- Description
- Phagocytes (e.g., neutrophils, monocytes) ingest pathogens
- Activation of the NADPH oxidase complex generates and releases reactive oxygen species (ROS; free radicals) that destroy the pathogens in phagosomes
- Mechanism
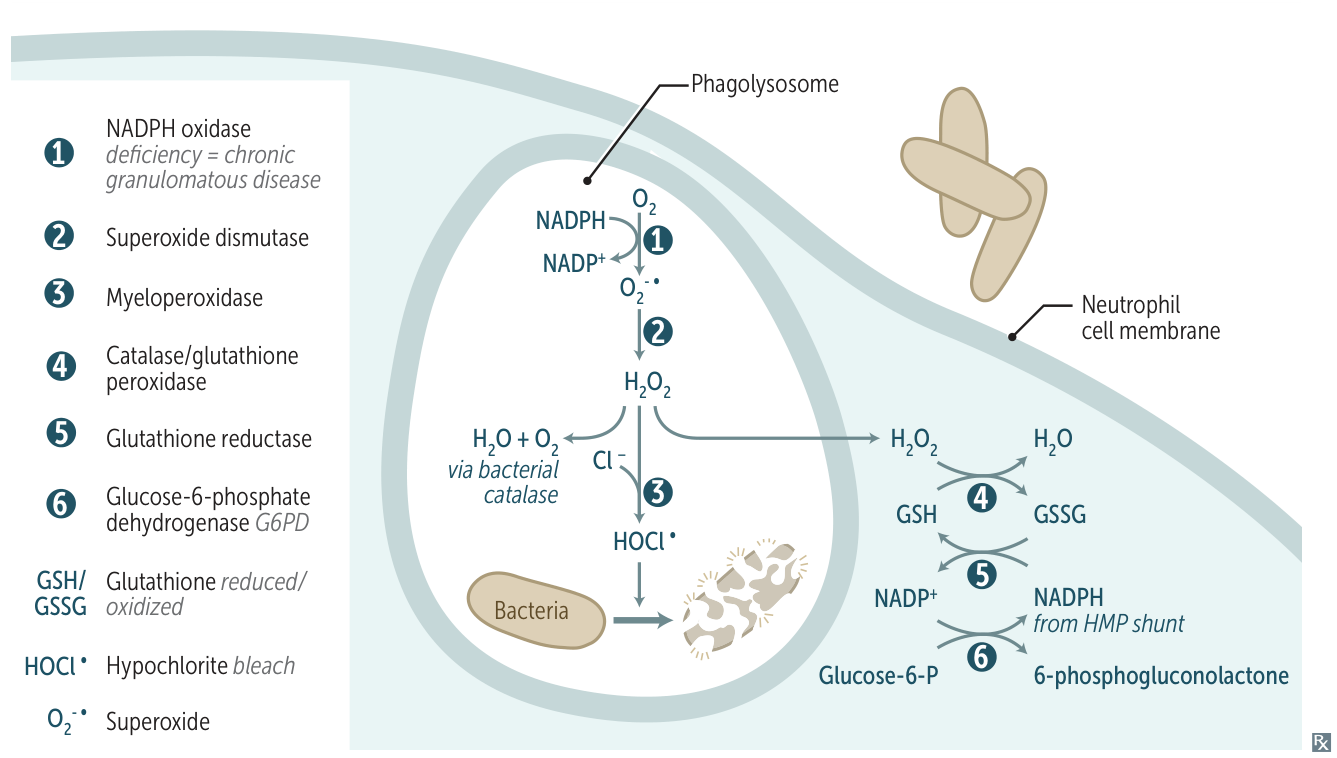
- 1. NADPH Oxidase (located on the phagosome membrane)
- This is the rate-limiting enzyme and the first step.
- Converts molecular oxygen (O₂) to superoxide (O₂•⁻).
- Reaction:
O₂ + NADPH → O₂•⁻ + NADP⁺ + H⁺
- A large amount of NADPH is consumed, leading to ↑ activity in the pentose phosphate pathway (HMP shunt) to regenerate NADPH.
- 2. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD)
- Converts superoxide to hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
- Reaction:
2O₂•⁻ + 2H⁺ → H₂O₂ + O₂
- 3. Myeloperoxidase (MPO)
- An enzyme contained within azurophilic granules of neutrophils.
- Converts H₂O₂ to hypochlorous acid (HOCl, i.e., bleach), a potent antimicrobial agent. MPO gives sputum its characteristic green color.
- Reaction:
H₂O₂ + Cl⁻ + H⁺ → HOCl + H₂O
- Release of oxidative burst causes K+ influx, which triggers secretion of lysosomal enzymes into the phagosome.
| Rank | ROS Species | Potency/Reactivity | Key USMLE Fact |
|---|
| 1 | Hydroxyl Radical (•OH) | Extreme | Most biologically reactive ROS; formed from H2O2 via the Fenton Reaction (non-enzymatic process). |
| 2 | Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) | Very High | ”Bleach”; produced by myeloperoxidase in neutrophils to kill pathogens. |
| 3 | Superoxide (O2•⁻) | Moderate | Initial ROS made by NADPH oxidase in the respiratory burst. |
| 4 | Hydrogen Peroxide (H2O2) | Low | Stable precursor to •OH and HOCl; can diffuse across membranes. |
- Associated Disease: Chronic Granulomatous Disease (CGD)
- Defect: Mutation in NADPH oxidase → absent oxidative burst t
- Inheritance: X-linked (most common) or autosomal recessive
- Clinical Features:
- Recurrent infections with catalase-positive organisms (S. aureus, Burkholderia, Serratia, Nocardia, Aspergillus)
- Granuloma formation (compensatory mechanism)
- Infections of skin, lungs, liver, bones
- Diagnosis: Abnormal NBT or DHR test (no color change)
- Treatment: Prophylactic TMP-SMX + itraconazole, IFN-γ, aggressive infection management
- Associated Disease: Myeloperoxidase Deficiency
- Less severe than CGD t
- ↑ susceptibility to Candida infections
- Most patients asymptomatic (H₂O₂ still produced)
