Epidemiology
Etiology
Pathophysiology
Clinical features
- Classic Triad: Episodic Palpitations, Headache, and Diaphoresis (sweating). This triad combined with hypertension is highly suggestive.
- Hypertension: Can be sustained or paroxysmal (episodic) and is the clinical hallmark. May present as a hypertensive crisis.
- Other Symptoms (the “5 Ps”): In addition to the triad, patients may experience high Pressure (HTN) and Pallor. Anxiety, a sense of impending doom, tremor, and weight loss are also common.
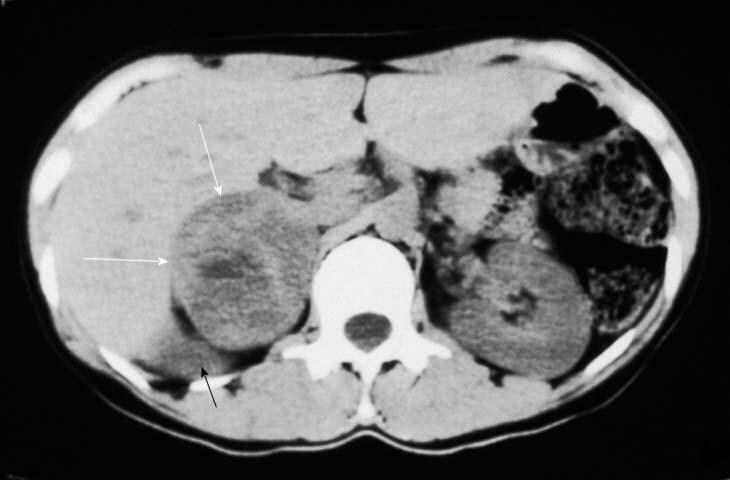
Diagnostics
Differential diagnostics
| Condition | Key Differentiating Features | Confirmatory Test |
|---|---|---|
| Anxiety/Panic | Psychological triggers; lacks severe paroxysmal HTN; may respond to psychiatric meds. | Normal metanephrines. |
| Hyperthyroidism | Persistent symptoms (not spells); goiter, proptosis; fine tremor. | Low TSH, High T4/T3. |
| Carcinoid Syndrome | Classic triad: Flushing, Diarrhea, Wheezing; right-sided heart valve disease. | High urinary 5-HIAA. |
| Illicit Drug Use | History of use; positive urine toxicology screen. | Positive tox screen; metanephrines normalize with abstinence. |
| Clonidine Withdrawal | History of abrupt clonidine cessation; symptoms resolve with clonidine re-administration. | Clonidine suppression test. |
| Essential HTN | Often asymptomatic; lacks paroxysmal spells; responds to standard antihypertensives. | Normal metanephrines. |
Treatment
<% tp.file.cursor() %>