- Key Enzymes & Pathway (Liver)
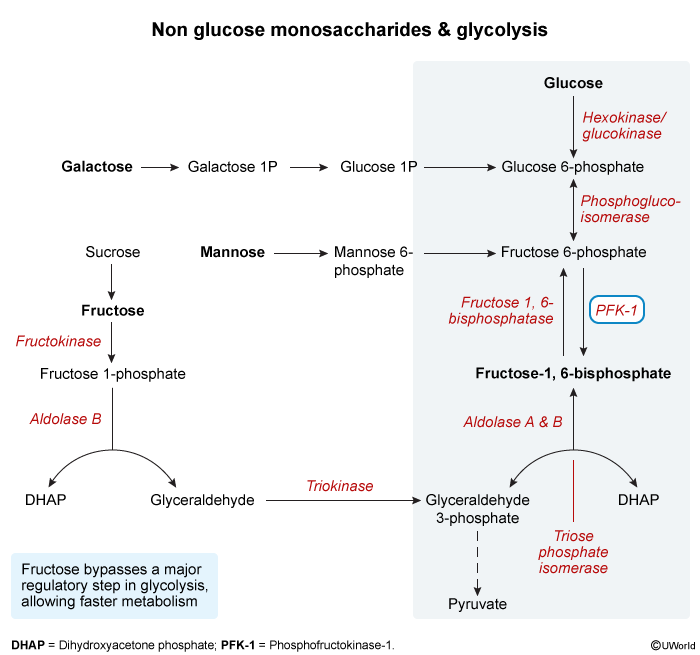
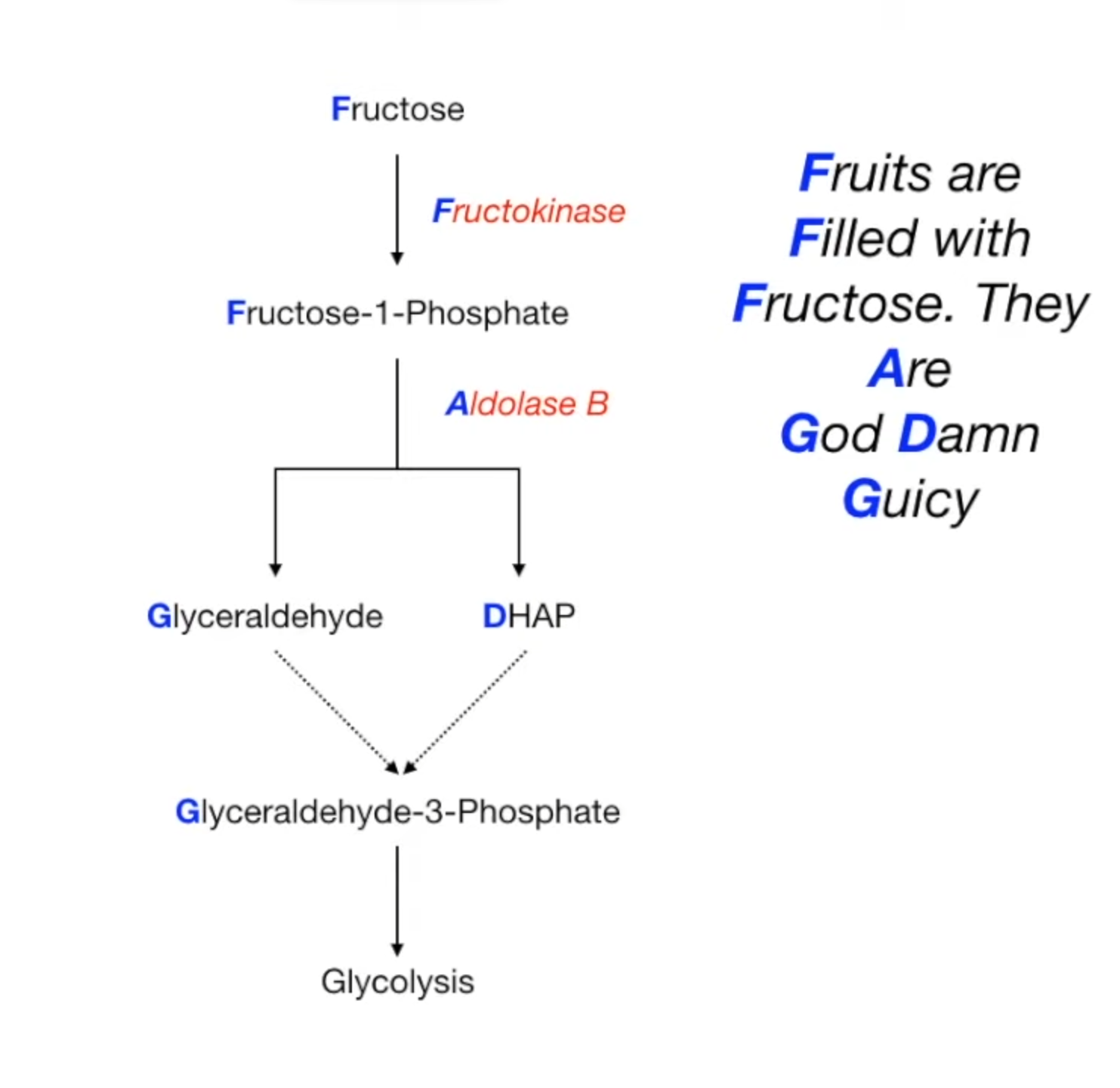
- 1. Fructokinase:
- Converts Fructose → Fructose-1-Phosphate (F-1-P).
