Epidemiology
Etiology
Mutation in the HGD gene
Pathophysiology
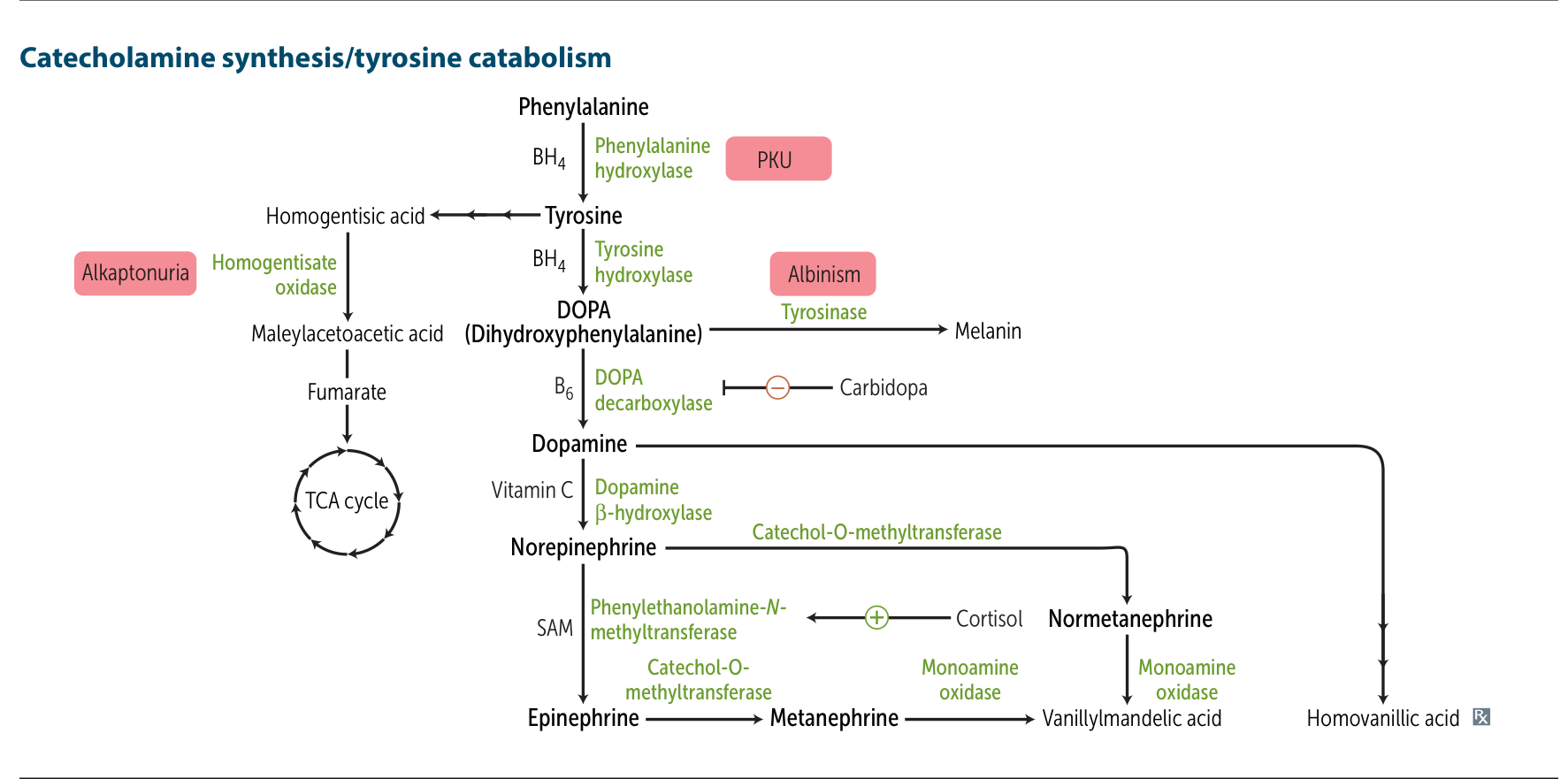

- Autosomal recessive metabolic disorder.
- Deficiency of homogentisate oxidase (also called homogentisic acid dioxygenase).
- Part of the tyrosine degradation pathway.
- Inability to convert homogentisic acid to maleylacetoacetic acid.
- ↑ Accumulation of homogentisic acid in tissues.
