Genetic code
Start and stop codons

Features of the genetic code
- Unambiguous (Specific)
- Each codon specifies only one amino acid.
- Example: UUU always codes for Phenylalanine.
- Degenerate (Redundant)
- Most amino acids are coded by multiple codons.
- This protects against mutations; silent mutations often occur in the 3rd position (Wobble hypothesis). t

- Exceptions: Only Methionine (AUG) and Tryptophan (UGG) are encoded by a single codon.
- Commaless / Non-overlapping
- The code is read from a fixed starting point as a continuous sequence of bases without punctuation.
- Altering the reading frame (e.g., via frameshift mutation) dramatically changes the protein product.
- Universal
- The code is conserved throughout evolution (bacteria to humans).
- Exception: Human mitochondria utilize a slightly different code (e.g., UGA codes for Tryptophan instead of Stop).
Transcription
Regulation of transcription
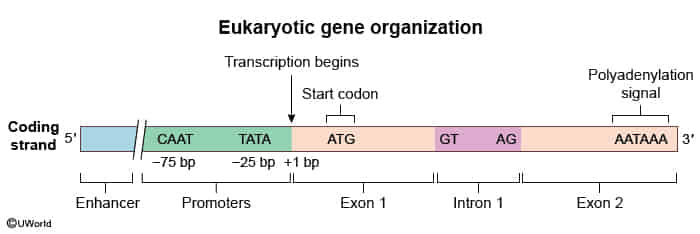
- Promoter: DNA sequence where RNA polymerase II and general transcription factors (e.g., TFIID) bind.
- TATA box (rich in A-T) usually located ~25 bp upstream.
- CAAT box located ~75 bp upstream.
- Mutation in the promoter results in a significant ↓ in the level of transcription.
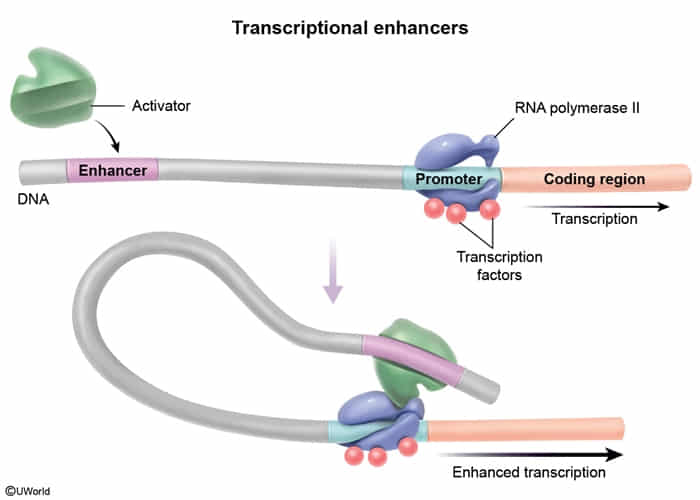
- Enhancers: DNA sequences that increase the rate of transcription by binding activator proteins.
- Silencers: DNA sequences that decrease the rate of transcription by binding repressor proteins.
- Note: Enhancers and silencers can be located far upstream, downstream, or even within introns of the gene they regulate. t
Transcription factor
- Definition
- Proteins that bind DNA to control the rate of transcription (DNA mRNA).
- Key Structural Motifs (Classic USMLE Question)
- Zinc Finger: Steroid receptors (Estrogen, Aldosterone, Cortisol), Thyroid hormone, Vit D, Vit A.
- Helix-Turn-Helix: Homeobox (HOX) genes (developmental axis patterning).
- Leucine Zipper: c-Myc, c-Jun, c-Fos (proto-oncogenes).
- Binding Sites
- Promoters (e.g., TATA box): Located immediately upstream (-25 bp). Bind basal factors/RNA Pol II.
- Enhancers/Silencers: Located anywhere (far upstream, downstream, or within introns). Regulate expression levels.
- Mechanism (Intracellular Receptors)
- Lipid-soluble hormones (Steroids, T3/T4) cross membrane bind cytosolic/nuclear receptor complex enters nucleus binds DNA via Zinc finger.
- Clinical Associations
- HOX Mutations: Appendages in wrong locations (synpolydactyly t ). Altered by Retinoic Acid (teratogenic).
- Li-Fraumeni: Mutation in p53 (a TF) inability to arrest cell cycle/induce apoptosis.
- PPAR drugs:
- Glitazones PPAR- (Diabetes).
- Fibrates PPAR- (Hypertriglyceridemia).
Translation process
Initiation
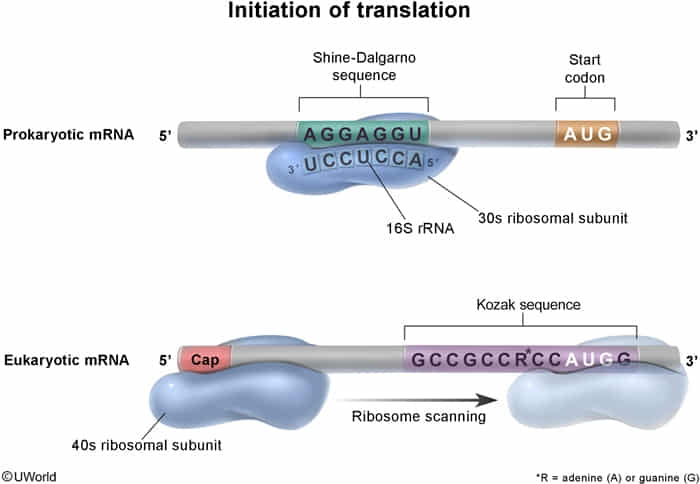
- Initiator met-tRNA, eukaryotic IF2 (eIF2), and GTP bind to the small ribosomal subunit to form a preinitiation complex (initially a 43s preinitiation complex).
