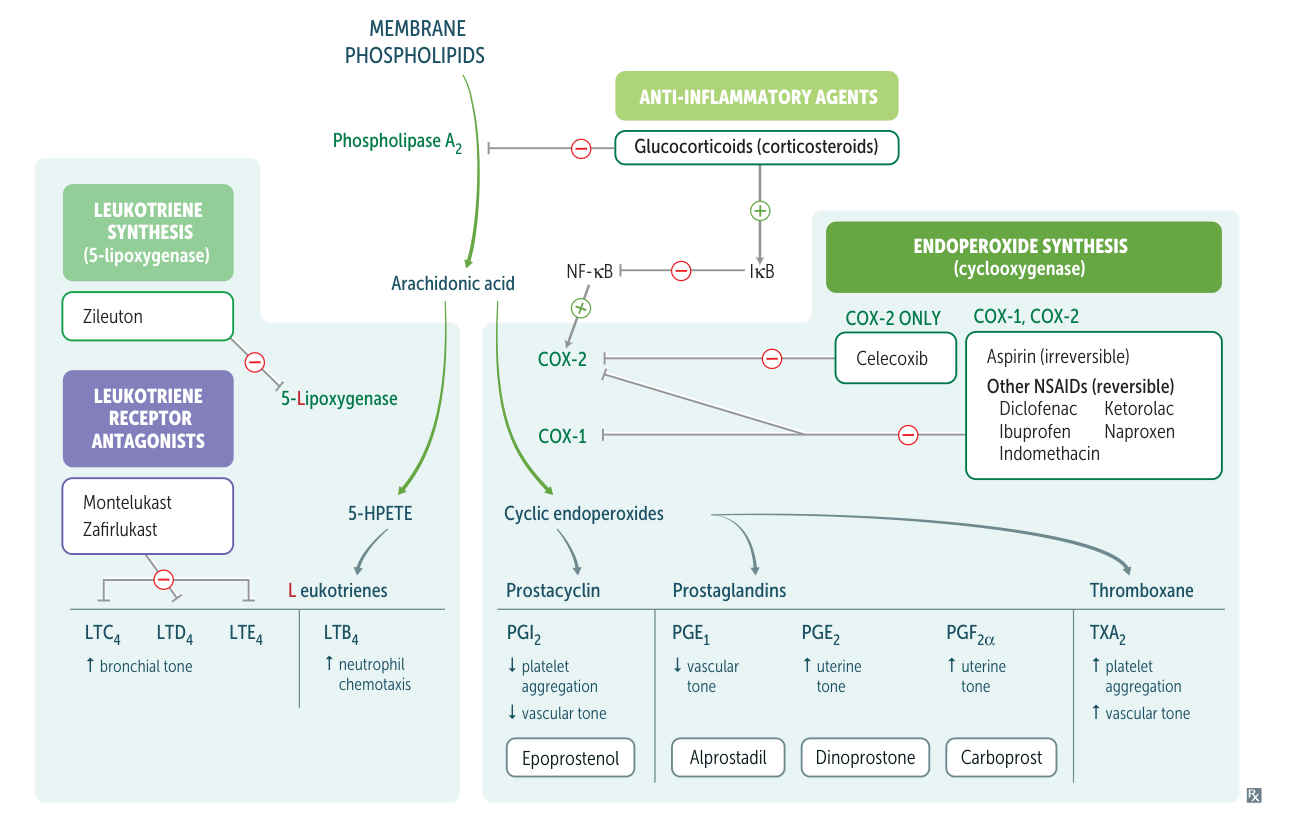
- Overview: A key inflammatory cascade that produces potent, short-acting lipid mediators called eicosanoids. It starts with the release of AA from the cell membrane phospholipids by phospholipase A2. AA is then metabolized by two major enzymatic pathways: cyclooxygenase (COX) and lipoxygenase (LOX).
Pharmacological Inhibition
- Corticosteroids: Inhibit phospholipase A2, preventing the release of AA from the membrane. This blocks the entire cascade, providing powerful, broad anti-inflammatory effects.
- NSAIDs: Inhibit COX enzymes.
- Zileuton: Inhibits 5-lipoxygenase.
- Montelukast, Zafirlukast: Block leukotriene receptors (specifically CysLT1 receptor for LTD4).
