Structure
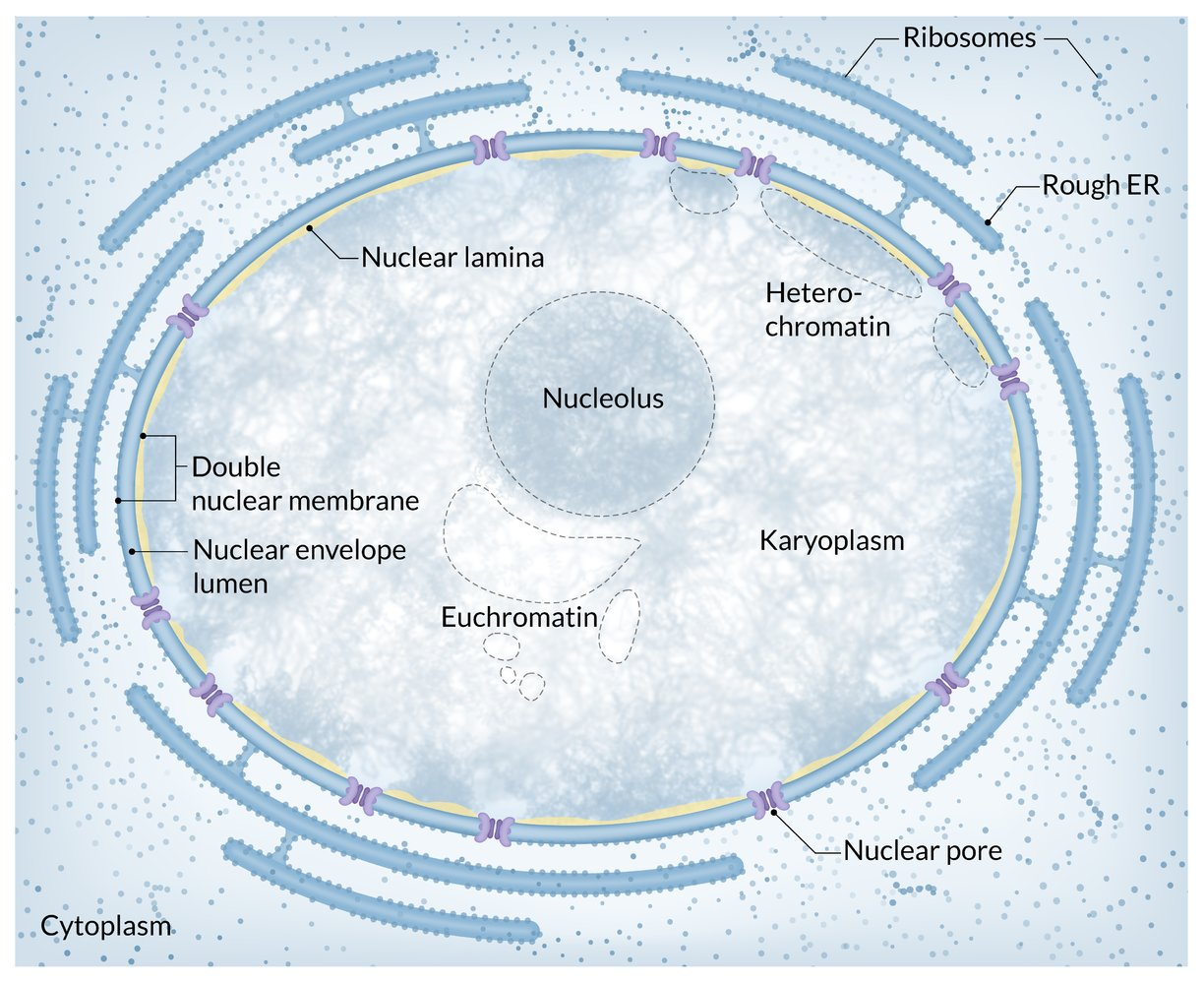
- Nuclear content
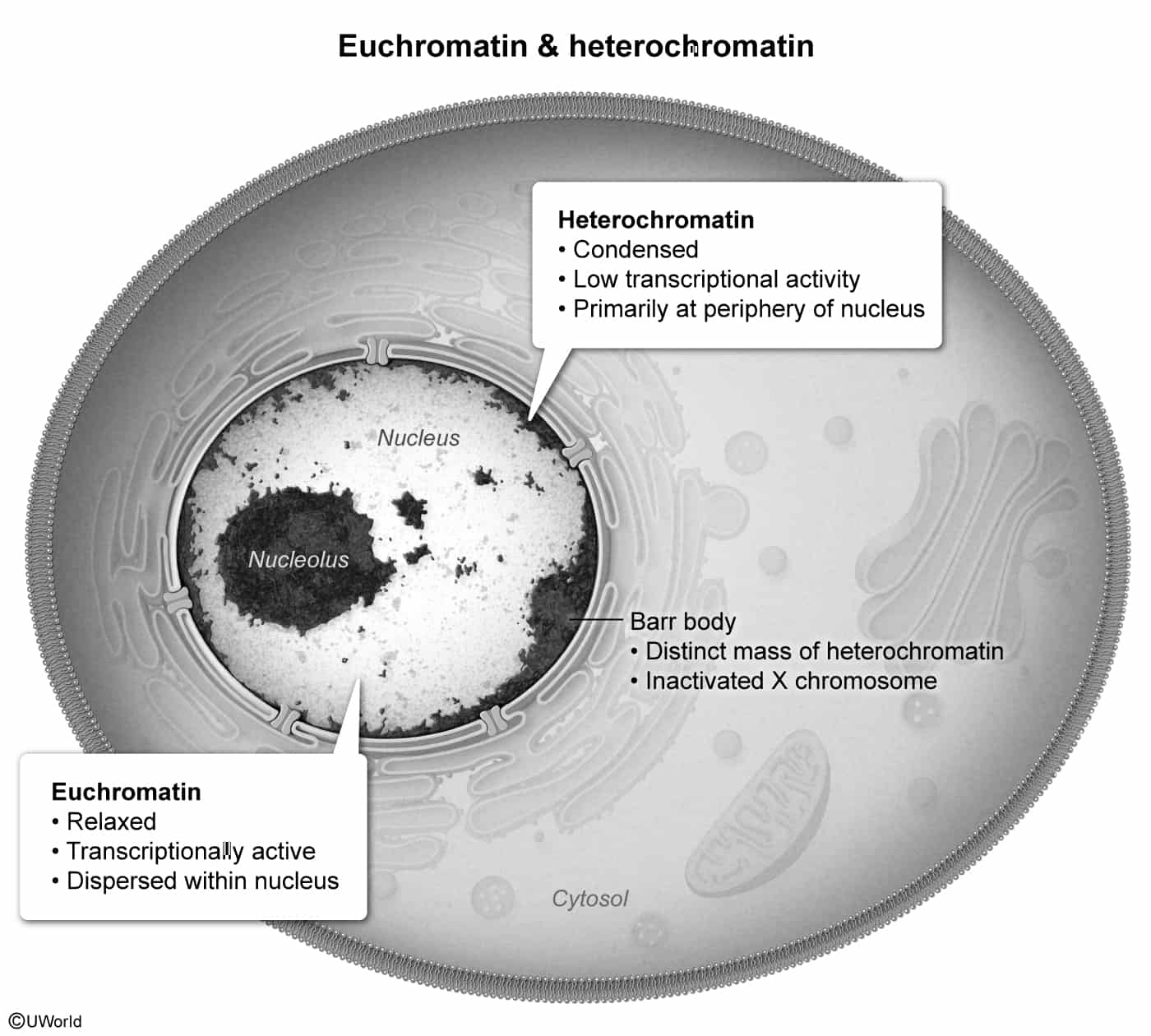
- Chromatin: complex of DNA, histones, and nonhistone proteins
- Nucleolus: Site of rRNA synthesis. Prominent in cells with high metabolic activity (e.g., malignancy). t
- Nucleoplasm: The fluid matrix inside the nucleus. Site of transcribing mRNA, snRNA, and miRNA precursors.
- Peripheral: Barr body
Functions
- Storage of the entire genetic information of an organism in the form of chromatin (except mitochondrial DNA)
- Duplication of genetic information before cell division (DNA replication): See the cell cycle for further information.
- Transcription: initial step of protein synthesis
- Synthesis of rRNA in the nucleolus
- Packaging and protection of inactive DNA by histones

