Thyroid cancer
Etiology
- Genetic factors
- Medullary carcinoma: associated with MEN2 (RET gene mutations) or familial medullary carcinoma
- Papillary carcinoma: associated with RET/PTC rearrangements and BRAF mutations
- Follicular carcinoma: associated with PAX8-PPAR-γ rearrangement and RAS mutation
- Undifferentiated/anaplastic carcinoma: associated with TP53 mutation
- Ionizing radiation (particularly during childhood): mostly associated with papillary carcinoma
Overview
| Feature | Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC) | Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma (FTC) | Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC) |
|---|---|---|---|
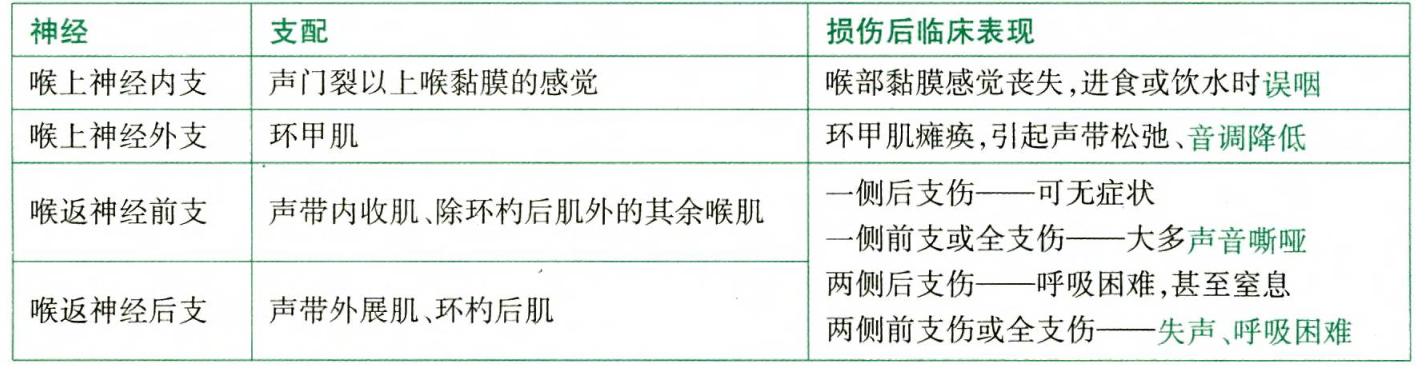
| Cell of Origin | Follicular cells | Follicular cells | Parafollicular cells (C cells) |
| Prevalence | Most common (75-85% of thyroid cancers) | Second most common (10-15% of thyroid cancers) | Rare (3-5% of thyroid cancers) |
| Age of Onset | Can occur at any age, most often 30-50 years | Usually affects people older than 50 years | Can occur at any age, sporadic cases often present later; hereditary cases can present earlier. |
| Spread (Metastasis) | Primarily spreads through lymphatics (to nearby lymph nodes) | Primarily spreads through blood vessels (hematogenous spread) to lungs, bones, brain, liver. Less likely to spread to lymph nodes compared to PTC. | Can spread to lymph nodes, lungs, liver, and bones. Early spread to regional lymph nodes is common. |
| Microscopic Features | Characteristic nuclear features: "Orphan Annie eye" nuclei (empty appearing), nuclear grooves, pseudoinclusions, psammoma bodies. Papillae (finger-like projections) are common. | Follicular architecture (small, round structures). Invasion of the capsule or blood vessels is key for diagnosis. Lacks the nuclear features of PTC. | Solid nests of cells, may contain amyloid. Cells stain positive for calcitonin, chromogranin A, and CEA. May have a variety of appearances (follicular, pseudopapillary, oncocytic). |
| Hormone Production | Produces thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Produces Thyroglobulin. | Produces thyroid hormones (T3 and T4). Produces Thyroglobulin | Produces calcitonin. Can also produce other hormones like corticotropin, serotonin, melanin, and prostaglandins. |
| Prognosis | Generally excellent prognosis, especially in younger patients. | Good prognosis, especially for small, minimally invasive tumors in young patients. Prognosis worsens with larger size, extensive vascular invasion, and older age. | Variable; depends on stage and whether it's sporadic or hereditary. The 5 year survival rate is about 93% for stages I to III. Stage IV has worse prognosis with 28% for 5 year survival rate. |
| Other | Most common type associated with prior radiation exposure. Multifocality is common. The accuracy of fine needle aspiration biopsy (FNA) is very high. | May arise from a pre-existing adenoma. | Can be part of Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN) type 2 syndromes (MEN2A and MEN2B). |
Tip
- Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (PTC): Originates from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. These cells are responsible for producing thyroid hormones. PTC is the most common type of thyroid cancer.