Clinical features
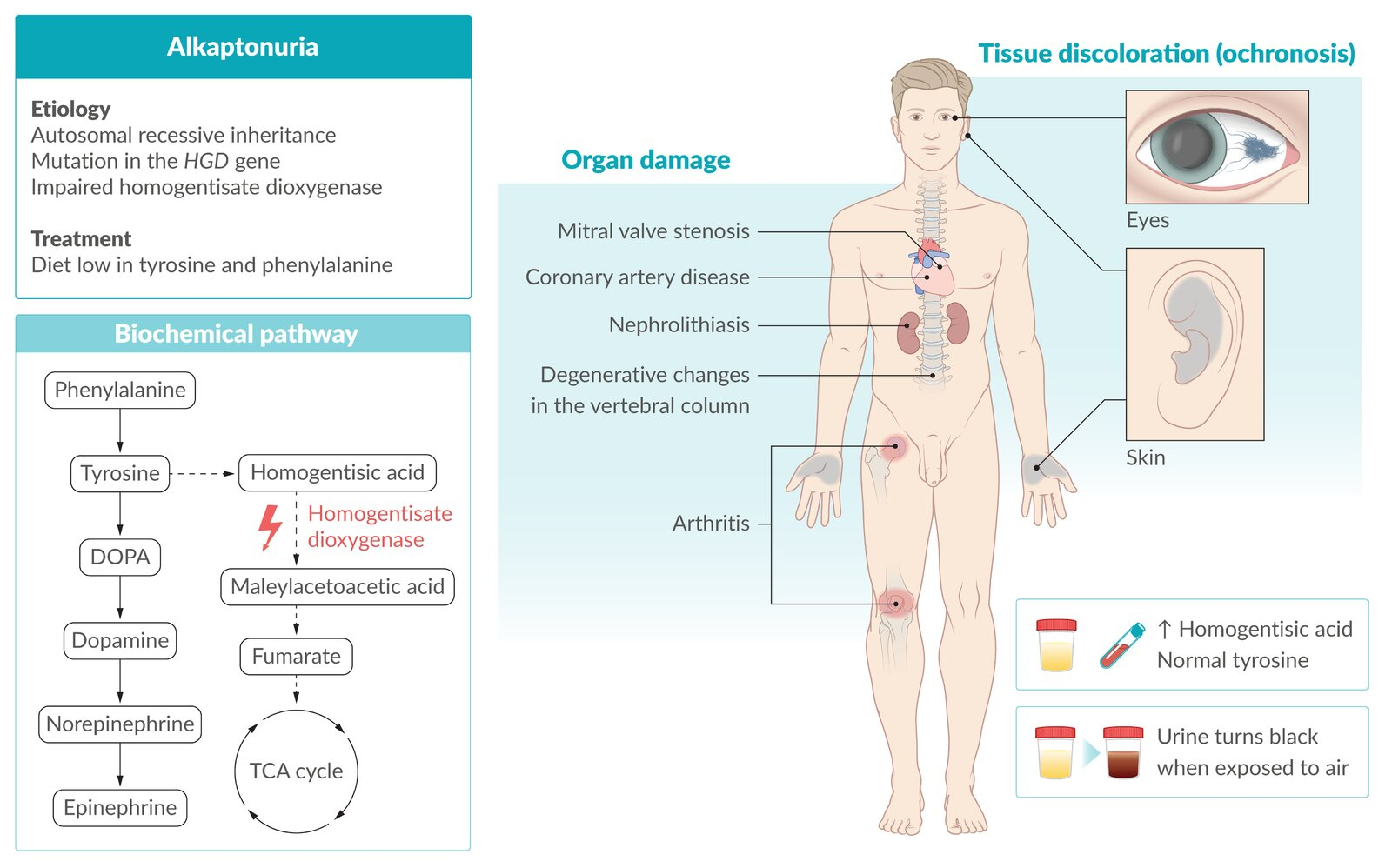
- The classic triad is often tested:
- Ochronotic arthropathy: Arthritis due to pigment deposition.
- Ochronosis: Bluish-black discoloration of connective tissues.
- Urine darkens on standing: Homogentisic acid oxidizes and polymerizes into a dark pigment upon exposure to air (alkalinization).
- Musculoskeletal:
- Severe, early-onset arthritis, often mimicking rheumatoid arthritis or ankylosing spondylitis.
- Affects large joints (knees, hips, shoulders) and the spine (intervertebral disc calcification).
- Dermatologic/Ocular:
- Scleral pigmentation (blue-gray spots) is a pathognomonic sign.
- Darkening of cartilage in the ears and nose.
- Cardiovascular:
- Aortic stenosis or regurgitation due to pigment deposition on valve leaflets.
- Calcification of aorta and coronary arteries.
- Other: Dark cerumen (earwax), black-stained diapers in infancy.