Supraventricular tachycardia
Clinical features
- Palpitations
- Fatigue
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Dyspnea
- Dizziness or presyncope
- Syncope (uncommon; occurs more frequently in older adults)
- Diaphoresis
- Symptom onset and resolution are typically abrupt, in contrast to sinus tachycardia (in which onset and resolution are more gradual).
Warning
Signs of unstable tachycardia due to SVT include acute pulmonary edema, hypotension, severe chest pain, and altered mental status.
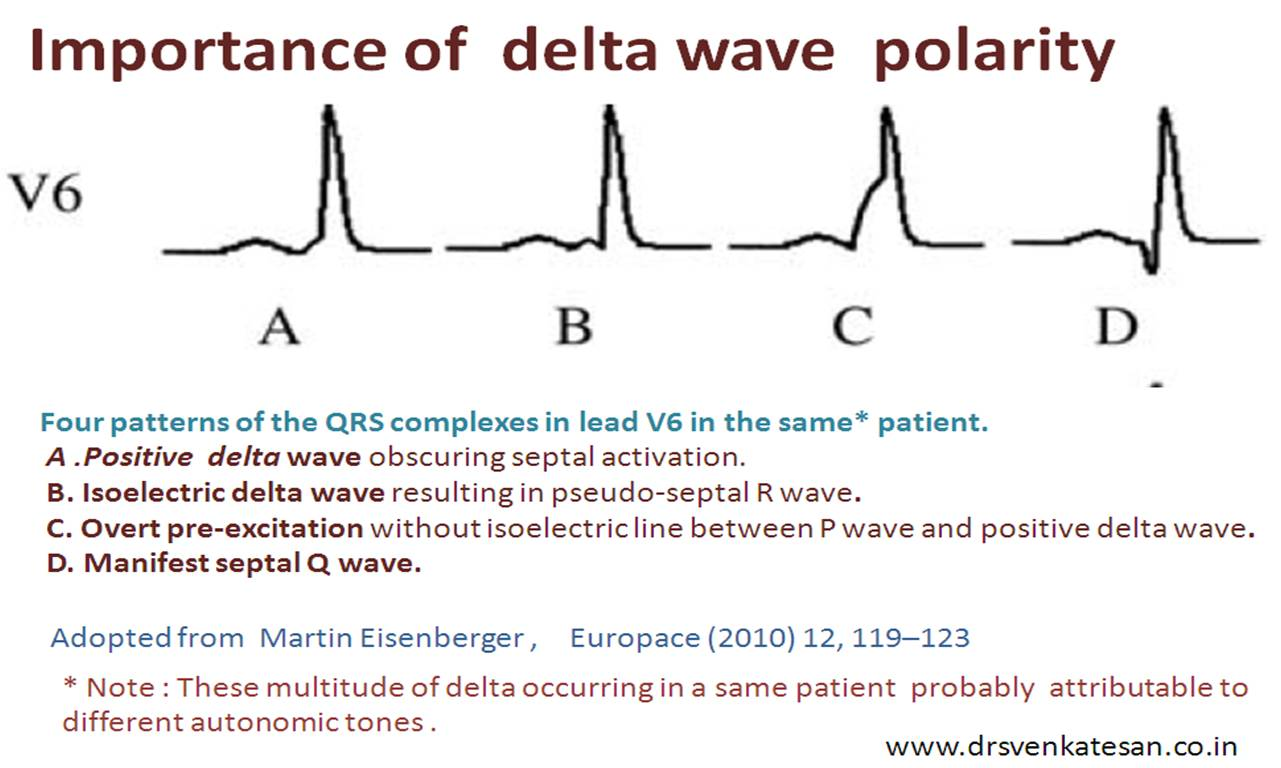
Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW) syndrome
WPW syndrome is a specific form of pre-excitation syndrome characterized by a congenital accessory pathway and tachyarrhythmias, while pre-excitation syndrome is a broader term that encompasses various syndromes involving early ventricular activation.
ECG
- PR interval < 120ms
- Delta wave: slurring slow rise of initial portion of the QRS
- The Delta wave is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex.
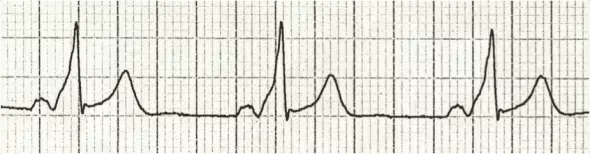
- The Delta wave is a slurred upstroke in the QRS complex.