- Follicular Thyroid Carcinoma (FTC): Also originates from the follicular cells of the thyroid gland. Follicular and Papillary carcinoma are differentiated thyroid cancers.
- Medullary Thyroid Carcinoma (MTC): Arises from the parafollicular cells (also known as C cells) of the thyroid gland. These cells are distinct from follicular cells, and they produce the hormone calcitonin, which is involved in calcium regulation. MTC is a neuroendocrine tumor.
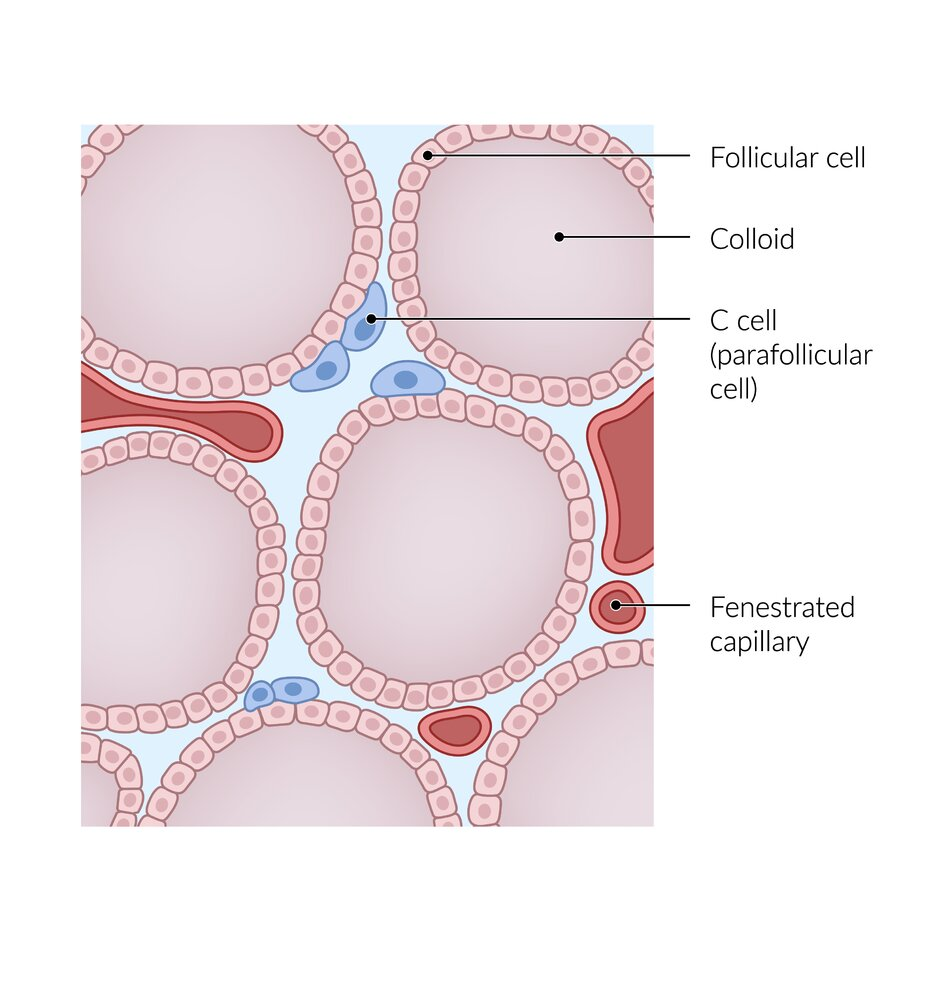
Papillary thyroid carcinoma
- Tissue of origin: Thyrocytes
- Well differentiated
- Characteristics
- Most common type of thyroid cancer
- Palpable lymph nodes due to metastatic spread (often detected before primary tumor)
- May be multifocal
- Very good prognosis
- Pathology
