- Core Logic
- Polycistronic mRNA encoding enzymes for lactose metabolism.
- E. coli prefers Glucose. Operon ON only if: Glucose Absent AND Lactose Present.
- Key Components
- lacZ: β-galactosidase (breaks down lactose).
- lacY: Permease (lactose transport).
- lacI: Repressor (constitutive; binds Operator to block transcription).
- Regulation Mechanism
- Glucose Signaling (CAP):
- ↓ Glucose → ↑ cAMP → CAP binds DNA → Helps RNA Pol bind.
- ↑ Glucose → ↓ cAMP → No CAP → Low/No Transcription.
- Lactose Signaling (Repressor):
- No Lactose: Repressor binds Operator → No Transcription.
- High Lactose: Allolactose binds Repressor → Repressor falls off → Transcription Possible.
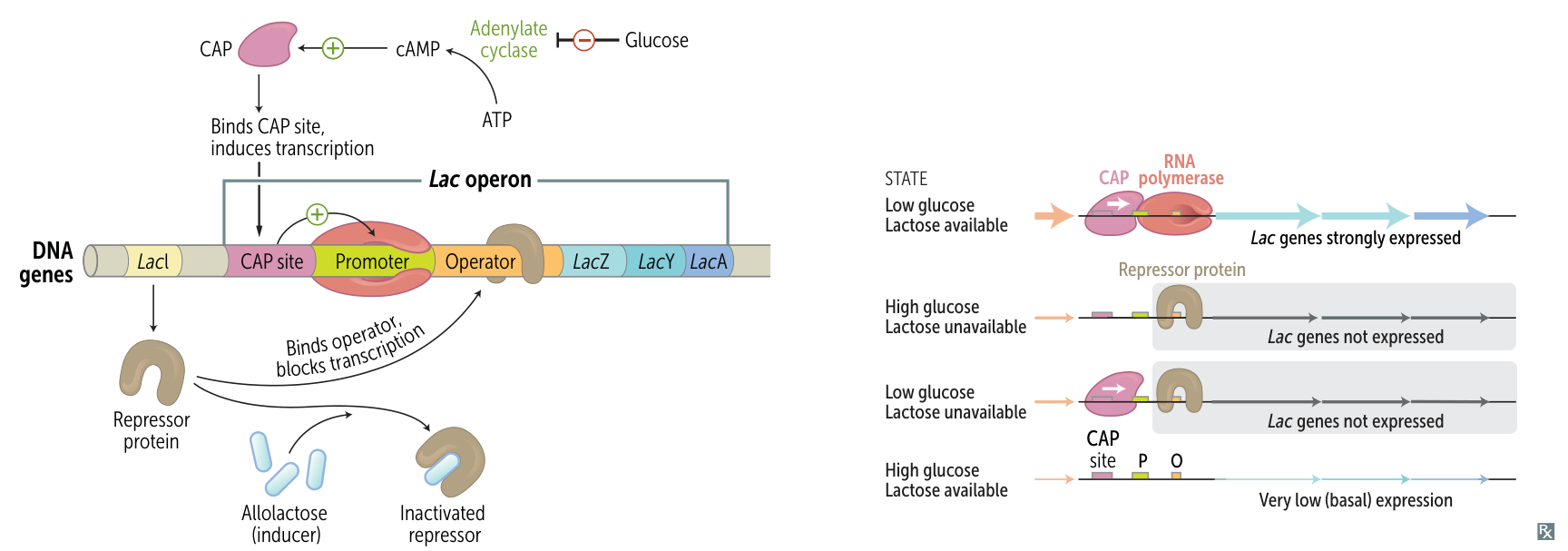
- Transcription Scenarios
- Low Glu / High Lac: High Transcription (CAP bound, Repressor off).
- High Glu / High Lac: Very Low Transcription (No CAP, Repressor off).
- Any “No Lac”: No Transcription (Repressor bound).
- Genetics (Mutations)
- lac I⁻ (No repressor): Constitutive (Always ON).
- lac Oᶜ (Mutated Operator): Constitutive (Repressor can’t bind).
- lac Iˢ (Super-repressor): Always OFF (Inducer can’t bind repressor).
