Antiphospholipid syndrome
Antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) is an autoimmune disease associated with increased risk of thrombosis due to the presence of procoagulatory antibodies.
Etiology
- Primary
- Idiopathic
- Secondary
- Systemic lupus erythematosus (most common cause of secondary APS)
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Neoplasms
Pathophysiology
- Formation of procoagulatory antiphospholipid antibodies
- In most cases, the antibodies are formed secondary to autoimmune diseases or infections.
- Antibodies form complexes with anticoagulant proteins, thereby inactivating them (e.g., protein C, protein S, antithrombin III).
- Antibodies activate platelets and vascular endothelium, leading to increased binding of platelets
- Induction of a hypercoagulable state → ↑ risk of thrombosis and embolism
Clinical features
APS usually manifests with recurring thrombotic events that may affect any organ.
- Venous
- Deep vein thrombosis
- There is diffuse edema and erythema of the right leg and foot. The diameter of the right calf is visibly greater than that of the left.
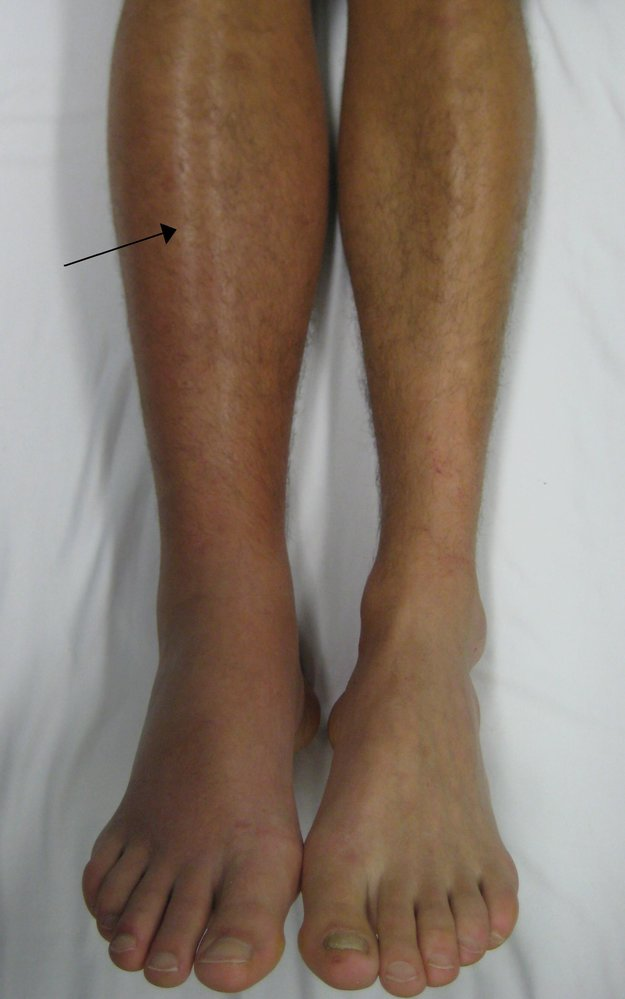
- There is diffuse edema and erythema of the right leg and foot. The diameter of the right calf is visibly greater than that of the left.
- Pulmonary embolism
- Livedo reticularis
- Blood clots in capillaries lead to swelling of venules, resulting in a purplish, net-like discoloration of the skin.
- Ulceration
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Arterial
- Stroke, transient ischemic attacks
- Occlusion of organ arteries (e.g., myocardial infarction)
- Occlusion of distal extremity arteries (ischemia and gangrene)
- Capillaries: splinter hemorrhages
- Pregnancy-related: recurrent miscarriages and premature births
- Caused by thrombosis of placental vessels and possible subsequent placental infarction
Diagnostics
Tip
Thrombosis in APS is typically unprovoked (e.g., unprovoked DVT), recurrent, and/or manifests in unusual sites (e.g., kidneys, liver, retina). It is most commonly seen in younger individuals (< 50 years of age) and in individuals with comorbid autoimmune diseases (e.g., SLE).
- Coagulation panel: paradoxically prolonged aPTT (caused by lupus anticoagulant, which interfere with in vitro aPTT test)
Antiphospholipid antibodies
- Lupus anticoagulant (LA): antibodies against certain phospholipids in cellular membranes; detection involves a three-step procedure
- These antibodies inhibit coagulation and therefore prolong aPTT in vitro, but have a procoagulatory effect in vivo.
- Screening for phospholipid-dependent coagulation with either:
- Paradoxical prolonged aPTT
- Prolonged dilute Russell viper venom time (dRVVT)
- Mixing study: The patient's plasma is mixed with normal plasma (which contains clotting factors).
- aPTT or dRVVT normalize: Presence of lupus anticoagulant ruled out; prolonged aPTT may be due to a lack of clotting factors.
- aPTT or dRVVT remain prolonged: Lupus anticoagulant may be present.
- Confirmation of phospholipid dependence: Phospholipid is added.
- aPTT or dRVVT normalize: Presence of lupus anticoagulants is confirmed.
- aPTT or dRVVT remain prolonged: Consider a factor deficiency.
- Anticardiolipin antibodies (IgG and IgM): antibodies against cardiolipin, a phospholipid in cellular membranes
- Anti-β2-glycoprotein antibodies (IgG and IgM): antibodies directed against the cardiolipin binding factor β2 glycoprotein I that have prothrombotic effects