- Psammoma bodies
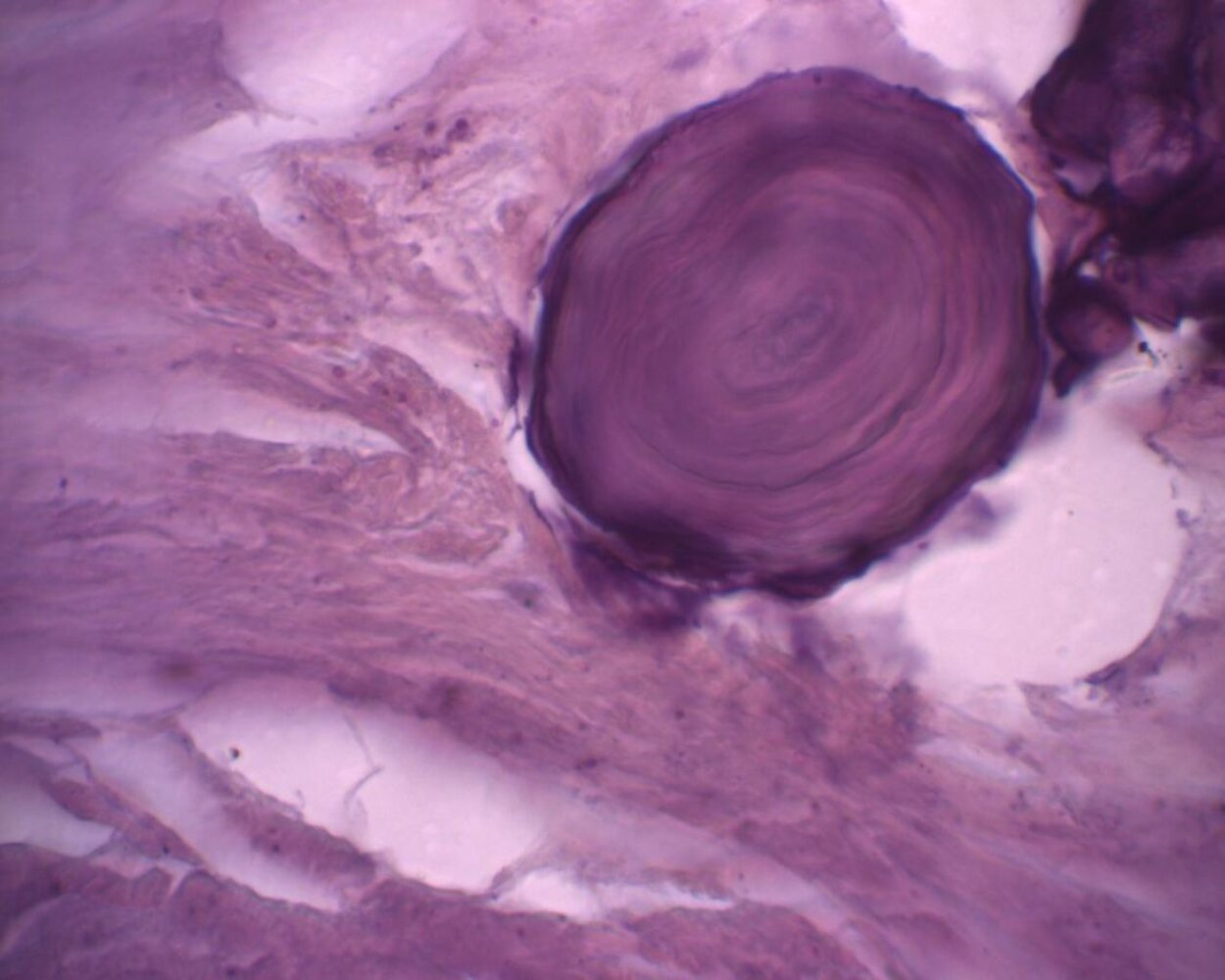
- Morphology: concentric lamellar calcifications
- Occurrence: seen in diseases associated with calcific degeneration
- Papillary thyroid carcinomas (evidence of psammoma bodies in thyroid tissue should always raise suspicion of malignancy)
- Serous papillary cystadenocarcinoma of ovary and endometrium
- Meningiomas
- Mesotheliomas
- Intranuclear inclusions (pseudoinclusions): These are not true inclusions of chromatin within the cytoplasm. They are actually invaginations (infoldings) of the nuclear membrane (the envelope that surrounds the nucleus). Because of this infolding, cytoplasm appears to be inside the nucleus, but it's actually still separated from the nuclear material by the folded nuclear membrane.
