Epidemiology
Etiology
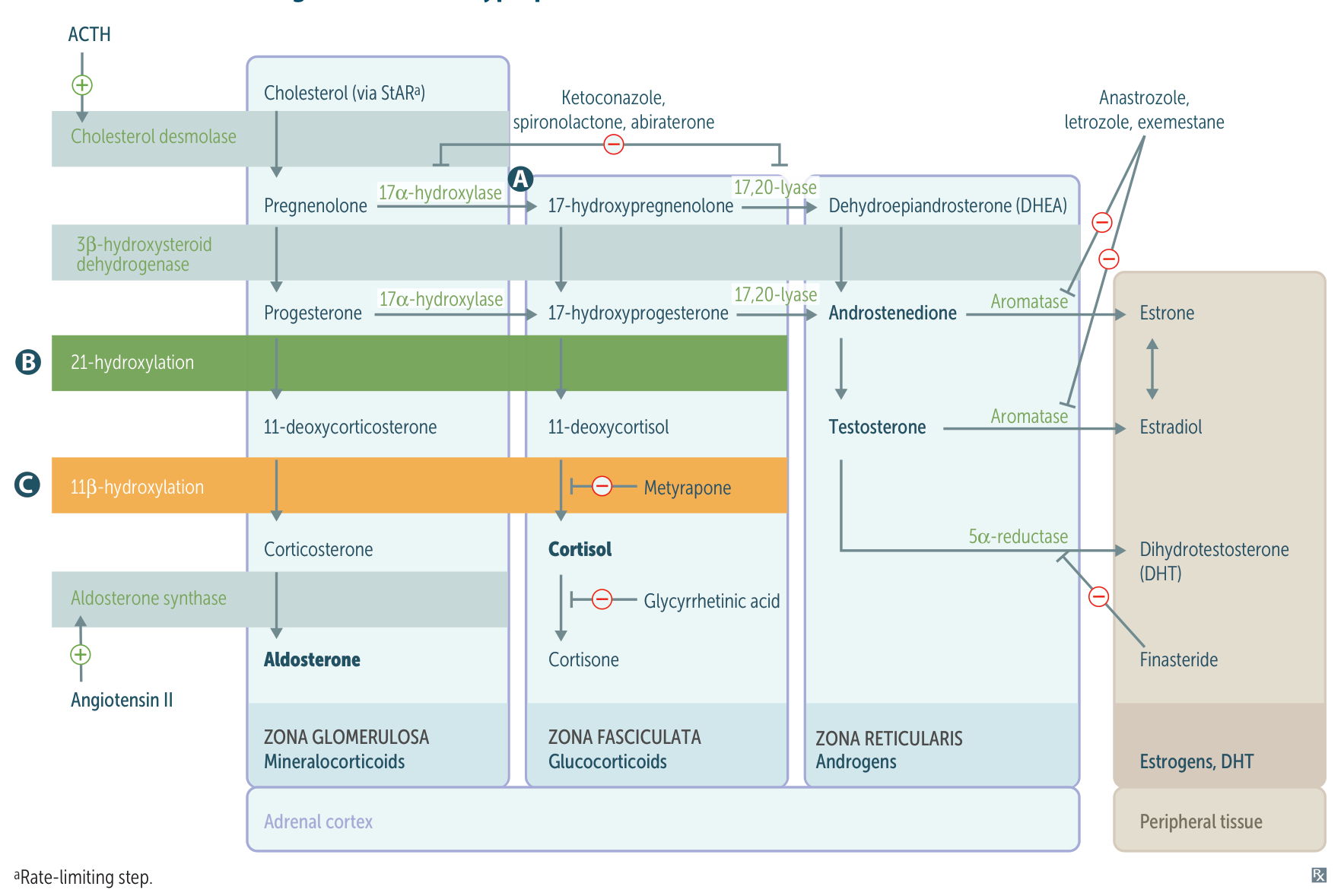
Pathophysiology
- There are three subtypes of CAH:
- 21β-hydroxylase (∼ 95% of CAH)
- 11β-hydroxylase (∼ 5% of CAH)
- 17α-hydroxylase (rare)
- Foa all 3 subtypes, cortisol production is defected.
- Low levels of cortisol → lack of negative feedback to the pituitary → increased ACTH → adrenal hyperplasia and increased synthesis of adrenal precursor steroids
| Feature | 21-Hydroxylase Deficiency | 11β-Hydroxylase Deficiency | 17α-Hydroxylase Deficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prevalence | Most Common (>90%) | ~5% | Rare |
| Mineralocorticoids | ↓ Aldosterone | ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone (weak activity) | ↑ Corticosterone (weak activity) |
| Blood Pressure | Hypotension (Salt-wasting) | Hypertension | Hypertension |
| Potassium (K+) | Hyperkalemia (↑) | Hypokalemia (↓) | Hypokalemia (↓) |
| Sex Steroids | ↑ Androgens | ↑ Androgens | ↓↓ Androgens & Estrogens |
| Genitalia (XX) | Virilization (Ambiguous) | Virilization (Ambiguous) | Female (Sexual Infantilism) |
| Genitalia (XY) | Normal | Normal | Ambiguous or Female |
| Key Lab | ↑ 17-hydroxyprogesterone | ↑ 11-deoxycorticosterone | ↑ Corticosterone, ↓ DHEA |
| Buzzword Triad | Hypotension + Virilization + ↑ K+ | Hypertension + Virilization + ↓ K+ | Hypertension + Sexual Infantilism + ↓ K+ |
Tip
For both 21- AND11- hydroxylase deficiencies: ↑ 17-OH substrates (i.e., 17-OH-progesterone and 17-OH-pregnenolone)
Tip
DOC (11-Deoxycorticosterone) has aldosterone-like activity, and in high levels, it causes hypertension and kaluresis and inhibits the production of renin and consequently aldosterone.
Mnemonic
- “1 DOC:” If the deficient enzyme starts with 1 (11β-, 17‑), there is increased DOC.
- “AND 1:” If the deficient enzyme ends with 1 (21-, 11β‑), androgens are increased.
Clinical features
Diagnostics
Treatment
- Glucocorticoid replacement therapy is indicated in all forms of CAH.
- Specific treatment
- 21β-hydroxylase deficiency
- Lifelong fludrocortisone therapy (aldosterone substitution)
- Sodium chloride (salt) supplements, especially during infancy and childhood
- 11β-hydroxylase deficiency
- Spironolactone to block mineralocorticoid receptors
- Reduced dietary sodium intake
- 17α-hydroxylase deficiency
- Spironolactone to block mineralocorticoid receptors
- Estrogen replacement therapy for female genotype; may be started in early puberty
- Reduced dietary sodium intake
- 21β-hydroxylase deficiency