Progressive muscular dystrophies
| Feature | Progressive Muscular Dystrophies (PMD) | Myotonic Syndromes (MyD) | Mitochondrial Myopathies (Mito) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Defect | Muscle protein gene defect (e.g., Dystrophin) | Trinucleotide repeat expansion | Mitochondrial DNA/nDNA gene defect |
| Inheritance | X-linked (DMD/BMD), Autosomal | Autosomal Dominant | Maternal (mtDNA), Autosomal (nDNA) |
| Weakness Pattern | Proximal > Distal | Distal > Proximal (DM1); Proximal (DM2) | Proximal, exercise intolerance |
| Myotonia | Absent | Present (grip, percussion) | Absent |
| Key Biopsy | Necrosis, fat/fibrous infiltration | Central nuclei, Type 1 atrophy (DM1) | Ragged Red Fibers |
| Systemic (Key) | Cardiomyopathy, respiratory failure | Multisystem (cataracts, cardiac, endocrine) | Multisystem (CNS, eye, ear, lactic acidosis) |
| CK | Markedly High | Mild-Mod High | Normal or Mild High |
| Buzzwords | Gower sign, calf pseudohypertrophy | "Can't let go," hatchet face, anticipation | Ragged red fibers, maternal inheritance |
Epidemiology
- Sex: only male individuals affected in DMD and BMD
- Age of onset
- DMD: 2–5 years
- BMD: adolescence or early adulthood, usually > 15 years
Etiology
- Inheritance pattern (DMD and BMD): X-linked recessive
- Chromosomal mutations affecting the dystrophin gene on the short arm of the X chromosome (Xp21)
- DMD: frameshift deletion or nonsense mutation → shortened or absent dystrophin protein
- BMD: in-frame deletion → partially functional dystrophin protein
- In about two-thirds of DMD or BMD cases, deleted segments are as large as one or more exons.
Pathophysiology
- Dystrophin protein: anchors the cytoskeleton of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells to the extracellular matrix by connecting cytoskeletal actin filaments to membrane-bound α- and β-dystroglycan, which are connected to extracellular laminin
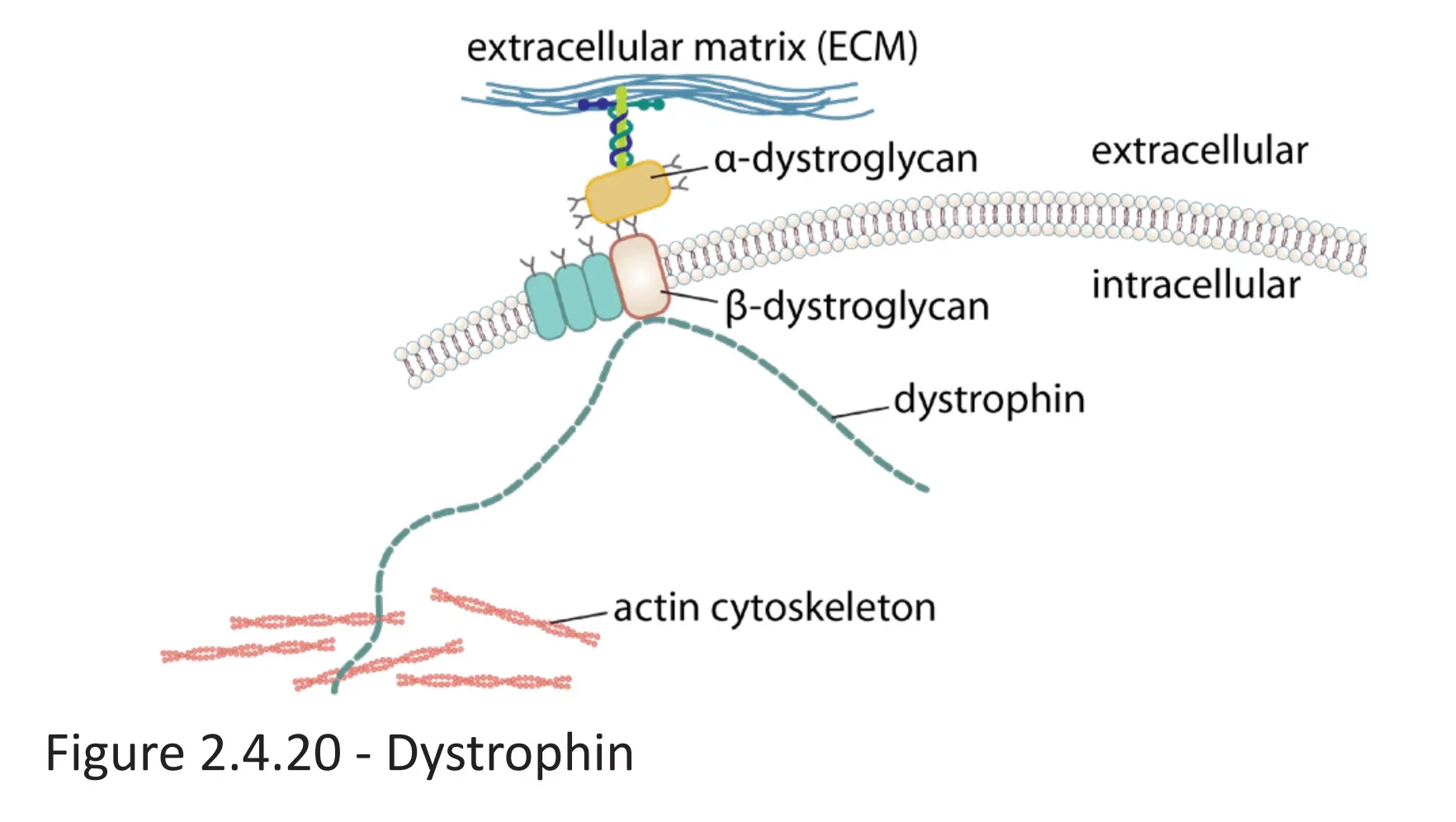
- Dystrophin gene: largest known protein-coding gene in the human DNA