- Nuclear grooves: These are also invaginations of the nuclear envelope, creating a groove or fold in the nucleus. It gives a characteristic appearance sometimes likened to a "coffee bean".
- “Orphan Annie” eyes nuclei
- Morphology: empty-appearing large oval nuclei with central clearing
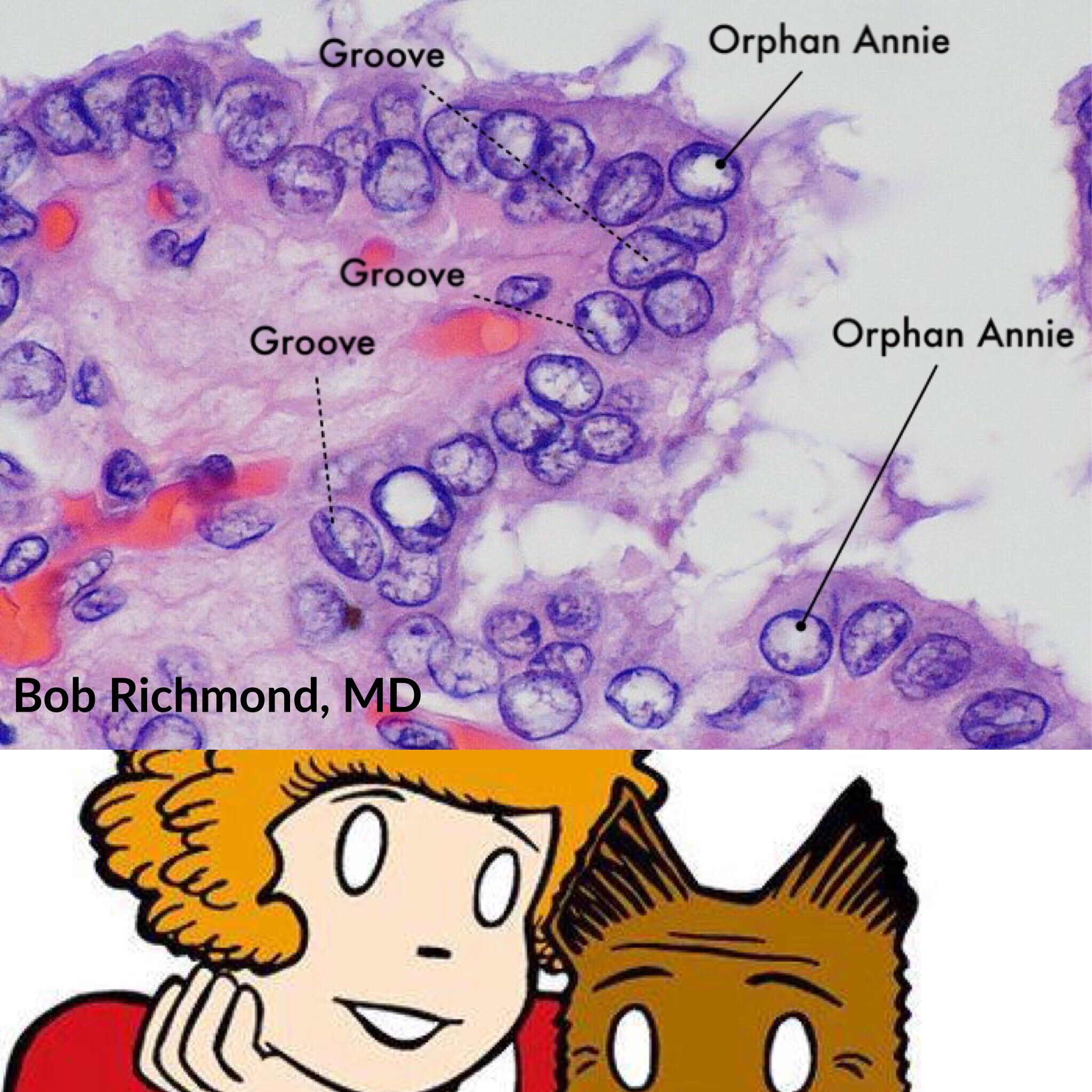
- Occurrence
- Papillary thyroid carcinomas
- Autoimmune thyroiditis (e.g., Hashimoto disease, Grave disease)
- Morphology: empty-appearing large oval nuclei with central clearing
- Psammoma bodies
Mnemonic
Papi and Moma adopted Orphan Annie.
