Colorectal cancer
Epidemiology
Colorectal carcinogenesis pathways (molecular pathology)
- Chromosomal instability pathway in colon cancer: The adenoma-carcinoma sequence is the progressive accumulation of mutations in oncogenes (e.g., KRAS) and tumor suppressor genes (e.g., APC, TP53) that results in the slow transformation of adenomas into carcinomas.

Mnemonic
This follows the alphabet: APC -> KRAS -> P53
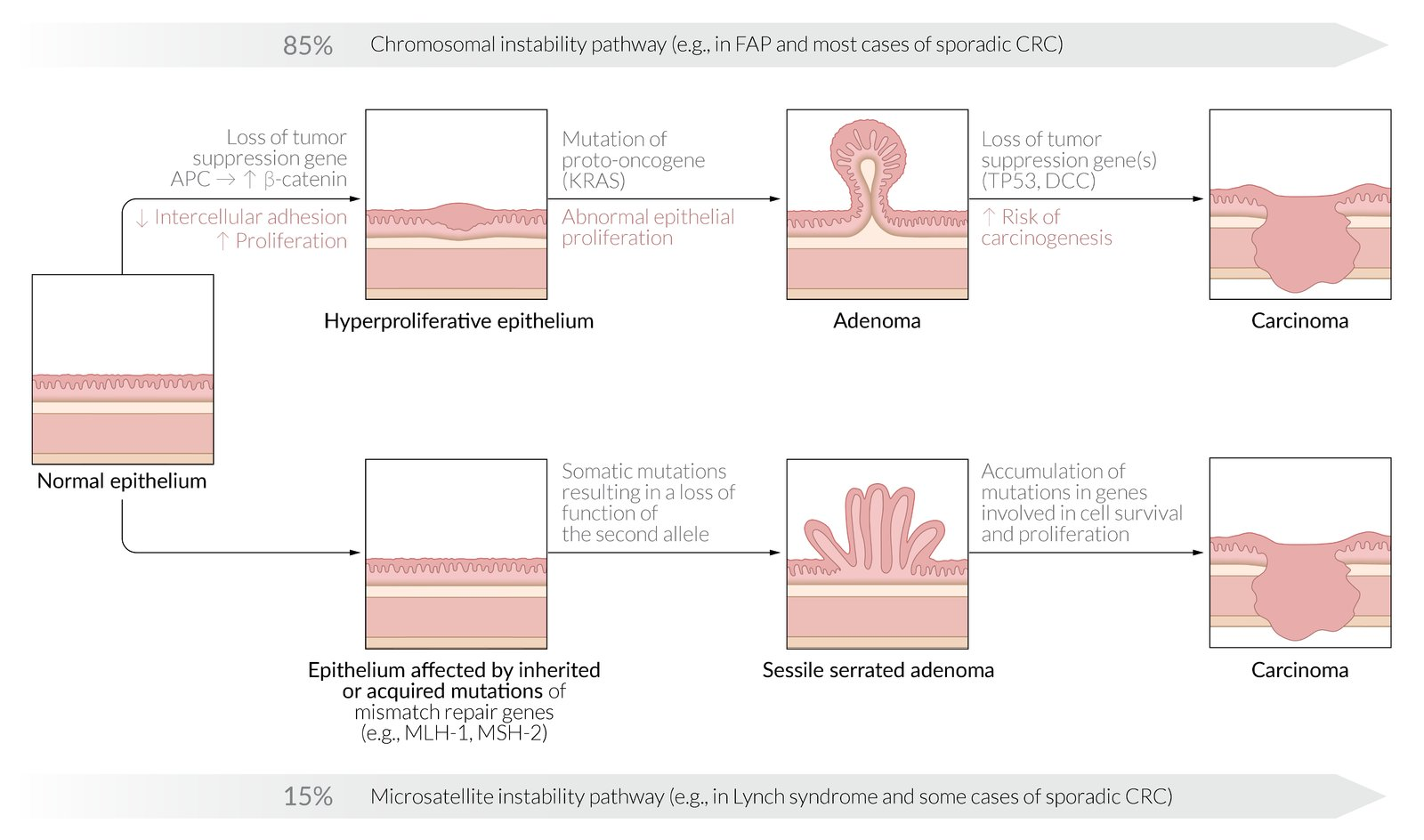
- Microsatellite instability pathway in colon cancer: due to methylation or mutations in mismatch repair genes (MMR genes, e.g., MLH1 or MSH2), see Lynch syndrome
- COX-2 overexpression
- Associated with colorectal cancer
- Possible protective effect of long-term use of aspirin and other NSAIDs
Etiology
Risk factors for colorectal cancer
- Hereditary syndromes
| Syndrome | Gene Mutation | Colon Cancer Risk | Other Associated Neoplasms |
|---|---|---|---|
| Familial adenomatous polyposis | APC | 100% | Upper gastrointestinal, Thyroid, Desmoids/osteomas |
| Lynch syndrome | MSH2/6, MLH1 | 50%-80% | Endometrial, Ovarian |
| Peutz-Jeghers syndrome | STK11 | 39% | Upper gastrointestinal, Pancreatic, Breast |
- Associated conditions
- Inflammatory bowel disease: chronic inflammation → hyperplasia → non-polypoid dysplasia → neoplasia
| Characteristics | Colitis-associated | Sporadic |
|---|---|---|
| Age | Younger (age 40-55) | Older (age >60) |
| Origin of dysplasia | Flat (nonpolypoid) lesions | Polypoid lesions |
| Location | Proximal > distal (particularly with CD) | Distal > proximal |
| Tumors | Multifocal | Singular |
| Histology | Mucinous and/or signet ring cells, Poorly differentiated | Rarely mucinous, Well differentiated |
| Mutations | Early p53 mutation, Late APC gene mutation | Early APC gene mutation, Late p53 mutation |
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
Right-sided colon carcinomas
- Large, bulky masses that protrude into the colonic lumen due to the relatively large caliber of the ascending colon
- Occult bleeding or melena
- Manifestations of iron deficiency anemia (due to chronic bleeding)
Left-sided colon carcinomas
- Often infiltrate the wall of the colon, encircling it and narrowing the lumen
- More likely to cause obstruction
- Changes in bowel habits (size, consistency, frequency)
- Blood-streaked stools
- Colicky abdominal pain (due to obstruction)
- Bowel obstruction occurs earlier in left-sided colon carcinomas because the distal colon has a smaller lumen than the proximal colon and contains solid fecal matter.