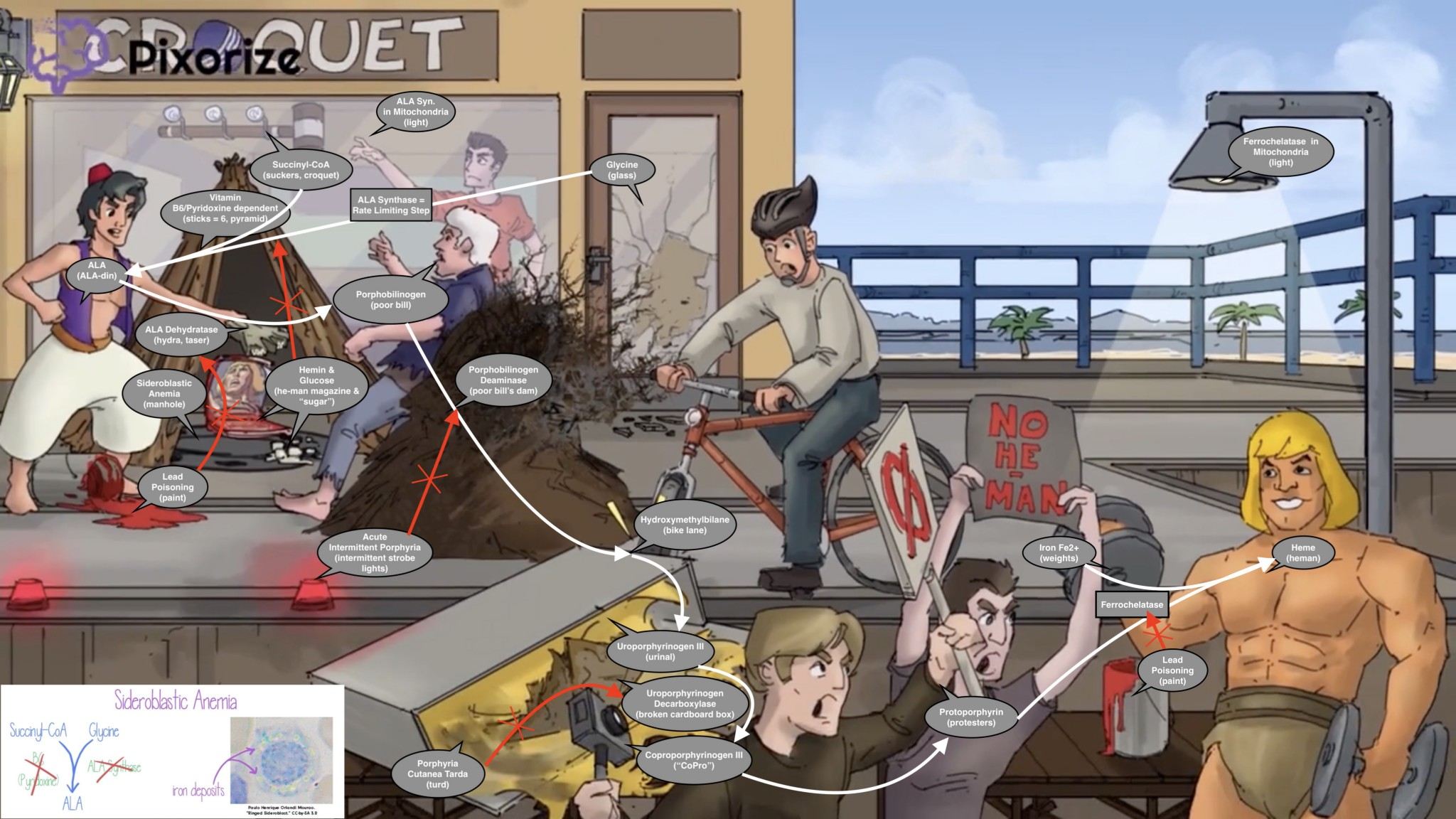
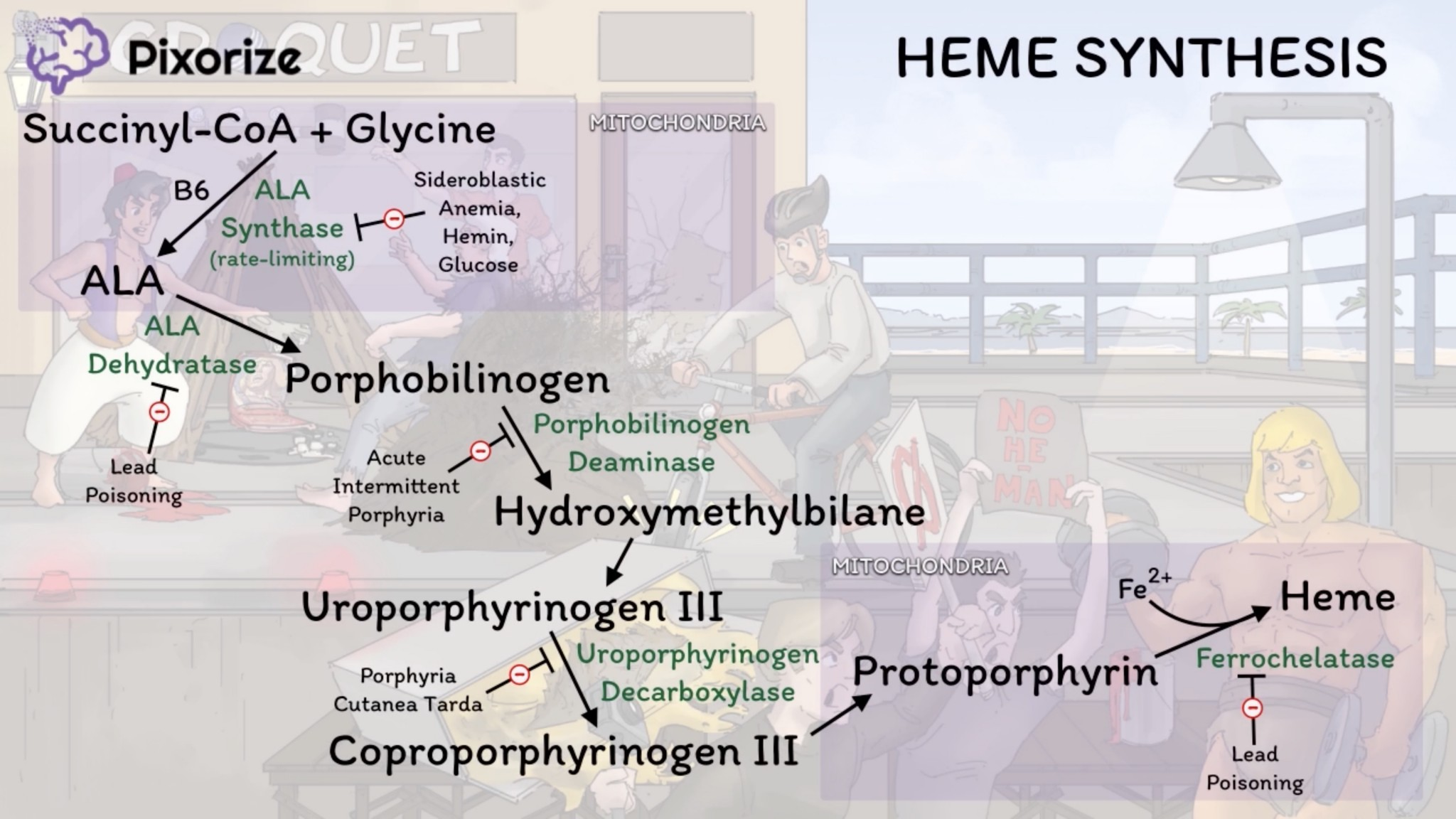
Mitochondria are necessary for the first and the final 3 steps.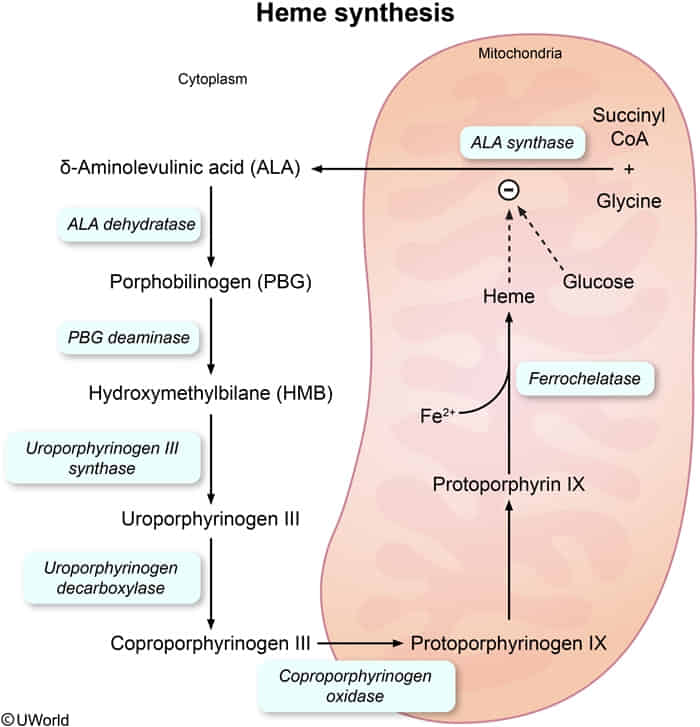
A useful mnemonic for the intermediates: “Great Students Always Produce Highly Useful Content Pertaining to Pathways & Heme.” (Glycine/Succinyl-CoA → ALA → Porphobilinogen → Hydroxymethylbilane → Uroporphyrinogen → Coproporphyrinogen → Protoporphyrinogen → Protoporphyrin → Heme)
The pathway starts and ends in the mitochondria, with intermediate steps in the cytoplasm.
1. Glycine + Succinyl-CoA → δ-Aminolevulinic acid (ALA)
- Enzyme: ALA synthase (Rate-limiting step)
- Location: Mitochondria
- Cofactor: Vitamin B6 (pyridoxine)
- Regulation: Inhibited by heme and glucose.
- Deficiency: X-linked Sideroblastic Anemia