Follicular thyroid carcinoma
- Well differentiated
- Characteristics
- Hematogenous metastasis especially to
- Lungs
- Bone (lytic lesions)
- Rarely multifocal
- Distinguishing a benign follicular adenoma from a well-differentiated follicular carcinoma depends on the presence of vascular or capsular invasion, which cannot be determined on a fine-needle aspiration specimen.
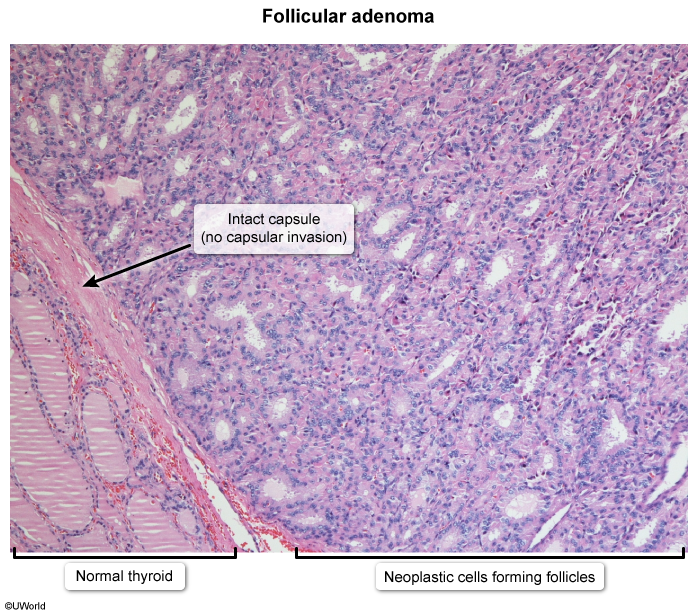
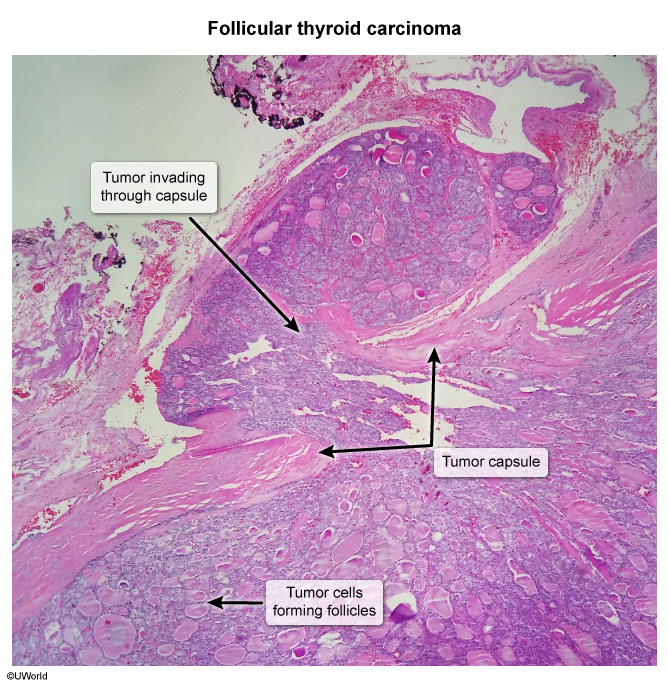
- Good prognosis
- Hematogenous metastasis especially to
Medullary carcinoma
- Tissue of origin: Parafollicular cells (C cells)
- The parafollicular cells are located in the connective tissue between the thyroid follicles, which can be considered a "medullary" (central) part of the thyroid gland, although not in the same sense as the medulla in other organs like the adrenal glands.
