- Patho/Etiology: Insulin, produced by pancreatic β-cells, is the primary anabolic hormone crucial for glucose homeostasis. Its secretion is a tightly regulated process primarily triggered by blood glucose levels.
- Key Stimulators of Insulin Release:
- Stimulators:
- Glucose (Primary).
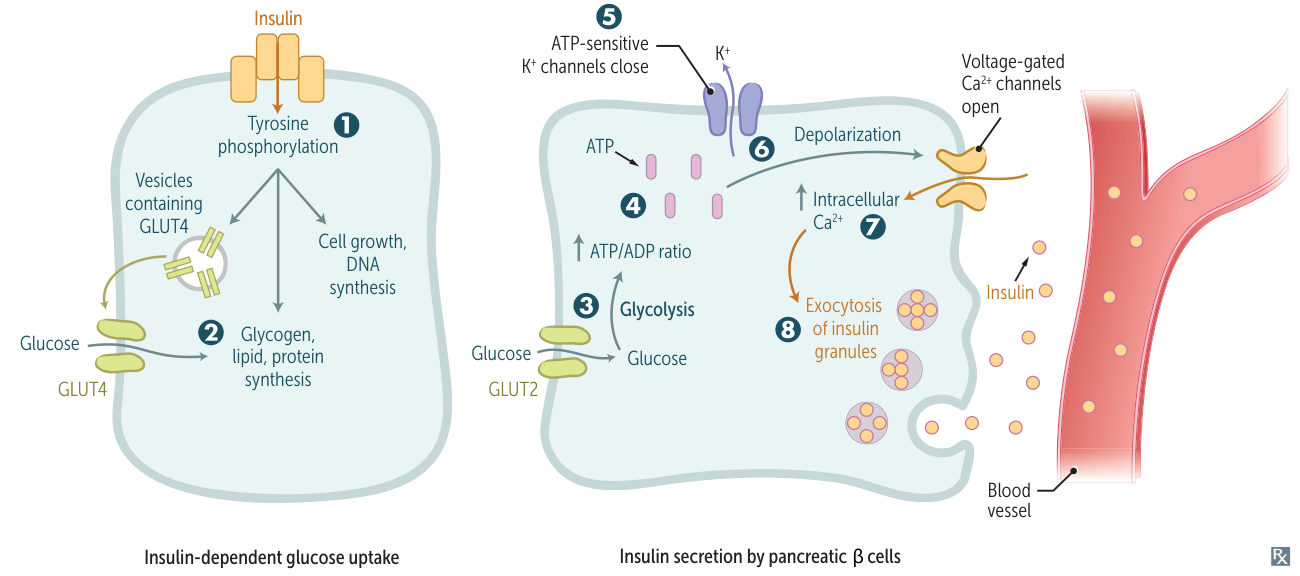
- Glucose enters β-cell via GLUT2 (insulin-independent).
- Metabolism → ↑ ATP.
- ATP binds/closes KATP channels → Membrane Depolarization.
- Voltage-gated Ca2+ channels open → Ca2+ influx.
- Exocytosis of Insulin + C-peptide.
- Incretins (GLP-1, GIP): Cause Oral glucose > IV glucose insulin response.
- β2-agonists.
- Amino Acids: Specifically Leucine and Arginine.
- Vagal Stimulation: Acetylcholine (M3 receptors) stimulates release.
- Free Fatty Acids
- Inhibitors:
- α2-agonists (Sympathetic α2 effect > β2 effect).
- Epinephrine/Norepinephrine inhibits insulin release to keep glucose available for the brain/muscles during stress.
- Somatostatin.
- Mechanism Highlights:
- Synthesis: Preproinsulin → proinsulin (ER) → insulin + C-peptide (Golgi, stored in granules).
- Secretion: Biphasic: 1st phase (rapid, release of readily releasable pool of granules); 2nd phase (sustained, mobilization and synthesis of new granules).
- Amplifying Pathway: Mechanisms beyond KATP channel closure and Ca2+ influx that augment insulin secretion, often involving cAMP and byproducts of glucose metabolism.
- Function & Mechanism
- Carbohydrates:
- ↑ Glucose uptake in skeletal muscle & adipose via GLUT4 (insulin-dependent transporter).
- Note: Brain, RBCs, Intestine, Cornea, Kidney, Liver use insulin-independent transporters (GLUT 1, 2, 3, 5).
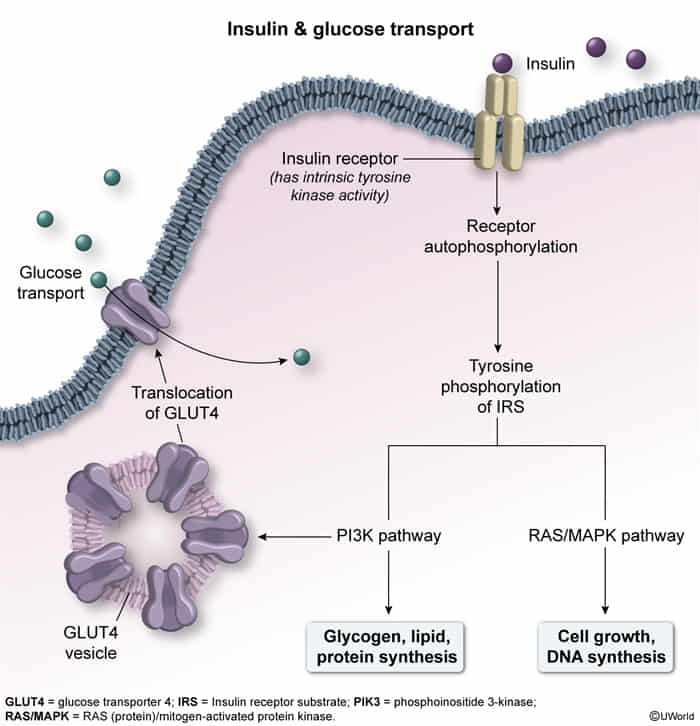
- ↑ Glycogen synthesis (↑ Glucokinase, ↑ Glycogen synthase).
- ↓ Gluconeogenesis & Glycogenolysis.
- Lipids:
- ↑ Triglyceride synthesis in adipose.
- ↓ Lipolysis (Inhibits Hormone-sensitive lipase).
- ↓ Serum Ketones (Inhibits ketogenesis).
- Proteins:
- ↑ Amino acid uptake; ↑ Protein synthesis.
- Electrolytes:
- ↑ Cellular K+ uptake: Increases Na+/K+-ATPase activity.
- Clinical Pearl: Insulin + Glucose is used to treat Hyperkalemia (shifts K+ intracellularly).
- Promotes K+ entry into cells
- The influx of potassium from the meal could cause a transient, but potentially fatal, hyperkalemia. Even a small rise in serum K+ can lead to cardiac arrhythmias. Thus need to be managed.
- Clinical Significance:
- Diabetes Mellitus (Type 1 & 2): Deficiency or resistance to insulin.
- Hyperinsulinemia/Insulinoma: Excessive insulin secretion (e.g., due to tumors, genetic defects like PHHI).
- Drug Targets: KATP channels (sulfonylureas, meglitinides, diazoxide), GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP-4 inhibitors (prevent incretin degradation).