- QRS prolongation > 110ms
- Discordant ST-segment and T-wave changes (i.e. in the opposite direction to the major component of the QRS complex)
- Pseudo-infarction pattern in up to 70% of patients — due to negatively deflected delta waves in inferior/anterior leads (“pseudo-Q waves”), or prominent R waves in V1-3 (mimicking posterior infarction)
AVNRT (Atrioventricular nodal reentrant tachycardia)
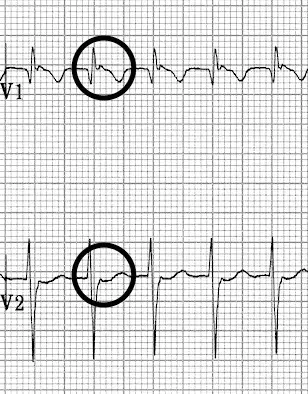
P wave is typically not visible (it falls in or is "buried" in the QRS complex)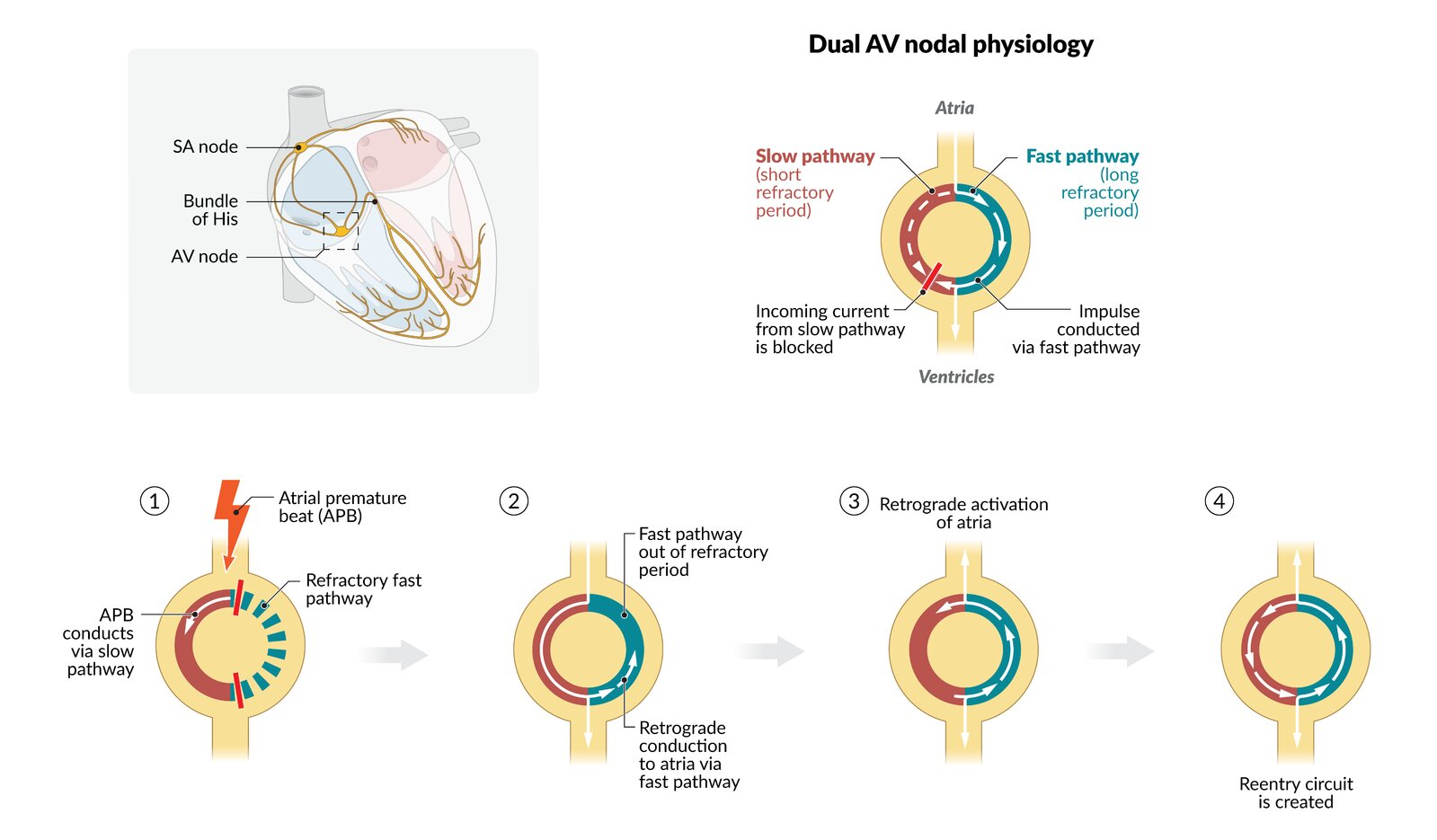
Vagal maneuver is the first step to treat AVNRT.
Tip
- Regular tachycardia ~140-280 bpm
- Narrow QRS complexes (< 120ms) unless there is co-existing bundle branch block, accessory pathway, or rate-related aberrant conduction
- P waves if visible exhibit retrograde conduction with P-wave inversion in leads II, III, aVF. They may be buried within, visible after, or very rarely visible before the QRS complex
SVT vs Sinus tachycardia
The real difference is the rate, practically.
SVT is generally 150 and above. Sinus tach is 100-150.