- Poorly differentiated
- Characteristics
- Sometimes a genetic predisposition → multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2 (MEN2) (25% of medullary carcinomas)
- Sporadic (75% of medullary carcinomas)
- Produces calcitonin
- Pathology
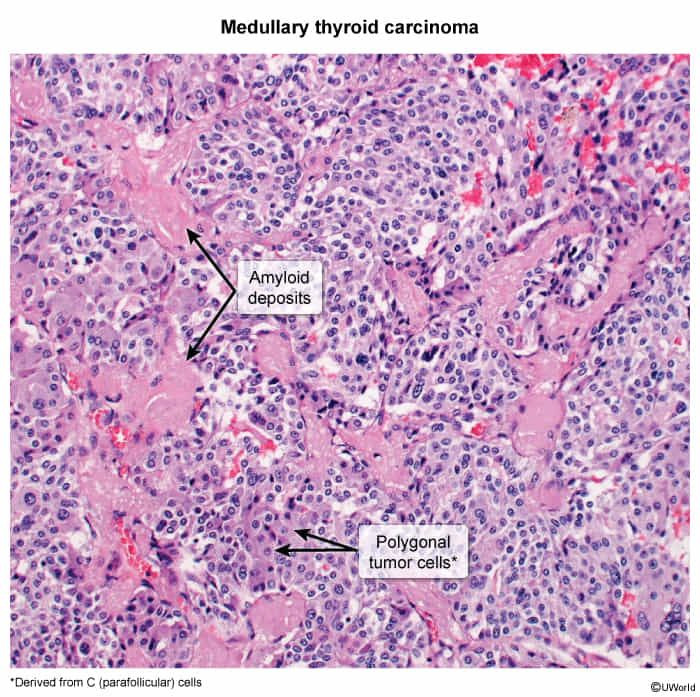
- Ovoid cells of C cell origin and therefore without follicle development
- Amyloid in the stroma (stains with Congo red)
- These amyloid deposits are derived from calcitonin secreted by the neoplastic C cells
Treatment
Thyroid surgery
Complications
- Transient/permanent postoperative hypoparathyroidism (most common) or hypothyroidism
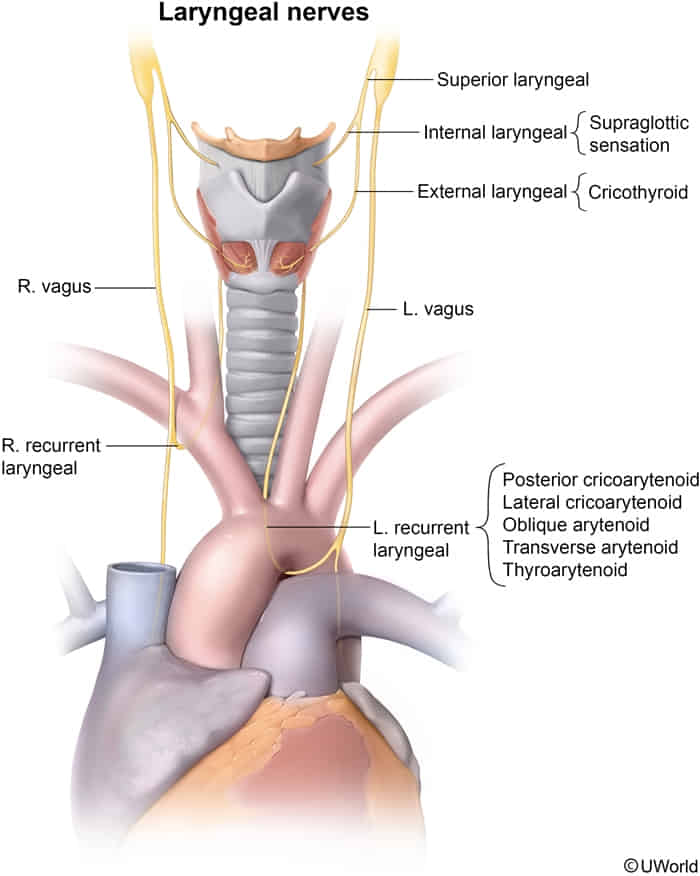
- Hematoma
- Transient/permanent recurrent laryngeal nerve palsy (controls all laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid muscle)
- Unilateral RLN palsy
- Husky/hoarse voice
- Ineffective cough
- Risk of aspiration pneumonia
- Bilateral RLN palsy
- Immediate postoperative dyspnea, stridor (on extubation)
- Unilateral RLN palsy
- Superior laryngeal nerve palsy → paralysis of cricothyroid muscle → easy voice fatigability; change in the timbre of voice