Overview
Etiology
- Route of transmission
- Airborne droplets
- Fecal‑oral route
- Vertical transmission
Clinical features
- Group A coxsackieviruses more commonly cause:
- Hand, foot, and mouth disease
- Herpangina
- Viral conjunctivitis
- Group B coxsackieviruses more commonly cause:
- Pleurodynia
- Viral myocarditis
- Viral pericarditis
- Dilated cardiomyopathy
Hand, foot, and mouth disease and herpangina
Definition
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) and herpangina are highly contagious febrile infections most commonly caused by group A coxsackieviruses.
- HFMD manifests with a cutaneous rash and painful oral lesions.
- Herpangina manifests with painful lesions limited to the oral cavity. (basically HFMD without cutaneous rash)
Epidemiology
- Most commonly affects children < 5 years of age
Clinical features
- Fever, malaise
- Painful oral lesions
- Initially manifest as discrete small papules that develop into 1–2 mm vesicles with surrounding erythema
- Enlarge over several days to form 3–4 mm ulcers that do not coalesce
- Typically affect the posterior oral cavity (e.g., tonsils, uvula, soft palate, oropharynx)
- Occasionally involve the perioral area and tip of the tongue
- Cutaneous lesions: macular, papular, and partially vesicular rash
- Predominantly on palmar surface of the hands and feet
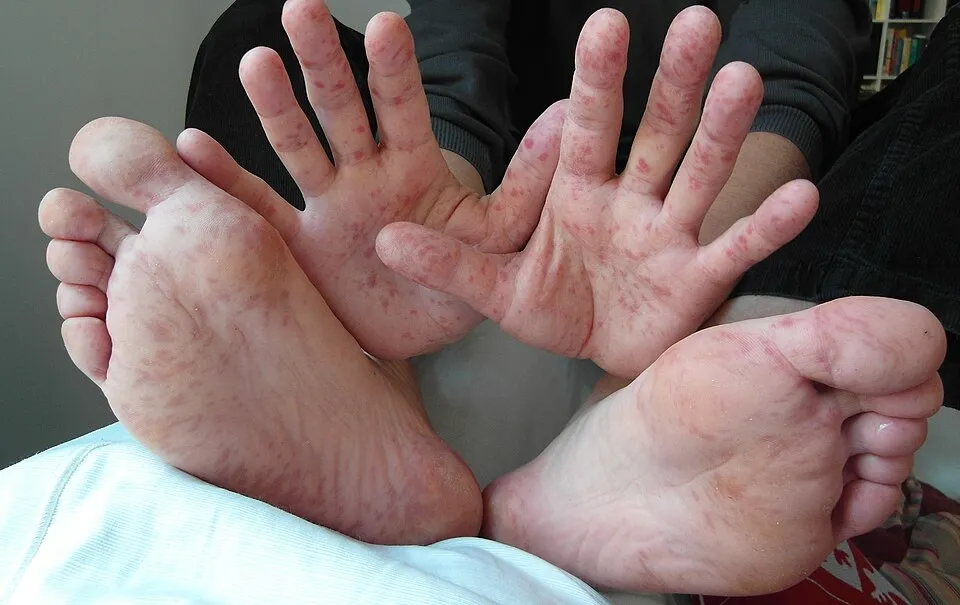
- Typically 2–6 mm in diameter
- May also affect:
- Buttocks
- Genitals
- Knees
- Elbows
- Predominantly on palmar surface of the hands and feet