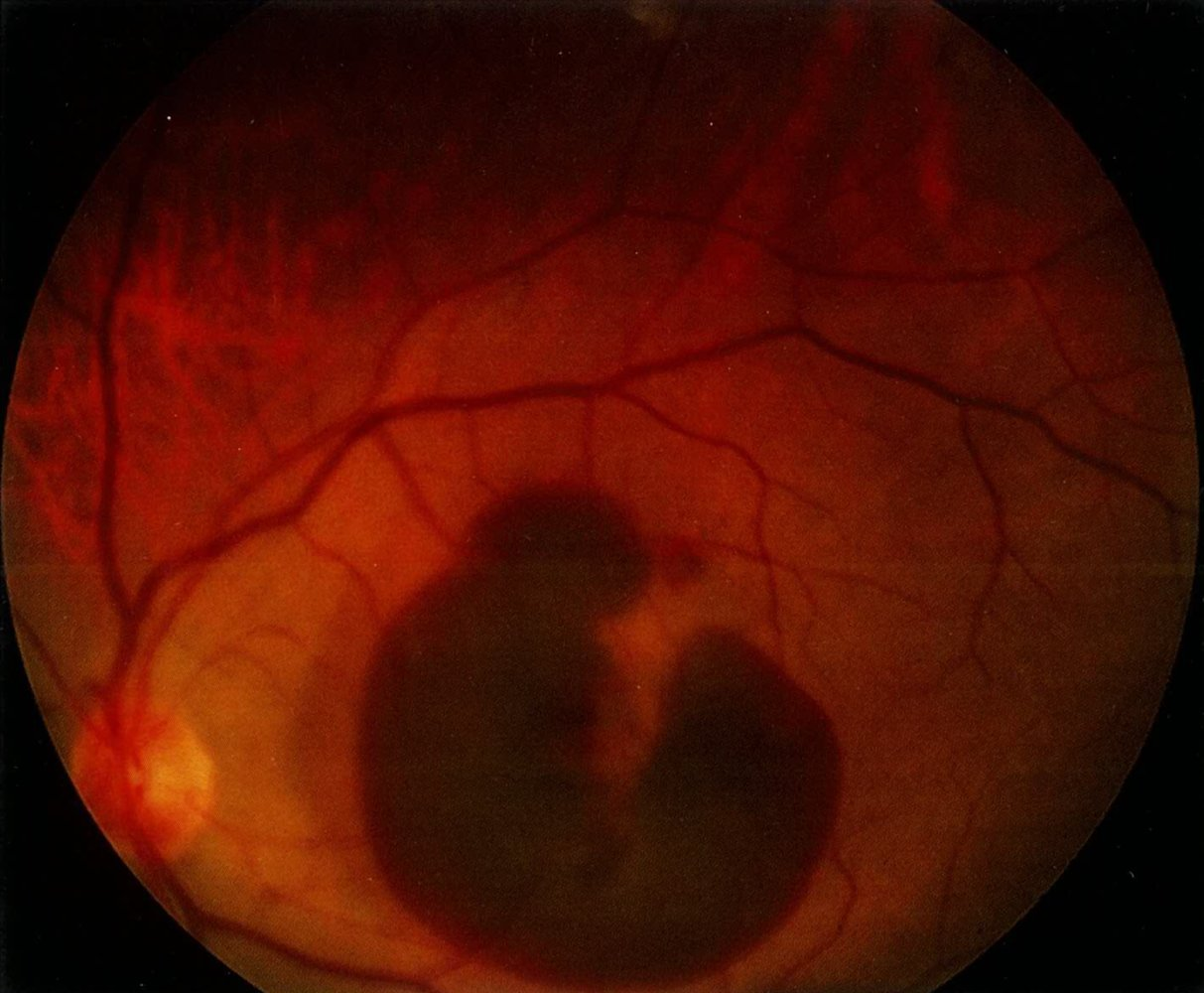
- Subretinal and intraretinal hemorrhage and/or exudate
- Dry AMD
Treatment
- Treatment of wet AMD
- First-line: injection of VEGF inhibitors (ranibizumab, bevacizumab, pegaptanib) into the vitreous body
Mnemonic
Ranibizumab → bizu 两个眼珠