Interferons and Tumor necrosis factor
Tip
- Interferons (General): Proteins that "interfere" w/ viral replication; key in innate antiviral defense; also modulate adaptive immunity & have anti-tumor activity.
- IFN-α & IFN-β (Type I IFNs):
- Source: IFN-α (leukocytes, esp. pDCs); IFN-β (fibroblasts, many cell types).
- Function: Potent antiviral activity (induce enzymes that degrade viral RNA, inhibit protein synthesis), ↑MHC Class I expression on all cells (alerts CD8+ T cells to infected cells)
IFN-β also used in MS treatment.
- IFN-γ (Type II IFN / "Immune Interferon"):
- Source: Primarily NK cells & activated T cells (Th1).
- Function: Activates macrophages (↑phagocytosis, killing ability, Ag presentation), ↑MHC Class I & II expression, promotes Th1 differentiation, anti-tumor activity. Key fo
intracellular pathogen defense.
- IFN-α & IFN-β (Type I IFNs):
- Tumor Necrosis Factor (TNF) (General): Pro-inflammatory cytokine.
- TNF-α ("Cachectin"):
- Source: Primarily activated macrophages; also T cells, NK cells.
- Function: Mediates acute inflammation (↑vascular permeability, recruits neutrophils, induces fever-endogenous pyrogen). Causes cachexia in chronic disease/malignancy. Can induce apoptosis in some tumor cells. Systemic effects: septic shock (vasodilation, ↓BP).
- TNF-β (Lymphotoxin-α / LT-α):
- Source: Primarily activated lymphocytes (T & B cells).
- Function: Similar pro-inflammatory & cytotoxic effects to TNF-α (binds same receptors). Involved in lymphoid organ development.
- TNF-α ("Cachectin"):
Overview of Interferons
Type I Interferons
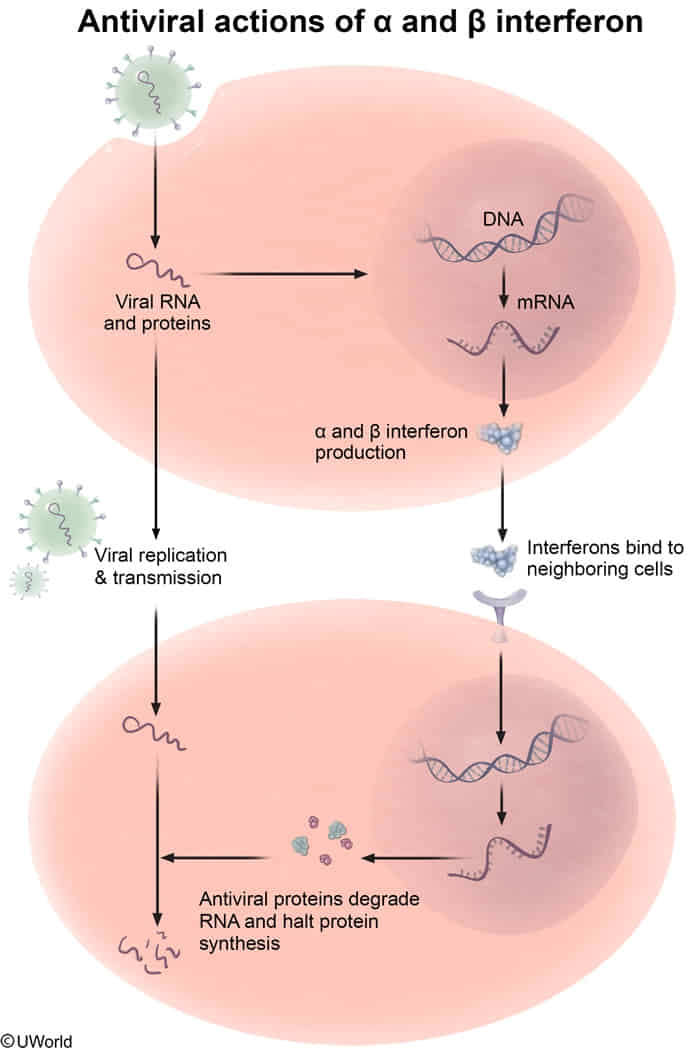
Interferon Alpha (IFN-α)
- Mainly Secreted By:
- Virus-infected cells and malignant cells
- Fibroblasts (interferon-β)
- Function:
- Acts as the first line of defense against all viral infections
- Inhibits viral protein synthesis by activating ribonuclease L, leading to the degradation of cellular and viral mRNA
- Promotes the expression of MHC class I molecules, aiding in the recognition of virus-infected cells and activation of NK cells and cytotoxic T cells
- Inhibits megakaryocyte stem cell differentiation and proliferation
- Therapeutic Use:
- Chronic hepatitis B
- Acute and chronic hepatitis C
- Kaposi sarcoma
- Adjuvant therapy for malignant melanoma
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Condyloma acuminatum
- Hairy cell leukemia
- Essential thrombocythemia
- Side Effects:
- Flu-like symptoms (fever, chills)
- Depression
- Myopathy
- Neutropenia
- Interferon-induced autoimmunity
- Gastrointestinal issues (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)
- Itchy skin
Interferon Beta (IFN-β)
- Therapeutic Use:
Type II Interferons
Interferon Gamma (IFN-γ)
- Mainly Secreted By:
- Th1 and NK cells (when stimulated by IL-12 from macrophages or antigen contact)
- Function:
- Activates macrophages to increase phagocytosis (positive reinforcement) and NK cells to eliminate virus-infected target cells
- Synergistic effect with tumor necrosis factor in stimulating macrophages to form granulomas, crucial against mycobacterial infections
- Suppresses a Th2 response (negative feedback)
- Promotes the expression of MHC class II molecules and antigen presentation in every cell
- Stimulates antigen class switching to IgG3
- Therapeutic Use:
- Chronic granulomatous diseases (e.g., leprosy, leishmaniasis, toxoplasmosis)
Tumor Necrosis Factor Superfamily
- Pro-inflammatory cytokines secreted by leukocytes in response to inflammation and/or infection
- Their signaling pathways regulate inflammation, apoptosis, and cellular proliferation and differentiation
- There are over 20 tumor necrosis factors, with cachectin and lymphotoxin-alpha being the most important
Cachectin (Tumor Necrosis Factor, formerly TNF-α)
Secreted by:
- Activated macrophages
Functions:
- Pyrogenic
- Cytotoxic and inhibits carcinogenesis of certain tumors
- Mediates septic shock by activating the endothelium, leading to:
- Vascular leakage
- Recruitment of white blood cells
- Causes malignant cachexia
- Its role in cachexia is explained by its influence on the hypothalamus, leading to appetite suppression. It also increases basal metabolic rate.
- Maintains granulomas, which are critical for defense against mycobacterial infections
Therapeutic Significance:
- TNF inhibitors like infliximab are used to treat refractory chronic inflammatory systemic diseases (e.g., Crohn disease)
Lymphotoxin-alpha (formerly TNF-β)
Secreted by:
- Activated lymphocytes
Functions:
- Cytotoxic, leading to inhibition of carcinogenesis
- Promotes colony stimulating factor synthesis, which leads to:
- Fibroblast proliferation
- Stimulation of wound healing
Therapeutic Significance:
- TNF inhibitor etanercept can bind lymphotoxin-alpha