- This “traps” fructose inside hepatocytes.
- Faster than glucokinase, not regulated by insulin.
- 2. Aldolase B:
- Cleaves F-1-P → Dihydroxyacetone Phosphate (DHAP) + Glyceraldehyde.
- DHAP enters glycolysis directly.
- Glyceraldehyde is phosphorylated to Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate (G3P) to enter glycolysis.
- 1. Fructokinase:
- Pathway Significance
- Fructose metabolism bypasses phosphofructokinase-1 (PFK-1), the major rate-limiting step of glycolysis.
- This means fructose provides carbon for acetyl-CoA and triglyceride synthesis in an unregulated fashion.
- High fructose consumption is linked to ↑ VLDL, hypertriglyceridemia, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD).
Essential fructosuria
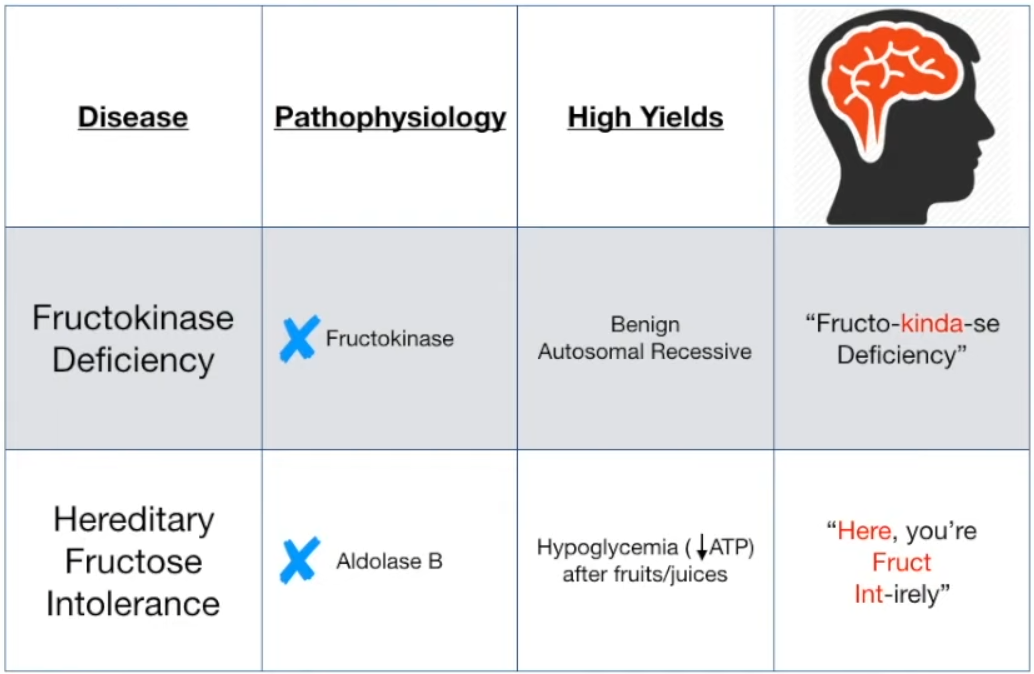
- Increased conversion of fructose to fructose-6-phosphate by hexokinase (hexokinase becomes the main pathway for turning fructose to fructose-6-phosphate)
- Unphosphorylated fructose does not get trapped in cells → remaining excess fructose → excretion of fructose (reducing sugar) in urine
Mnemonic
Fructokinase deficiency is kinder
Hereditary fructose intolerance
- Accumulation of fructose-1-phosphate → decrease in available phosphates → inhibition of glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis → hypoglycemia
- Phosphates are trapped in F-1-P, can’t be used in elsewhere
- Clinical features
- Symptoms begin when the child is weaned off breast milk and starts consuming food that contains sucrose (e.g., fruit, juice, honey)
- Fructose are like poisonous to them
- Bloating, sweating, vomiting
- Failure to thrive
- Jaundice (can progress to cirrhosis)
- Bleeding tendency
- Severe hypoglycemia: seizures, hypotonia, poor feeding, cyanosis, irritability
- Hepatomegaly
- Symptoms begin when the child is weaned off breast milk and starts consuming food that contains sucrose (e.g., fruit, juice, honey)
- Treatment: lifelong adherence to a fructose-free, sorbitol-free, and sucrose-free diet
- Some of the ingested sorbitol gets broken down into fructose during digestion.
- Sucrose, also known as table sugar, is a disaccharide sugar molecule. It’s made up of two simpler sugars: fructose and glucose.