- eIF2: a small G protein
- Binds initiator met-tRNA (ternary complex) and forms the final initiation complex by hydrolyzing GTP to GDP
- Reconverted to the GTP-bound form by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B
- eIF2: a small G protein
- Kozak sequence: Eukaryotic consensus sequence around the start codon that enhances initiation efficiency. t
Elongation
- An aminoacyl-tRNA complex with eukaryotic elongation factor 1 (eEF1) hydrolyzes GTP, thereby releasing eEF1 and GDP and providing the energy for aminoacyl-tRNA to bind the A site (anticodon matches the codon of the mRNA).
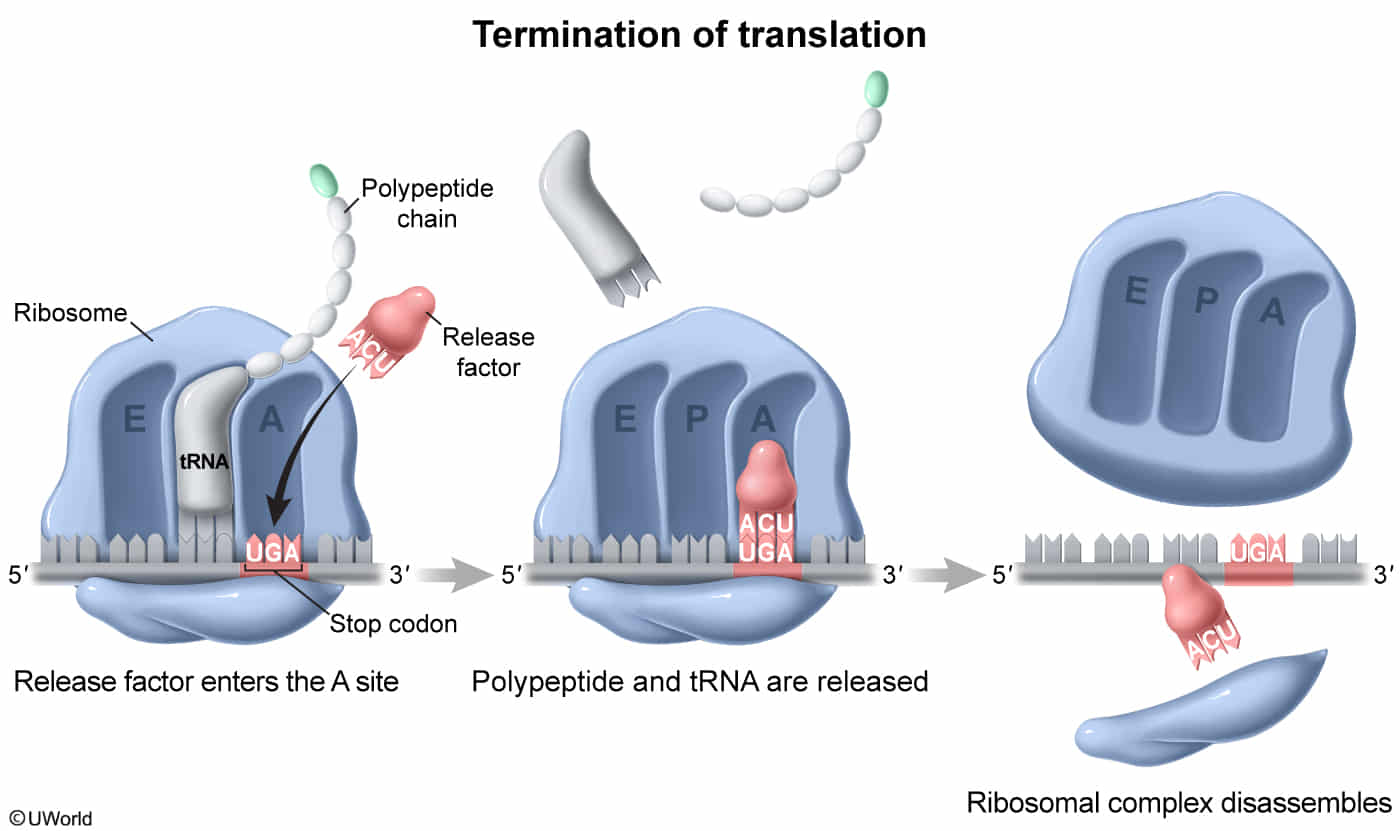
Termination
- A release factor recognizes the stop codon, halts translation, and hydrolytically cleaves the peptidyl tRNA bonds (requires GTP), leading to release of the protein.