- Because of its size, the dystrophin gene is at increased risk for spontaneous mutations.
- Mutations affecting the dystrophin gene→ alterations of dystrophin protein structure → partial (BMD) or almost complete (DMD) impairment of protein function → disturbance of numerous cellular signaling pathways → necrosis of affected muscle cells → replacement with connective tissue and fatty tissue → affected muscles are weak even though they appear larger (“pseudohypertrophy”)
- Errors in splicing in the DMD gene can also cause DMD.
Clinical features
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD)
- Progressive muscle paresis and atrophy
- Starts in the proximal lower limbs (pelvic girdle)
- Extends to the upper body and distal limbs as the disease progresses
- Weak reflexes
- Waddling gait (i.e., Duchenne limp) with bilateral Trendelenburg sign
- Gower maneuver
- The individual arrives at a standing position by supporting themselves on their thighs and then using the hands to “walk up” the body until they are upright.

- Classic sign of DMD, but also occurs in inflammatory myopathies (e.g., dermatomyositis, polymyositis) and other muscular dystrophies (e.g., BMD)
- The individual arrives at a standing position by supporting themselves on their thighs and then using the hands to “walk up” the body until they are upright.
- Calf pseudohypertrophy
- Mutations affecting the dystrophin gene→ alterations of dystrophin protein structure → partial (BMD) or almost complete (DMD) impairment of protein function → disturbance of numerous cellular signaling pathways → necrosis of affected muscle cells → replacement with connective tissue and fatty tissue → affected muscles are weak even though they appear larger (“pseudohypertrophy”)
- vs Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease, which has calf atrophy
Becker muscular dystrophy (BMD)
- Symptoms similar to those of DMD, but less severe
- Slower progression (patients often remain ambulatory into adult life)
Mnemonic
Becker is better