- Presents as microcytic anemia with iron accumulation in mitochondria.
- Dx: Ringed sideroblasts in bone marrow (Prussian blue stain).
2. ALA → Porphobilinogen (PBG)
- Enzyme: ALA dehydratase
- Location: Cytoplasm
- Inhibited by: Lead
3. Porphobilinogen (PBG) → Hydroxymethylbilane
- Enzyme: Porphobilinogen (PBG) deaminase
- Location: Cytoplasm
- Deficiency: Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) (Autosomal Dominant)
- Accumulates: PBG, ALA.
- Presentation (The 5 P’s):
- Painful abdomen
- Port-wine colored urine (darkens on standing)
- Polyneuropathy
- Psychological disturbances
- Precipitated by triggers (e.g., CYP450 inducers, alcohol, starvation).
- Tx: Glucose and heme (inhibit ALA synthase).
4. Uroporphyrinogen III → Coproporphyrinogen III
- Enzyme: Uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase
- Location: Cytoplasm
- Deficiency: Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT) (Most common porphyria)
- Accumulates: Uroporphyrin (tea-colored urine).
- Presentation: Blistering cutaneous photosensitivity and hyperpigmentation.
- Associations: Hepatitis C, alcohol use, hemochromatosis.
5. Protoporphyrin IX + Fe2+ → Heme
- Enzyme: Ferrochelatase
- Location: Mitochondria
- Inhibited by: Lead
Lead Poisoning
- Mechanism: Inhibits ALA dehydratase and Ferrochelatase.
- Accumulates: Protoporphyrin, ALA in blood.
- Presentation:
- Lead lines on gingivae (Burton lines) & on long bone metaphyses.
- Encephalopathy & Erythrocyte basophilic stippling.
- Abdominal colic & sideroblastic Anemia.
- Drops (wrist and foot drop).
- Dx: ↑ blood lead level, basophilic stippling on peripheral smear.
- Tx: Chelation therapy (e.g., EDTA, Dimercaprol, Succimer for kids).