Epidemiology
Etiology
- Iatrogenic
- Vascular interventions, e.g., percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
- Cardiac surgery
Pathophysiology
Atherosclerosis → rupture of atherosclerotic plaque (most commonly from the aorta) → blockage and inflammation of small to medium arteries by cholesterol crystals → formation of multiple small peripheral, muscular, or visceral emboli → end-organ damage
Clinical features
- Features of renal damage
- Signs of acute kidney injury
- Peripheral skin manifestations
- Livedo reticularis
- Necrosis
- Purpura
- Blue toe syndrome: ischemia due to small vessel occlusion that manifests as toe discoloration (pulses typically remain palpable as large arteries are unaffected)
- Signs of gastrointestinal involvement (e.g., intestinal ischemia or pancreatitis)
- Signs of CNS involvement (e.g., ischemic stroke or TIA)
- Signs of retinal involvement
- Hollenhorst plaques on retinal exam
- Amaurosis fugax
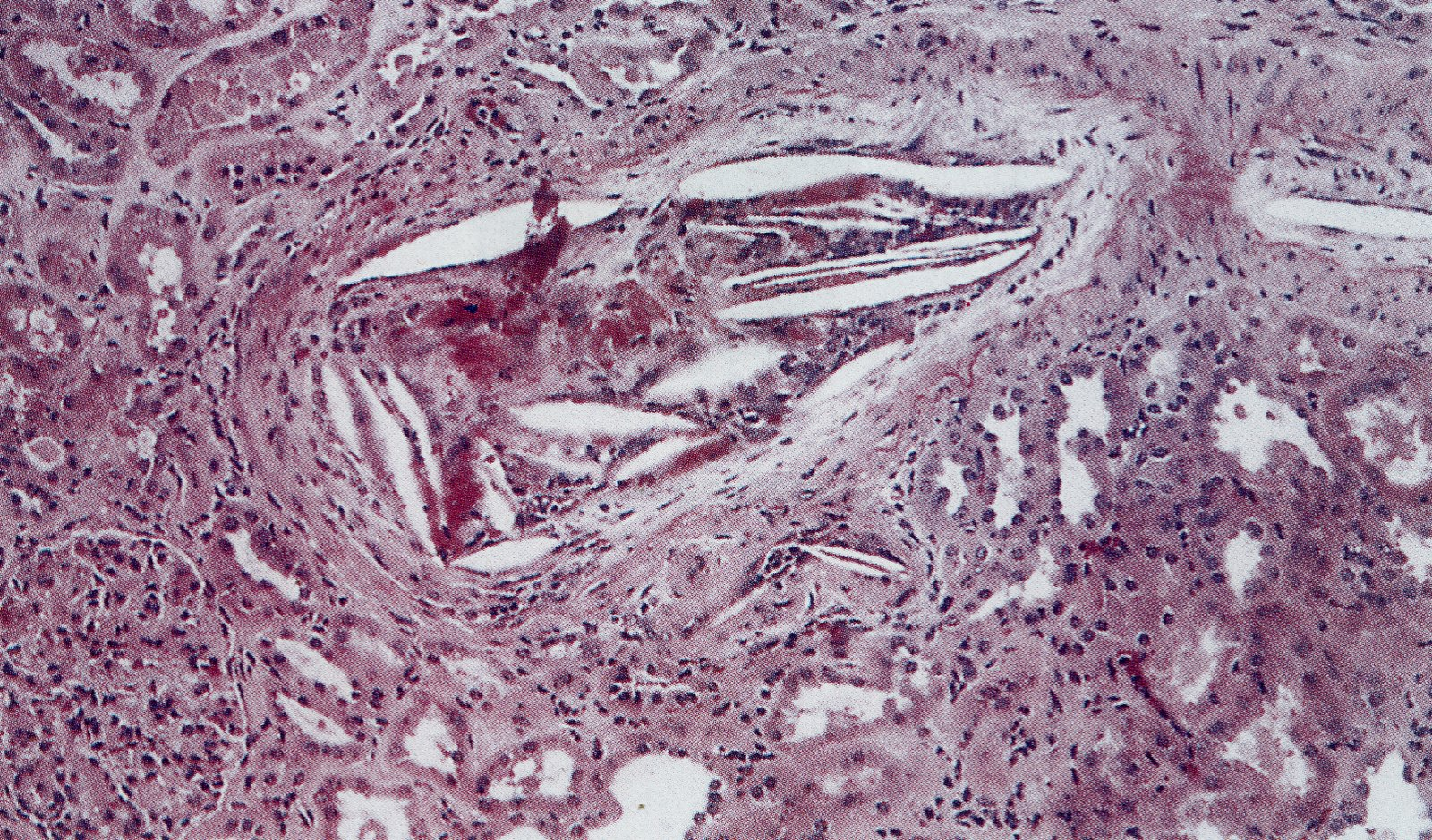
Diagnostics
- Biopsy
- Amorphous, eosinophilic material in the vessel lumen
- Spindle-shaped spaces (cholesterol clefts), formed when the fat molecules in cholesterol emboli dissolve during sample processing