- Epidemiology & Risk Factors
- Tobacco & Alcohol: Major risk factors; synergistic effect (↑ risk when combined).
- HPV (Human Papillomavirus):
- Specifically HPV-16.
- Strongly associated with Oropharyngeal cancer (tonsils, base of tongue).
- Better prognosis compared to HPV-negative cancers.
- EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus): Strongly associated with Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC).
- Betel Nut: Chewing is a major risk factor in Southeast Asia.
- Plummer-Vinson Syndrome: Associated with post-cricoid carcinoma (hypopharynx).
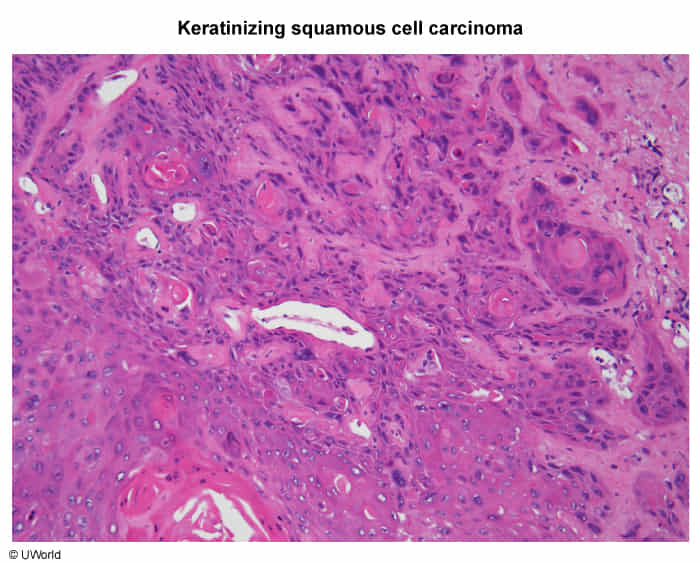
- Pathology
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): >90% of cases.
- Field Cancerization: Carcinogen exposure (smoking) creates a widespread field of genetically altered mucosa, leading to ↑ risk of second primary tumors.
- Clinical Features
- General:
- Dysphagia, Odynophagia (“hot potato” voice).
- Persistent sore throat.
- Referred Otalgia: Pain mediated via CN IX (glossopharyngeal) or CN X (vagus).
- Neck Mass: Often the presenting sign (cervical lymph node metastasis).
- Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma (NPC) Specifics:
- Demographics: Endemic in Southern China, Northern Africa, Inuits.
- Presentation: Unilateral nasal obstruction, epistaxis, unilateral serous otitis media (adult with fluid in one ear = cancer until proven otherwise).
- CN Involvement: Can invade cavernous sinus → deficits in CN III, IV, V, VI.
- Diagnostics
- Biopsy: Gold standard (via panendoscopy or fine-needle aspiration of neck mass).
- Imaging: CT/MRI for staging (evaluating depth of invasion and nodal involvement).
- HPV Testing: p16 immunohistochemistry for oropharyngeal tumors.
- EBV Serology: IgA against viral capsid antigen (VCA) useful for screening NPC in endemic areas.
- Treatment
- Early Stage: Surgery or Radiation Therapy (XRT).
- Advanced Stage: Chemoradiation (e.g., Cisplatin + XRT).
- Cetuximab: EGFR inhibitor used in select cases.
- Differential Diagnosis
- Lymphoma (non-tender lymphadenopathy, B-symptoms).
- Branchial cleft cyst (lateral neck mass in younger pts).
- Thyroglossal duct cyst (midline neck mass, moves with swallowing).
