- Hair Follicle Cycles
- Anagen: Growth phase.
- Telogen: Resting phase.
- Telogen Effluvium: Stress-induced (e.g., pregnancy, surgery) diffuse hair loss; premature entry into telogen.
- Folliculitis
- Infectious:
- Staph aureus: Most common cause overall.
- Pseudomonas aeruginosa: “Hot tub folliculitis” (exposure to contaminated water).
- Non-Infectious:
- Pseudofolliculitis barbae: “Razor bumps”; common in African American men; curly hair re-enters skin, causing inflammation.
- Infectious:
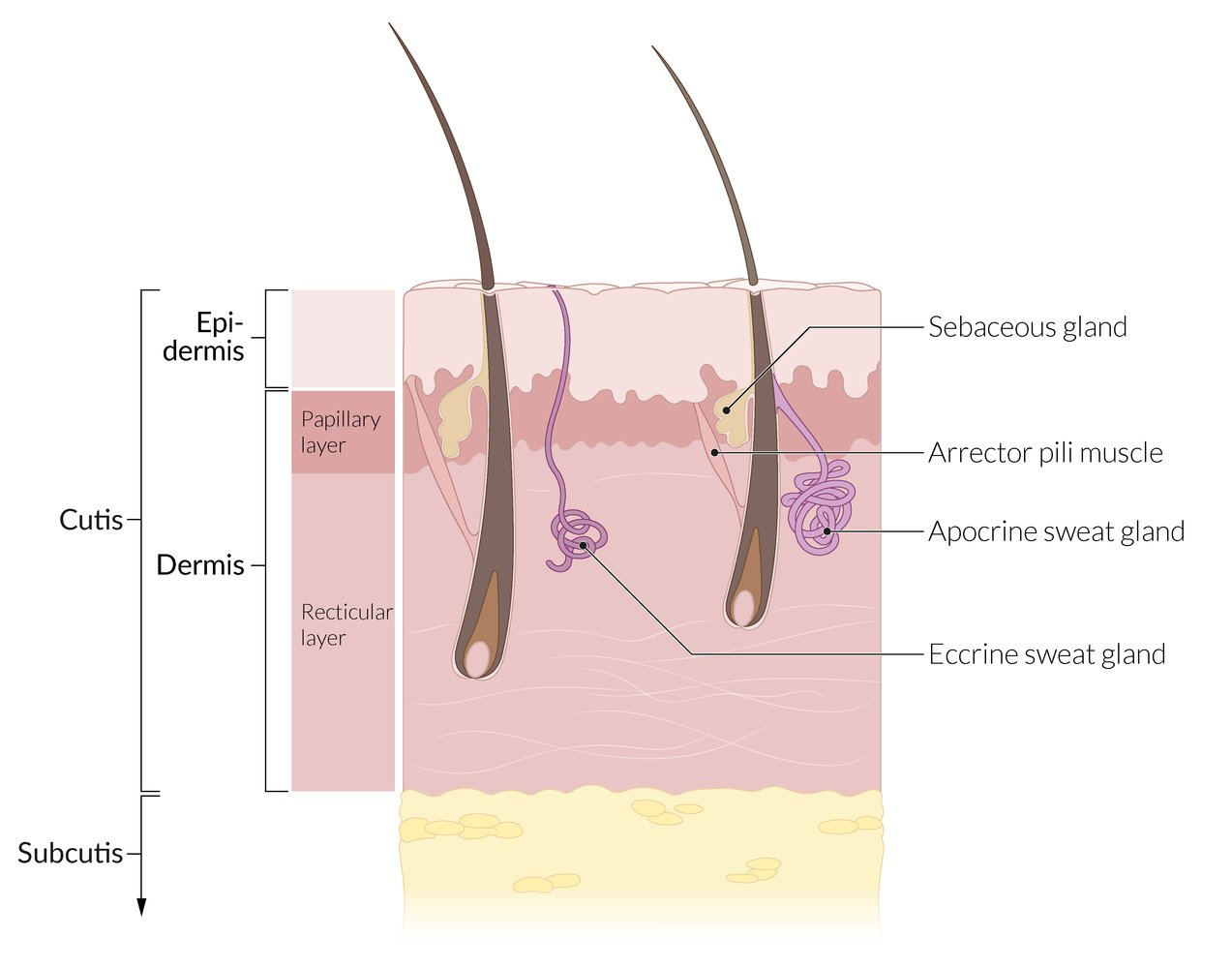
- Gland Secretion Mechanisms (High-Yield)
- Holocrine: Cell lysis releases contents (e.g., Sebaceous glands).
- Apocrine: Budding of apical cytoplasm (e.g., Mammary glands).
- Merocrine: Exocytosis; no cell loss (e.g., Eccrine/Sweat, Salivary).
- Sebaceous Glands
- Product: Sebum.
- Stimulus: Androgens (↑ in puberty).
- Clinical: Acne vulgaris (obstructed follicles + C. acnes infection).
- Eccrine Glands (Sweat)
- Apocrine Glands
- Location: Axilla, areola, perineum.
- Primary Function: Secretion of a thick, protein/lipid-rich fluid into hair follicles in response to emotional stress and sexual stimulation (unlike eccrine glands, which respond to heat).
- Onset: Functional at puberty.
- Odor: Due to bacterial breakdown of secretions.
- Clinical: Hidradenitis suppurativa (chronic inflammation in these areas).

Tip
Sweat gland is only innervated by sympathetic nerve, while regarding nerve fibers, it is innervated by cholinergic nerve (M receptor; acting on the whole body, eccrine sweat glands) and adrenergic nerve (α1 receptor; acting on the palms and soles, ?)