1. Cyclooxygenase (COX) Pathway
| Feature | COX-1 | COX-2 |
|---|---|---|
| Role | Physiologic / Housekeeping | Inflammatory / Inducible |
| Key Products | • GI Protection (mucus) • Thromboxane A2 (TXA2) → Pro-platelet aggregation | • Prostaglandins → Inflammation, Pain, Fever • Prostacyclin (PGI2) → Anti-platelet aggregation |
| Inhibition Side Effect | GI toxicity (ulcers, bleeding) | Increased cardiovascular risk (MI, stroke) |
| Inhibitor Examples | Non-selective NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) & Aspirin inhibit both. | Selective Inhibitors (Celecoxib) were designed to spare GI tract. |
- Products & Functions:
- Prostaglandins (PGE2, PGD2): Mediate inflammation (vasodilation, increased vascular permeability), pain (sensitize nerve endings), and fever. PGE2 also maintains a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) and protects gastric mucosa.
- Prostacyclin (PGI2): Produced by vascular endothelium. Causes vasodilation and inhibits platelet aggregation.
- Thromboxane A2 (TXA2): Produced by platelets. Causes vasoconstriction and promotes platelet aggregation.
- Clinical Correlations:
- NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen, Indomethacin): Reversibly inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2.
- Therapeutic effects: Anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antipyretic.
- Adverse effects (due to COX-1 inhibition): Gastric ulcers, GI bleeding, renal damage (by constricting afferent arteriole).
- Aspirin: Irreversibly inhibits COX-1 and COX-2. Its anti-platelet effect lasts for the life of the platelet (~8-10 days).
- Celecoxib (COX-2 selective inhibitor): Provides anti-inflammatory effects with less risk of GI side effects. However, it can increase the risk of cardiovascular events (MI, stroke) by tipping the balance towards a prothrombotic state (↓ PGI2, unopposed TXA2).
- NSAIDs (e.g., Ibuprofen, Indomethacin): Reversibly inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2.
| Feature | Aspirin (Low-Dose) | Traditional NSAIDs (Ibuprofen) | Celecoxib |
|---|---|---|---|
| COX-1 Inhibition | Irreversible, strong | Reversible, strong | Minimal to none |
| COX-2 Inhibition | Minimal to moderate (dose-dependent) | Reversible, strong | Reversible, strong |
| Effect on Platelet TXA2 | ↓↓↓ (long-lasting) | ↓ (temporary) | No change |
| Effect on Vascular PGI2 | Minimal change | ↓ (temporary) | ↓↓↓ |
| Net Platelet Effect | Anti-aggregation | Mild, temporary anti-aggregation | No effect (or pro-thrombotic) |
| Net Vascular/Thrombotic Risk | Cardioprotective | Neutral / slight ↑ risk | Increased risk |
2. Lipoxygenase (LOX) Pathway
- Enzyme: 5-Lipoxygenase converts AA into 5-HPETE, which is then converted to leukotrienes (LTs).
- Products & Functions:
- Leukotriene B4 (LTB4): A potent neutrophil chemotactic agent. “Neutrophils get here B4 others.”
- Cysteinyl-Leukotrienes (LTC4, LTD4, LTE4):
- Bronchoconstriction (potent effect).
- Increase vascular permeability.
- Mediate vasoconstriction.
- Lipoxins: Have anti-inflammatory effects, helping to resolve inflammation.
- Clinical Correlations:
- Asthma & Allergic Rhinitis: Leukotrienes are key mediators.
- Zileuton: 5-LOX inhibitor, used for asthma.
- Montelukast, Zafirlukast: Leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs), block the effects of LTC4, LTD4, and LTE4. Used for asthma, especially aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease (AERD).
- Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease (AERD): NSAID-induced inhibition of the COX pathway shunts AA down the LOX pathway, leading to an overproduction of pro-inflammatory leukotrienes, causing bronchospasm in susceptible individuals.
- Asthma & Allergic Rhinitis: Leukotrienes are key mediators.
| Feature | Prostaglandins (PGs) | Prostacyclin (PGI2) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Source | Most tissues, inflammatory cells | Vascular Endothelium |
| Vascular Action | Vasodilation (e.g., PGE2) | Potent Vasodilation |
| Platelet Action | No direct pro-aggregatory effect (unlikeThromboxane A2) | Potently INHIBITS platelet aggregation |
| Key Roles | Mediates fever, pain, uterine contraction, & gastric protection. | Maintains vascular homeostasis; prevents thrombosis on healthy endothelium. |
| Clinical Use | - Misoprostol (PGE1 analog): Labor induction, gastric protection. - Latanoprost (PGF2α analog): Glaucoma Tx. | - Epoprostenol, Iloprost (PGI2 analogs): Pulmonary HTN Tx. |
| Inhibition | NSAIDs block synthesis of both PGs and PGI2. | NSAIDs block synthesis. |